Abstract
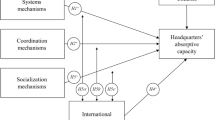
In this paper we explore the impact of organisational mechanisms on inter-unit knowledge flows in multinational corporations (MNCs). A comprehensive model, based on agency theory and socialisation theory, is tested on a sample of 134 Finnish and Chinese MNC subsidiaries. Our findings indicate that MNCs can influence inter-unit knowledge transfer by specifying the objectives of the subsidiary and by utilising corporate socialisation mechanisms. However, we found no support for the hypothesised impact of management compensation systems and the use of expatriate managers on the extent of knowledge transfers from foreign subsidiaries to other parts of the MNC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, T.J. (1977) Managing the Flow of Technology: Technology Transfer and the Dissemination of Technological Information within the R&D Organization, MIT Press: Cambridge, MA.
Andersson, U., Forsgren, M. and Holm, U. (2002) ‘The strategic impact of external networks: subsidiary performance and competence development in the multinational corporation’, Strategic Management Journal 23(11): 979–996.
Argote, L. and Ingram, P. (2000) ‘Knowledge transfer: a basis for competitive advantage in firms’, Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Process 82(1): 150–169.
Birkinshaw, J. and Hood, N. (1998) ‘Multinational subsidiary evolution: capability and charter change in foreign-owned subsidiary companies’, Academy of Management Review 23(4): 773–795.
Boyacigiller, N. (1990) ‘The role of expatriates in the management of interdependence, complexity and risk in multinational corporations’, Journal of International Business Studies 21(3): 357–381.
Cantwell, J. (1992) ‘The theory of technological competence and its implications for competitiveness’, in O. Granstrand, H. Hakanson and S. Sjolander S (eds.) Technology Management and International Business, Wiley: Chichester pp: 137–162.
Chang, E. and Taylor, M.S. (1999) ‘Control in multinational corporations (MNCs): the case of Korean manufacturing subsidiaries’, Journal of Management 25(4): 541–565.
Cohen, W.M. and Levinthal, D.A. (1990) ‘Absorptive capacity: a new perspective on learning and innovation’, Administrative Science Quarterly 35(1): 128–152.
Davenport, T.H. and Prusak, L. (1998) Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know, Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA.
Doz, Y.L. and Prahalad, C.K. (1993) ‘Managing DMNCs: a search for a new paradigm’, in S. Ghoshal and E. Westney (eds.) Organizational Theory and the Multinational Corporation, St Martin's Press: New York pp: 24–50.
Edström, A. and Galbraith, J.R. (1977) ‘Transfer of managers as a coordination and control strategy in multinational organizations’, Administrative Science Quarterly 22(2): 248–268.
Eisenhardt, K. (1988) ‘Agency- and institutional-theory explanations: the case of retail sales compensation’, Academy of Management Journal 31(3): 488–512.
Eisenhardt, K. (1989) ‘Agency theory: an assessment and review’, Academy of Management Review 14(1): 57–74.
Forsgren, M. (1997) ‘The advantage paradox of the multinational corporation’, in I. Bjorkman and M. Forsgren (eds.) The Nature of the International Firm: Nordic Contributions to International Business Research, Copenhagen Business School Press: Copenhagen pp: 69–85.
Forsgren, M., Johansson, J. and Sharma, D. (2000) ‘Development of MNC centres of excellence’, in U. Holm and T. Pedersen (eds.) The Emergence and Impact of MNC Centres of Excellence, Macmillan: London pp: 45–67.
Foss, N.J. and Pedersen, T. (2002) ‘Transferring knowledge in MNCs: the role of sources of subsidiary knowledge and organizational context’, Journal of International Management 8(1): 1–19.
Frost, T. (2001) ‘The geographic sources of foreign subsidiaries’ innovations’, Strategic Management Journal 22(2): 101–123.
Frost, T., Birkinshaw, J.M. and Ensign, P.C. (2002) ‘Centers of excellence in multinational corporations’, Strategic Management Journal 23(4): 997–1018.
Ghoshal, S. and Bartlett, C.A. (1990) ‘The multinational corporation as an interorganizational network’, Academy of Management Review 15(4): 603–625.
Ghoshal, S. and Moran, P. (1996) ‘Bad for practice: a critique of the transaction cost theory’, Academy of Management Review 21(1): 13–47.
Grant, R.M. (1996) ‘Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm’, Strategic Management Journal 17(Winter Special Issue): 109–122.
Gupta, A.K. and Govindarajan, V. (2000) ‘Knowledge flows within multinational corporations’, Strategic Management Journal 21(4): 473–496.
Hansen, M.T. (1999) ‘The search-transfer problem: the role of weak ties in sharing knowledge across organization subunits’, Administrative Science Quarterly 44(1): 82–111.
Harvey, M., Speier, C. and Novecevic, M.M. (2001) ‘A theory-based framework for strategic human resource staffing policies and practices’, International Journal of Human Resource Management 12(6): 898–915.
Hedlund, G. and Kogut, B. (1993) ‘Managing the MNC: the end of the missionary era’, in: G. Hedlund (ed.) Organization of Transnational Corporations, Vol. 6 in The United Nations Library on Transnational Corporations, Routledge: New York.
Hendry, J. (2002) ‘The principal's other problems: honest incompetence and the specification of objectives’, Academy of Management Review 27(1): 98–113.
Hennart, J.-F. and Park, Y.-R. (1993) ‘Greenfield vs acquisition: the strategy of Japanese investors in the United States’, Management Science 39(9): 1054–1071.
