Abstract
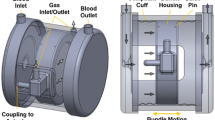
Intravascular oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal remains a potentially attractive means for respiratory support in patients with acute or chronic respiratory failure. Our group has been developing an intravascular hollow fiber artificial lung that uses a pulsating balloon located within the fiber bundle to augment gas transfer. We previously reported on a simple compartmental model for simulating O2 exchange in pulsating intravascular artificial lungs. In this study we evaluate the O2 exchange model with gas exchange and PO2 measurements performed on an idealized intravascular artificial lung (IIVAL) tested in a water perfusion loop. The IIVAL has well-defined bundle geometry and can be operated in balloon pulsation mode, or a steady perfusion mode for determining the mass transfer correlation required by the model. The O2 exchange rates and compartmental O2 tensions measured with balloon pulsation in the IIVAL are within 10% of model predictions for flow and pulsation conditions relevant to intravascular oxygenation. The experiments confirmed that a significant buildup of PO2 occurs within the fiber bundle, which reduces the O2 exchange rate. The agreement between experiments and predictions suggests that the model captures the cardinal processes dictating gas transfer in pulsating intravascular artificial lungs. © 2000 Biomedical Engineering Society.
PAC00: 8780-y, 8710+e
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Conrad, S. A.et al. Major findings from the clinical trials of the intravascular oxygenator. Artif. Organs18:846–863, 1994.
Federspiel, W. J., T. J. Hewitt, M. S. Hout, F. R. Walters, L. W. Lund, P. Sawzik, G. D. Reeder, H. S. Borovetz, and B. G. Hattler. Recent progress in engineering the Pittsburgh Intravenous Membrane Oxygenator. ASAIO J.42:M435-M442, 1996.
Federspiel, W. J., P. Sawzik, H. Borovetz, G. D. Reeder, and B. G. Hattler. Temporary support of the lungs—The artificial lung, edited by D. K. C. Cooper, L. W. Miller, G. A. Patterson. The Transplantation and Replacement of Thoracic Organs, Boston: Kluwer Academic, 1996, p. 824.
Federspiel, W. J., M. S. Hout, T. J. Hewitt, L. W. Lund, S. A. Heinrich, P. Litwak, F. R. Walters, G. D. Reeder, H. S. Borovetz, and B. G. Hattler. Development of a low flow resistance intravenous oxygenator. ASAIO J.43:M725-M730, 1997.
Hattler, B. G., G. D. Reeder, P. J. Sawzik, L. W. Lund, F. R. Walters, A. S. Shah, J. Rawleigh, J. S. Goode, M. Klain, and H. S. Borovetz. Development of an intravenous membrane oxygenator: enhanced intravenous gas exchange through convective mixing of blood around hollow fiber membranes. Artif. Organs18:806–812, 1994.
Hewitt, T. J., B. G. Hattler, and W. J. Federspiel. A mathematical model of gas exchange in an intravenous membrane oxygenator. Ann. Biomed. Eng.26(1):166–178, 1998.
High, K. M., M. T. Snider, R. Richard, G. B. Russell, J. K. Stene, D. B. Campbell, T. X. Aufiero, and G. A. Thieme. Clinical trials of an intravenous oxygenator in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesiology77:856–863, 1992.
Makarewicz, A. J., and L. F. Mockros. Modeling oxygen transfer to blood from crossflow membrane oxygenators. ASME: Bioengineering Division29:467–468, 1995.
Mortensen, J. D.Intravascular oxygenator: A new alternative method for augmenting blood gas transfer in patients with acute respiratory failure. Artif. Organs16:75–82, 1992.
Niranjan, S. C., J. W. Clark, K. Y. San, J. B. Zwischenberger, and A. Bidani. Analysis of factors affecting gas exchange in intravascular blood gas exchanger. J. Appl. Physiol.77:1716–1730, 1994.
Nodelman, V., H. Baskaran, and J. S. Ultman. Enhancement of O2 and CO2 transfer through microporous hollow fibers by pressure cycling. Ann. Biomed. Eng.26:1044–1054, 1998.
Tao, W., and J. B. Zwishenberger. Intracorporeal gas exchange: Taking further steps. ASAIO J.44(3):224–226, 1998.
Vaslef, S. N., L. F. Mockros, K. E. Cook, R. J. Leonard, J. C. Sung, and R. W. Anderson. Computer-assisted design of an implantable, intrathoracic artificial lung. Artif. Organs18(11):813–817, 1994.
Vaslef, S. N., L. F. Mockros, R. W. Anderson, and R. J. Leonard. Use of a mathematical model to predict oxygen transfer rates in hollow fiber membrane oxygenators. ASAIO J.40:990–996, 1994.
Wickramasinghe, S. R., M. J. Semmens, and E. L. Cussler. Hollow fiber modules made with hollow fiber fabric. J. Membr. Sci.84:1–14, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Federspiel, W.J., Hewitt, T.J. & Hattler, B.G. Experimental Evaluation of a Model for Oxygen Exchange in a Pulsating Intravascular Artificial Lung. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 28, 160–167 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1114/1.240
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1114/1.240