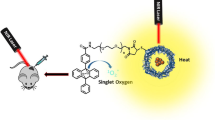
Abstract
Magnetic iron oxide modified pyropheophorbide-a fluorescence nanoparticles, Fe3O4@SiO2@APTES@PPa (FSAP), were designed as magnetically targeted photodynamic antineoplastic agents and prepared through continuous covalent chemical modification on the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The properties of the intermediates and the final product were comprehensively characterized by transmission electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, zeta potential measurement, ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence emission spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. In this work, we demonstrated the in vitro photodynamic therapy (PDT) of FSAP against ovarian cancer (SKOV-3) cells, which indicated that FSAP could be taken up successfully and showed low dark toxicity without irradiation, but remarkable phototoxicity after irradiation. Meanwhile, FSAP had showed good biocompatibility and low dark toxicity against normal cells in the biological experiments on mouse normal fibroblast cell lines (L929 cells). In addition, in the photochemical process of FSAP mediated photodynamic therapy, the Type-II photo-oxygenation process (generated singlet oxygen) played an important role in the induction of cell damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes and references
J. M. Dąbrowski and L. G., Arnaut, Photodynamic therapy (PDT) of cancer: from local to systemic treatment, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015, 14 1765–1780
T.-G. Ahn, B.-R. Lee, E.-Y. Choi, D. W. Kim and S.-J. Han, Photodynamic therapy for breast cancer in a BALB/c mouse model, J. Gynecol. Oncol., 2012, 23 115–119
M. G. Bredell, E. Besic, C. Maake and H., Walt, The application and challenges of clinical PD-PDT in the head and neck region: A short review, J Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2010, 101 185–190
A. M., Bugaj, Targeted photodynamic therapy - a promising strategy of tumor treatment, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2011, 10 1097–1109
P. Agostinis, K. Berg, K. A. Cengel, T. H. Foster, A. W. Girotti, S. O. Gollnick, S. M. Hahn, M. R. Hamblin, A. Juzeniene, D. Kessel, M. Korbelik, J. Moan, P. Mroz, D. Nowis, J. Piette, B. C. Wilson and J., Golab, Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update, CA-Cancer J. Clin., 2011, 61 250–281
D. E. Dolmans, D. Fukumura and R. K., Jain, Photodynamic therapy for cancer, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2003, 3 380–387
K. Stefflova, J. Chen and G., Zheng, Using molecular beacons for cancer imaging and treatment, Curr. Med. Chem., 2007, 12 4709–4721
T. Liu, L. Y. Wu, J. K. Choi and C. E., Berkman, In vitro targeted photodynamic therapy with a pyropheophorbide-a conjugated inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen, Prostate, 2009, 69 585–594
A. A. Ryan and M. O., Senge, How green is green chemistry? Chlorophylls as a bioresource from biorefineries and their commercial potential in medicine and photovoltaics, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015, 14 638–660
M. Kaplanová and L., Parma, Effect of excitation and emission wavelength on the fluorescence lifetimes of chlorophyll a, Gen. Physiol. Biophys., 1984, 3 127–134
I. Stamati, M. K. Kuimova, M. Lion, G. Yahioglu, D. Phillips and M. P., Deonarain, Novel photosensitisers derived from pyropheophorbide-a: uptake by cells and photodynamic efficiency in vitro, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, 9 1033–1041
Y. N. Konan, R. Gurny and E., Allemann, State of the art in the delivery of photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2002, 66 89–106