Holm, U. and Pedersen, T. (2000) ‘The centres of excellence project: methods and some empirical findings’, in U. Holm and T. Pedersen (eds.) The Emergence and Impact of MNC Centres of Excellence, Macmillan: London pp: 23–44.
Jensen, M. and Meckling, W.H. (1976) ‘Theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency cost, and ownership structure’, Journal of Financial Economics 3(4): 305–360.
Lane, P.J. and Lubatkin, M. (1998) ‘Relative absorptive capacity and interorganizational learning’, Strategic Management Journal 19(5): 461–477.
Levitt, B. and March, J.G. (1988) ‘Organizational learning’, Annual Review of Sociology 14: 319–340.
Lubatkin, M.H., Lane, P.J. and Schultze, W.S. (2001) ‘A strategic management model of agency relationships in firm governance’, in M.A. Hitt, R.E. Edwards and J.S. Harrison (eds.) The Blackwell Handbook of Strategic Management, Blackwell Business: Oxford pp: 229–258.
Martinez, J.I. and Jarillo, J.C. (1989) ‘The evolution of research on coordination mechanisms in multinational corporations’, Journal of International Business Studies 20(3): 489–514.
Nohria, N. and Ghoshal, S. (1994) ‘Differentiated fit and shared values: alternatives for managing headquarters–subsidiary relations’, Strategic Management Journal 15(6): 491–503.
O’Donnell, S.W. (2000) ‘Managing foreign subsidiaries: agents of headquarters, or an interdependent network?’, Strategic Management Journal 21(5): 525–548.
Ouchi, W.G. (1979) ‘A conceptual framework for the design of organizational control mechanisms’, Management Science 25(9): 833–848.
Porter, M.E. (1985) Competitive Advantage, Free Press: New York.
Roth, K. and O’Donnell, S. (1996) ‘Foreign subsidiary compensation strategy: an agency theory perspective’, Academy of Management Journal 39(3): 678–703.
Roth, K., Schweiger, D.M. and Morrison, A.J. (1991) ‘Global strategy implementation at the business unit level: operational capabilities and administrative mechanisms’, Journal of International Business Studies 22(3): 369–402.
Rugman, A. and Verbeke, A. (2001) ‘Subsidiary-specific advantages in multinational enterprises’, Strategic Management Journal 22(3): 237–250.
Schulz, M. (2001) ‘The uncertain relevance of newness: organizational learning and knowledge flows’, Academy of Management Journal 44(4): 661–681.
Simonin, B.L. (1999) ‘Ambiguity and the process of knowledge transfer in strategic alliances’, Strategic Management Journal 20(7): 595–623.
Spender, J.-C. (1996) ‘Making knowledge the basis of a dynamic theory of the firm’, Strategic Management Journal 17(Winter Special Issue): 45–62.
Stroh, L.K., Brett, J.M., Baumann, J.P. and Reilly, A.H. (1996) ‘Agency theory and variable pay compensation strategies’, Academy of Management Journal 39(3): 751–768.
Szulanski, G. (1996) ‘Exploring internal stickiness: impediments to the transfer of best practice within the firm’, Strategic Management Journal 17(Winter Special Issue): 27–43.
Szulanski, G. (2000) ‘The process of knowledge transfer: a diachronic analysis of stickiness’, Organisational Behavior and Human Decision Process 82(1): 9–27.
Szulanski, G. (2003) Sticky Knowledge: Barriers to Knowing in the Firm, Sage: London.
Tosi, H.L. and Gomez-Mejia, L.R. (1989) ‘The decoupling of CEO pay and performance: an agency theory perspective’, Administrative Science Quarterly 34(2): 169–189.
Tosi, H.L., Katz, J.P. and Gomez-Meija, L.R. (1997) ‘Disaggregating the agency contract: the effects of monitoring, incentive alignment, and term in office on agent decision making’, Academy of Management Journal 40(3): 584–602.
Tsai, W. (2001) ‘Knowledge transfer in intraorganizational networks: effects of network position and absorptive capacity on business unit innovation and performance’, Academy of Management Journal 44(5): 996–1004.
Tsai, W. and Ghoshal, S. (1998) ‘Social capital and value creation: the role of intrafirm networks’, Academy of Management Journal 41(5): 464–476.
Van Maanen, J. and Schein, E.H. (1979) ‘Toward a theory of organizational socialization’, in B.M. Staw (ed.) Research in Organizational Behaviour, Vol. 1 JAI Press: Greenwich, CT pp: 209–264.
Zander, U. and Kogut, B. (1995) ‘Knowledge and the speed of the transfer and imitation of organizational capabilities: an empirical test’, Organisation Science 6(1): 76–92.
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out within the Academy of Finland-financed project ‘Managing knowledge creation and transfer in multinational corporations: a Finnish perspective’. We thank Anette Björkman and Patrick Furu for their contributions to the data collection. We would also like to thank the editors of the focused issue Nicolai Foss and Torben Pedersen, as well as the three JIBS reviewers for valuable comments and suggestions on an earlier version of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Accepted by Nicolai Juul Foss and Torben Pedersen, Departmental Editors, 31 March 2004. This paper has been with the author for one revision.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Björkman, I., Barner-Rasmussen, W. & Li, L. Managing knowledge transfer in MNCs: the impact of headquarters control mechanisms. J Int Bus Stud 35, 443–455 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400094
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400094