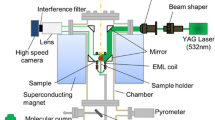
Abstract—
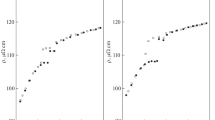
The resistivity of liquid Fe–Mn–C alloys containing from 5 to 25 wt % manganese and from 0.4 to 2.2 wt % carbon has been measured by the rotating magnetic field method. The measurements have been made during heating from 1340 to 1810°C and subsequent cooling of the samples. The resistivity of the melts during heating was considerably lower than that during subsequent cooling, which was accompanied by a decrease in the temperature coefficient of resistivity. The temperature dependence of resistivity for some of the alloys has been found to have an anomaly in the form of a break during heating to temperatures in the range 1550–1680°C. The addition of manganese and carbon has been shown to influence the resistivity of the melts and its temperature coefficient. We have calculated the effective resistivity of a liquid alloy with the composition (wt %) Fe–10Mn–1C as a heterogeneous system using analytical relations for conductivity of inhomogeneous media, a unit-cell method, and geometric models of isolated and interpenetrating inclusions. The temperature t* = 1730°C thus obtained for the transition from isolated to interpenetrating inclusions in the Fe–10Mn–1C melt agrees with the experimentally determined temperature t* = 1680°C of the beginning of the portion common to the temperature dependences of resistivity obtained during heating and cooling. The temperature 1540°C of the transition from isolated to interpenetrating inclusions agrees with the experimentally determined temperature 1550°C corresponding to the break in the temperature dependence of resistivity.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Popova, N., Dement, T., Nikonenko, E., Kurzina, I., and Kozlov, E., Structure and phase composition of manganese steels modified by alloying elements, AIP Conf. Proc., 2017, vol. 1800, no. 1, paper 030001.https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4973033
Davydov, N.G., Vysokomargantsevaya stal’ (High-Manganese Steel), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1979.
Volynova, T.F., Vysokomargantsovistye stali i splavy (High-Manganese Steels and Alloys), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1988.
Volkov, V.N., Dibrov, A.B., and Andronov, P.P., Effect of the structure of 110G13L high-manganese steel on the magnetism and mechanical properties of castings, Vestn. VKGTU, 2005, no. 1, pp. 8–14.
Kveglis, L.I., Noskov, F.M., Kazantseva, V.V., Abylkalykova, R.B., et al., Fe–Mn–C alloys with anomalous volume of crystal lattice, Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci.: Phys., 2008, vol. 72, no. 8, pp. 1169–1171
Sinitskii, E.V., Nefed’ev, A.A., Akhmetova, A.A., Ovchinnikova, M.V., et al., Survey of results of studies aimed at improving the properties of high-manganese steel castings, Liteinoe Proizvod., 2016, no. 2, pp. 45–57.
Chen, C., Lv, B., Feng, X., Zhang, F., and Beladi, H., Strain hardening and nanocrystallization behaviors in Hadfield steel subjected to surface severe plastic deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2018, vol. 729, pp. 178–184.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.05.059
Ten, E.B. and Likholobov, E.Y., Control of 110G13L steel smelting on the basic of oxygen-activity measurement, Steel Transl., 2012, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 25–27.https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091212010196
Vdovin, K.N., Feoktistov, N.A., Gorlenko, D.A., et al., Effect of the crystallization process on the properties of 110G13L steel, Liteinye Protsessy, 2016, no. 14, pp. 29–36.
Budanov, E.N., Preparation of 110G13L steel castings by vacuum film molding, Liteinoe Proizvod., 2014, no. 9, pp. 30–35.