W. M. Sharman, J. E. Van-Lier and C. M., Allen, Targeted photodynamic therapy via receptor mediated delivery systems, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2004, 56 53–76
M. R. Hamblin, M. D. Governatore, I. Rizvi and T., Hasan, Biodistribution of charged 17.1A photoimmunoconjugates in a murine model of hepatic metastasis of colorectal cancer, Br. J. Cancer, 2000, 83 1544–1551
A. O. Abu-Yousif, A. C. E. Moor, X. Zheng, M. D. Savellano, W. Yu, P. K. Selbo and T., Hasan, Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted photosensitizer selectively inhibits EGFR signaling and induces targeted phototoxicity in cervical cancer cells, Cancer Lett., 2012, 321 120–127
C. Tuerk and L., Gold, Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase, Science, 1990, 249 505–510
M. R. Hamblin, J. L. Miller, I. Rizvi, B. Ortel, E. V. Maytin and T., Hasan, Pegylation of a chlorin (e6) polymer conjugate increases tumor targeting of photosensitizer, Cancer Res., 2001, 61 7155–7162
Y. Min, M. Akbulut, K. Kristiansen, Y. Golan and J., Israelachvili, The role of interparticle and external forces in nanoparticle assembly, Nat. Mater., 2008, 7 527–538
D. G. Yu, X. Y. Li, X. Wang, J. H. Yang, S. W. Bligh and G. R., Williams, Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 26 18891–18897
Y. Cheng, A. Csamia and J., Dmeyers, Highly efficient drug delivery with gold nanoparticle vectors for in vivo photodynamic therapy of cancer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130 10643–10647
H. Kariminezhad, S. Khayatomrani and S., Habibzadeh, The Synthesis of methylene blue photosensitiser conjugated with gold nanoparticles, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, 829 299–303
M. E. Wieder, D. C. Hone, M. J. Cook, M. M. Handsley, J. Gavrilovic and D. A., Russell, Intracellular photodynamic therapy with photosensitizer-nanoparticle conjugates: cancer therapy using a ‘Trojan horse’, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2006, 5 727–734
V. Raghavan, J. M. Connolly, H. M. Fan, P. Dockery and A., Wheatley, Gold Nanosensitisers for Multimodal Optical Diagnostic Imaging and Therapy of Cancer, J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol., 2014, 5 238–243
M. K. K. Oo, X. Yang, H. Du and H., Wang, 5-Aminolevulinicacid-conjugated gold nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy of cancer, Nanomedicine, 2008, 3 777–786
J. Chomoucka, J. Drbohlavova, D. Huska, V. Adam, R. Kizekand and J., Hubalek, Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering, Pharmacol. Res., 2010, 62 144–149
H. Hu, H. Yang, D. Li, K. Wang, J. Ruan, X. Zhang, J. Chen, C. Bao, J. Ji, D. Shi and D., Cui, The potential of magnetic nanocluster and dual-functional protein-based strategy for noninvasive detection of HBV surface antibodies, Analyst, 2011, 136 679–683
L. Li, M. Nurunnabi, M. Nafiujjaman, Y. Y. Jeong, Y. k. Lee and K. M., Huh, A pho tosensitizer-conjugated magnetic iron oxide/gold hybrid nanoparticle as an activatable platform for photodynamic cancer therapy, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014, 2 2929–2937
P. Huang, Z. Li, J. Lin, D. Yang, G. Gao, C. Xu, L. Bao, C. Zhang, K. Wang and H., Song, Photosensitizer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for in vivo simultaneous magnetofluorescent imaging and targeting therapy, Biomaterials, 2011, 32 3447–3458
O. Penon, M. J. Marín, D. B. Amabilino, D. A. Russell and L. Pérez-García, Iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with novel hydrophobic and hydrophilic porphyrins as potential agents for photodynamic therapy, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, 462 154–165
S. Zhang, L. Yang, X. Ling, P. Shao, X. Wang, W. B. Edwards and M., Bai, Tumor mitochondria-targeted photodynamic therapy with a translocator protein (TSPO)-specific photosensitizer, Acta Biomater., 2015, 28 160–170
