Abstract
Background, Aim and Scope
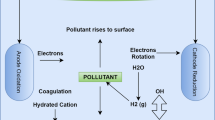
Electrocoagulation (EC) may be a potential answer to environmental problems dealing with water reuse and rational waste management. The aim of this research was to assess the feasibility of EC-process for industrial contaminated effluents from copper production, taking into consideration technical and economical factors. EC-technology claims to offer efficient removal rates for most types of wastewater impurities at low power consumption and without adding any precipitating agents.
Materials and Methods
Real wastewater from Saraka stream with high concentrations of heavy metals was provided by RTB-BOR, a Serbian copper mining and smelting complex. Runs were performed on a 10 1 EC-reactor using aluminum plates as sacrificial electrodes and powered by a 40 A supply unit. Results concerning key factors like pH, conductivity and power consumption were measured in real time. Analysis of dissolved metal concentrations before and after treatment were carried out via ICP-OES and confirmed by an independent test via AAS.
Results
Several aspects were taken into account, including current density, conductivity, interfacial resistivity and reactor settings throughout the runs, in order to analyze all possible factors playing a role in neutralization and metal removal in real industrial wastewater.
Discussion
Electrode configurations and their effects on energy demand were discussed and exemplified based on fundamentals of colloidal and physical chemistry.
Conclusions
Based on experimental data and since no precipitating agents were applied, the EC-process proved to be not only feasible and environmentally-friendly, but also a cost-effective technology.
Recommendations and Perspectives
The EC-technology provides strategic guidelines for further research and development of sustainable water management processes. However, additional test series concerning continuous operation must be still performed in order to get this concept ready for future large-scale applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dieterich A (1906): Electric water purifier. US Patent 823671
UNEP (2003): 1st World Water Development Report: Water for people, water for life. UN Environment Programme, Paris
Fennell E, Wennerström H (1999): The colloidal domain. Wiley-VCH, ISBN 0-471-24247-0
Henry M, Jolivet JP, Livage J (1992): Aqueous chemistry of metal cations; hydrolysis, condensation and complexation. Structure and bonding. Band 77, Springer-Verlag, pp 155
CECW-ET (2001): Engineering and Design — Precipitation, Coagulation, Flocculation. US Army Corp of Engineers EM1110-1-4012
Wetter C, Pöppinghaus K (1992): Literaturstudie über Verfahren zur Schwermetallentfernung aus Abwasserschlämmen. FiW Forschungsbericht AZ 279–85
Hem S, White J, Nail S (1976) Structure of aluminum hydroxide gel I: initial precipitate. Pharm Sci (65) 1188–1191
Georgantas D, Grigoropoulou H (2006): Phosphorus and organic matter removal from synthetic wastewater using alum and aluminum hydroxide. Global NEST J (8) 121–130
Mahesh S et al. (2006): Electrochemical degradation of pulp and paper mill wastewater. Ind Eng Chem (45) 2830–2839
Weigl J (1977): Elektrokinetische Grenzflächevorgänge. erlag Chemie, ISBN 3-527-25718-7
Pavlović J, Stopić S, Friedrich B, Kamberović Ž (2006): Selective removal of heavy metals from metal-bearing wastewater in a cascade line reactor. Env Sci Pollut Res 14(7) 518–522
Rodriguez J, Schweda M, Stopić S, Friedrich B (2007): Techno-economical comparison of conventional hydroxide precipitation and electrocoagulation for heavy metal removal from industrial wastweater. Metall Journal, No 3/07
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ESS-Submission Editor: Dr. Lee Young (youngrisk@bresnan.net)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, J., Stopić, S., Krause, G. et al. Feasibility assessment of electrocoagulation towards a new sustainable wastewater treatment. Env Sci Poll Res Int 14, 477–482 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.05.424
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.05.424