Grässel, O. and Frommeyer, G., Effect of martensitic phase transformation and deformation twinning on mechanical properties of Fe–Mn–Si–Al steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1998, vol. 14, no. 14, pp. 1213–1217.https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1998.14.12.1213
Frommeyer, G., Brüx, U., and Neumann, P., Supra-ductile and high-strength manganese-TRIP/TWIP steels for high energy absorption purposes, ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 438–446.https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.43.438
Grässel, O., Krüger, L., Frommeyer, G., and Meyer, L.W., High strength Fe–Mn–(Al,Si) TRIP/TWIP steels development–properties–application, Int. J. Plast., 2000, vol. 16, no. 10, pp. 1391–1409.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(00)00015-2
Huang, B.X., Wang, X.D., Rong, Y.H., Wang, L., and Jin, L., Mechanical behavior and martensitic transformation of an Fe–Mn–Si–Al–Nb alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, vols. 438–440, pp. 306–311.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.150
Martin, S., Wolf, S., Martin, U., Krüger, L., and Rafaja, D., Deformation mechanisms in austenitic TRIP/TWIP steel as a function of temperature, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2684-4
Galindo-Nava, E.I. and Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J., Understanding martensite and twin formation in austenitic steels: a model describing TRIP and TWIP effects, Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 128, pp. 120–134.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.004
Malamud, F., Castro, F., Guerrero, M.L., Sade, M., and Baruj, A., High-precision face-centered cubic-hexagonal close-packed volume-change determination in high-Mn steels by X-ray diffraction data refinements, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2020, vol. 53, pp. 34–44.https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576719015024
Benzing, J.T., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Raabe, D., and Wittig, J.E., Experimental and numerical study of mechanical properties of multi-phase medium-Mn TWIP–TRIP steel: influences of strain rate and phase constituents, Acta Mater., 2019, vol. 177, pp. 250–265.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.07.036
Madivala, M., Schwedt, A., Wong, S.L., Prahl, U., and Bleck, W., Temperature dependent strain hardening and fracture behavior of TWIP steel, Int. J. Plast., 2018, vol. 104, pp. 80–103.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2018.02.001
Field, D.M., Qing, J., and Van Aken, D.C., Chemistry and properties of medium-Mn two-stage TRIP steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 4615–4632.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4798-6
Injeti, V.S.Y., Li, Z.C., Yu, B., Cai, Z.H., and Ding, H., Macro to nanoscale deformation of transformation-induced plasticity steels: impact of aluminum on the microstructure and deformation behavior, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 745–755.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.11.011
Verzhbolovich, S.A., Singer, V.V., Radovskii, I.Z., et al., Resistivity and distinctive features of interparticle interaction in Fe-Mn-C melts, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., 1985, no. 2, pp. 66–68.
Vostryakov, A.A., Vatolin, N.A., and Esin, O.A., Viscosity and resistivity of manganese–silicon, manganese–iron, and manganese–carbon melts, Zh. Neorg. Khim., 1964, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1911–1914.
Arsent’ev, P.P., Yakovlev, V.V., Krasheninnikov, M.G., et al., Fiziko-khimicheskie metody issledovaniya metallurgicheskikh protsessov (Physicochemical Methods for Assessing Metallurgical Processes), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1988.
Voronkov, V.V., Ivanova, I.I., and Turovskii, B.M., On the application of the rotating magnetic field method to measurements of the electrical conductivity of melts, Magn. Gidrodinam., 1973, no. 2, pp. 147–149.
Ryabina, A.B., Kononenko, V.I., and Razhabov, A.A., Electrodeless method for measuring the resistivity of solid and liquid metals and experimental setup for implementing it, Rasplavy, 2009, no. 1, pp. 34–42.
Tyagunov, G.V., Tsepelev, V.S., Baum, B.A., et al., Resistivity measurements by the rotating magnetic field method, Zavod. Lab., 2003, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 36–38.
Tyagunov, A.G., Baryshev, E.E., Tyagunov, G.V., et al., Polytherms of the physical properties of metallic melts, Steel Transl., 2017, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 250–256.
Nagel, S.R. and Tauc, J., Nearly-free-electron approach to the theory of metallic glass alloys, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1975, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 380–383.https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.380
Faber, T.E. and Ziman, J.M., A theory of the electrical properties of liquid metals, Philos. Mag. A, 1965, vol. 11, no. 109, pp. 153–173.https://doi.org/10.1080/14786436508211931
Dul’nev, G.N. and Novikov, V.V., Protsessy perenosa v neodnorodnykh sredakh (Transport Processes in Inhomogeneous Media), Leningrad: Energoatomizdat, 1991.
Lepinskikh, B.M., Belousov, A.A., Bakhvalov, S.G., et al., Transportnye svoistva metallicheskikh i shlakovykh rasplavov: Spravochnoe izdanie (Transport Properties of Molten Metals and Slags: A Handbook), Vatolin, N.A., Ed., Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1995.
Guntherodt, H.-J., Hauser, E., Kunzi, H.U., and Muller, R., The electrical resistivity of liquid Fe, Co, Ni and Pd, Phys. Lett. A, 1975, vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 291–292.https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(75)90263-7
Ono, Y., Hirayama, K., and Furukawa, K., Electric resistivity of molten Fe–C, Fe–Si and Fe–C–Si alloys, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1976, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 153–160.https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational1966.16.153
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 19-33-90198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Tsarev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinitsin, N.I., Chikova, O.A. & V’yukhin, V.V. Resistivity of Fe–Mn–C Melts. Inorg Mater 57, 86–93 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002016852101012X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002016852101012X