F. Wang, X. Chen, Z. Zhao, S. Tang, X. Huang, C. Lin, C. Cai and N., Zheng, Synthesis of magnetic, fluorescent and mesoporous core-shell-structured nanoparticles for imaging, targeting and photodynamic therapy, J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21 11244–11252
L. O. Cinteza, T. Y. Ohulchanskyy, Y. Sahoo, E. J. Bergey, R. K. Pandey and P. N., Prasad, Diacyllipid micelle-based nanocarrier for magnetically guided delivery of drugs in photodynamic therapy, Mol. Pharm., 2006, 3 415–423
J. Gao, X. Ran, C. Shi, H. Cheng, T. Cheng and Y., Su, One-step solvothermal synthesis of highly water-soluble, negatively charged superparamagnetic Fe3O4 colloidal nanocrystal clusters, Nanoscale, 2013, 5 7026–7033
J. J. Cheng, G. H. Tan, W. T. Li, J. H. Li, Z. Q. Wang and Y. X., Jin, Preparation, characterization and in vitro photodynamic therapy of a pyropheophorbide-a-conjugated Fe3O4 multifunctional magnetofluorescence photosensitizer, RSC Adv., 2016, 6 37610–37620
J. N. Park, K. J. An, Y. S. Hwang, J.-G. Park, H.-J. Noh, J.-Y. Kim, J.-H. Park, N.-M. Hwang and T. H., Hyeon, Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals, Nat. Mater., 2004, 3 891–895
K. P. Naidek, F. Bianconi, T. C. R. da Rocha, D. Zanchet, J. A. Bonacin, M. A. Novak, M. G. F. Vaz and H., Winnischofer, Structure and morphology of spinel MFe2O4 (M=Fe, Co, Ni) nanoparticles chemically synthesized from heterometallic complexes, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 358 39–46
F. Liu, X. Zhou, S. Ni, X. Wang, Y. Zhou and Z., Chen, Preparation and properties of photosensitizer loaded magnetic nanocarriers, Curr. Nanosci., 2009, 5 293–296
Z. Li, C. Wang, L. Cheng, H. Gong, S. Yin, Q. Gong, Y. Li and Z., Liu, PEG-functionalized iron oxide nanoclusters loaded with chlorin e6 for targeted, NIR light induced, photodynamic therapy, Biomaterials, 2013, 34 9160–9170
S. Shi, X. Zhu, Z. Zhao, W. Fang, M. Chen, Y. Huang and X., Chen, Photothermally enhanced photodynamic therapy based on mesoporous Pd@Ag@mSiO2 nanocarriers, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013, 1 1133–1141
P. Huang, Z. Li, J. Lin, D. Yang, G. Gao, C. Xu, L. Bao, C. Zhang, K. Wang, H. Song, H. Hu and D., Cui, Photosensitizer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for in vivo simultaneous magnetofluorescent imaging and targeting therapy, Biomaterials, 2011, 32 3447–3458
W. T. Li, G. H. Tan, J. J. Cheng, L. S. Zhao, Z. Q. Wang and Y. X., Jin, A Novel Photosensitizer 31,131-phenylhydrazine-Mppa (BPHM) and its in vitro Photodynamic Therapy against SKOV-3 Cells, Molecules, 2016, 21 558–569
J. P., Kehrer, The Haber-Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity, Toxicology, 2000, 149 43–50
J. R. Sparrow, J. Zbou and B., Cai, DNA is a target of the photodynamic effects elicited in A2E-Laden RPE by blue-light illumination, Invest. Ophthalmol Visual Sci., 2003, 44 2245–2251
T. Ashikaga, M. Wada, H. Kobayashi, M. Moria, Y. Katsumura, H. Fukui, S. Kato, M. Yamaguchi and T., Takamatsu, Effect of the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 on plasmid DNA, Mutat. Res., 2000, 466 1–7
E. S. Nyman and P. H., Hynninen, Research advances in the use of tetrapyrrolic photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2004, 73 1–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, G., Li, W., Cheng, J. et al. Magnetic iron oxide modified pyropheophorbide-a fluorescence nanoparticles as photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy against ovarian cancer (SKOV-3) cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 15, 1567–1578 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6pp00340k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6pp00340k