Abstract
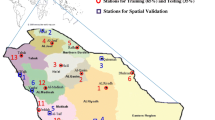
Gene Expression Programming (GEP) was used to develop new mathematical equations for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration (ET ref) for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The daily climatic variables were collected by 13 meteorological stations from 1980 to 2010. The GEP models were trained on 65% of the climatic data and tested using the remaining 35%. The generalised Penman-Monteith model was used as a reference target for evapotranspiration (ET) values, with h c varies from 5 to 105 cm with increment of a centimetre. Eight GEP models have been compared with four locally calibrated traditional models (Hargreaves-Samani, Irmak, Jensen-Haise and Kimberly-Penman). The results showed that the statistical performance criteria values such as determination coefficients (R 2) ranged from as low as 64.4% for GEP-MOD1, where the only parameters included (maximum, minimum, and mean temperature and crop height), to as high as 95.5% for GEP-MOD8 with which all climatic parameters included (maximum, minimum and mean temperature; maximum, minimum and mean humidity; solar radiation; wind speed; and crop height). Moreover, an interesting founded result is that the solar radiation has almost no effect on ET ref under the hyper arid conditions. In contrast, the wind speed and plant height have a great positive impact in increasing the accuracy of calculating ET ref. Furthermore, eight GEP models have obtained better results than the locally calibrated traditional ET ref equations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alazba, A.A., Estimating palm water requirements using Penman–Monteith mathematical model, J. King Saud Univ., 2004, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 137–152.
Alazba, A.A., Comparison of the ASCE standardized and other Penman Monteith type equations under hyper-arid area, ASABE Annual Meeting, Michigan: Am. Soc. of Ag. Biol. Eng., St. Joseph, 2004.
Alazba, A., Mattar, M.A., El-Nesr, M.N., and Amin, M.T., Field assessment of friction head loss and friction correction factor equations, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., ASCE, 2012, Vol. 138, No. 2, pp.166–176.
Allen, R.G., Pereira, L.S., Raes, D., and Smith, M., Crop evapotranspiration guidelines for computing crop water requirements, FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Rome, 1998, No. 56.
Aytek, A. and Kii, O., Genetic programming approach to suspended sediment modelling, J. Hydrol., 2008, Vol. 351, No. 3–4, pp. 288–298.
Azamathulla, H.Md., Gene-expression programming to predict friction factor for Southern Italian Rivers, Neural Comput. Appl., 2012, doi: 10.1007/s00521–0121091–2.
Azamathulla, H.Md. and Ahmad, Z., Gene-expression programming for transverse mixing coefficient, J. Hydrol., 2012, Vol. 434–435, pp. 142–148.
Azamathulla, H.Md., Ghani, A.A., Leow, C.S., Chang, K.C., and Zakaria, N.A, Gene-expression programming for the development of a stage-discharge curve of the Pahang River, Wat. Res. Manag., 2011, Vol. 25, pp. 2901–2916.
Dai, X., Shi, H., Li, Y., Ouyang, Z., and Huo, Z., Artificial neural network models for estimating regional reference evapotranspiration based on climate factors, Hydrol. Process., 2009, Vol. 23, pp. 442–450.
Fernando, A.K., Shamseldin, A.Y., and Abrahart, R.J., Use of gene expression programming for multimodel combination of Rainfall-Runoff models, J. Hydrol. Eng., 2012, Vol. 17, No. 9, pp. 975–985.
Ferreira, C., Gene Expression Programming in Problem Solving, 6th Online World Conference on Soft Computing in Industrial Applications, 2001.
Ferreira, C., Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems, Complex Syst., 2001, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 87–129.
Ferreira, C., Gene Expression Programming: Mathematical Modeling by an Artificial Intelligence, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2006.
Gandomi, A.H., Babanajad, S.K., Alavi, A.H., and Farnam, Y., Novel approach to strength modeling of concrete under triaxial compression, J. Mater. Civ. Eng., 2012, Vol. 24, No. 9, pp. 1132–1143.
Gavilan, P., Berengena, J., and Allen, R.G., Measuring versus estimating net radiation and soil heat flux: impact on Penman–Monteith reference ET estimates in semiarid regions, Agr. Wat. Manag., 2007, Vol. 89, pp. 275–286.
Gavilan, P., Lorite, I.J., Tornero, S., and Berengena, J., Regional calibration of Hargreaves equation for estimating reference ET in a semiarid environment, Agr. Wat. Manag., 2006, Vol. 81, pp. 257–281.
Ghani, A.A. and Azamathulla, H.Md., Gene-expression programming for sediment transport in Sewer Pipe Systems, J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract., 2011, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 102–106.
Guven, A. and Aytek, A., A new approach for stage-discharge relationship: gene-expression programming, J. Hydrol. Eng., 2009, Vol. 14, No. 8, pp. 812–820.
