Abstract
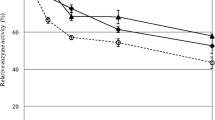
Through determination of cellulase in terms of protein content in the hydrolyzate after hydrolysis, it was found that 50.15–67.21% of the originally added protein was still remained in the hydrolyzate. Tannin flocculation followed by PEG desorption was coupled to recover this portion of cellulase. About 94.99% of the protein in the hydrolyzate was precipitated into Tannin-cellulase compound under tannin concentration of 5% (w/v) with pH 5.0 and NaCl concentration of 1.0%. In order to desorb cellulase from Tannin-cellulase compound, PEG 6000 was employed as a desorbent. The recovered enzyme activity reached 133.25% when the PEG concentration was 1.5% (w/v). This, to some extent, indicated that PEG was also an effective activator of cellulase. The article is published in the original.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grethlein, H.E., Biotechnol. Adv., 1984, vol. 2, no 1, pp. 43–62.
Marchal, R., Ropars, M., Pourquie, J., Fayolle, F., and Vandecasteele, J.E., Bioresource Technol., 1992, vol. 42, pp. 205–217.
Lynd, L.R., van Zyl, W.H., McBride, J.E., and Laser, M., Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 577–583.
Knauf, M. and Moniruzzaman, M., Int. Sugar J., 2004, vol. 106, pp.147–150.
Moreira, N., Sci. News Online, 2005, vol. 168, no. 14, pp. 209–224.
Mandels, M., Kostick, J., and Parizek, J., J. Polym. Sci., Part C, 1971, vol. 36, pp. 445–459.
Castanon, M. and Wilke, C.R., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1980, vol. 22, pp. 1037–1053.
Kim, D.W., Kim, T.S., Jeong, Y.K., and Lee, J.K., J. Ferment. Bioeng., 1992, vol. 73, no. 6, pp. 46–466.
Yu, A.H.C., Lee, D., and Saddler, J.N., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1995, vol. 45, pp. 328–336.
Castanon, M. and Wilke, C.R., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1981, vol. 23, pp. 1365–1372.
Chen, H.Z., Study on Microbial Conversion and Full Utilization of Cellulosic Biomass, Ph. D. Dissertation, Institute of Chemical Metallurgy, CAS, 1998.
Ghose, T.K., Pure Appl. Chem., 1987, vol. 59, pp. 257–268.
Bradford, M.M., Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Otter, D.E., Munro, P.A., Scott, G.K., and Geddes, R., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 1989, vol. 34, pp. 291–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Prikladnaya Biokhimiya i Mikrobiologiya, 2009, Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 344–347.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Chen, H. Coupling recovery strategy of cellulase in hydrolyzate after hydrolysis with Tannin flocculation and PEG desorption. Appl Biochem Microbiol 45, 309–312 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683809030120
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683809030120