Hupet, F. and Vanclooster, M., Effect of the sampling frequency of meteorological variables on the estimation of the reference evapotranspiration, J. Hydrol., Vol. 243, pp. 192–204.
Irmak, S., Irmak, A., Allen, R.G., and Jones, J.W., Solar and net radiation based equations to estimate reference evapotranspiration in humid climates, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., ASCE, 2003, Vol. 129, No. 5, pp. 336–347.
Jain, S.K., Nayak, P.C., and Sudhir, K.P., Models for estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural networks, and their physical interpretation, Hydrol. Process., 2008, Vol. 22, No. 13, pp. 2225–2234
Kisi, O. and Ozturk, O., Adaptive neuro-fuzzy computing technique for evapotranspiration estimation, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., ASCE, 2007, Vol. 133, No. 4, pp. 368–379.
Kisi, O. and Guven, A., Evapotranspiration modeling using linear genetic programming technique, J. Irrig. Drain Eng., 2010, Vol. 136, No. 10, pp. 715–723.
Kumar, R., Jat, M.K., and Shankar, V., Methods to estimate irrigated reference crop evapotranspiration— a review, Water Science Technology, IWA Publishing, 2012, Vol. 66, No. 3, pp. 525–535.
Kumar, M., Raghuwanshi, N.S., Singh, R., Wallender, W.W., and Pruitt, W.O., Estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural network, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., ASCE, 2002, Vol. 128, No. 4, pp. 224–233.
Landeras, G., Barredo, A.O., and Lopez, J.J., Comparison of artificial neural network models and empirical and semi-empirical equations for daily reference evapotranspiration estimation in the Basque Country (Northern Spain), Agr. Wat. Manag., 2008, Vol. 95, pp. 553–565.
Legates, D.R. and McCabe, J., Evaluating the use of “goodness-of fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation, Wat. Resour. Res., 1999, Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 233–241.
Mollahasani, A., Alavi, A.H., and Gandomi, A.H., Empirical modeling of plate load test moduli of soil via gene expression programming, Comput. Geotechnics, 2011, Vol. 38, pp. 281–286.
Naoum, S. and Tsanis, K.I., Hydroinformatics in evapotranspiration estimation, Environ. Modelling Software, 2003, Vol. 18, pp. 261–271.
Nazari, A., Prediction performance of PEM fuel cells by gene expression programming, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2010, Vol. 37, pp. 18972–18980.
Parasuraman, K., Elshorbagy, A., and Carey, S., Modeling the dynamics of the evapotranspiration process using genetic programming, Hydrolog. Sci. J., 2007, Vol. 52, No. 3, pp. 563–578.
Rivas, R. and Caselles, V., A simplified equation to estimate spatial reference evaporation from remote sensing-based surface temperature and local meteorological data, Remote Sensing Environ., 2004, Vol. 93, pp. 68–76.
Samadianfard, S., Gene expression programming analysis of implicit Colebrook–White equation in turbulent flow friction factor calculation, J. Petroleum Sci. Eng., 2012, Vol. 92–93, pp. 48–55.
Saridemir, M., Genetic programming approach for prediction of compressive strength of concretes containing rice husk ash, Construction Building Mater., 2010, Vol. 24, pp. 1911–1919.
Seckin, G., Yilmaz, T., Guven, A., Yuceer, A., Basibuyuk, M., and Ersu, C.B., Modeling the performance of up flow anaerobic filters treating paper-mill wastewater using gene-expression programming, Ecol. Eng., 2011, Vol. 37, pp. 523–528.
Shiri, J., Kisi, O., Landeras, G., Lopez, J.J., Nazemi, A.H., and Stuyt, L., Daily reference evapotranspiration modeling by using genetic programming approach in the Basque Country (Northern Spain), J. Hydrology, 2012, Vol. 414–415, pp. 302–316.
Steve, R.G., Kirkham, M.B., and Brent, E.C., Root uptake and transpiration: from measurements and models to sustainable irrigation, J. Agr. Wat. Manag., 2006, Vol. 86, pp. 165–176.
Trajkovic, S., Testing hourly reference evapotranspiration approaches using lysimeter measurements in a semiarid climate, Hydrology Res., 2010, Vol. 41, No. 1, pp. 38–49.
Trajkovic, S. and Kolakovic, S., Comparison of simplified pan-based equations for estimating reference evapotranspiration, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., 2010, Vol. 136, No. 2, pp. 137–140.
Traore, S. and Guven, A., Regional-specific numerical models of evapotranspiration using gene-expression programming interface in Sahel, Wat. Res. Manag., 2012, Vol. 26, pp. 4367–4380.
Traore, S., Wang, Y., and Kerh, T., Artificial neural network for modeling reference evapotranspiration complex process in Sudano-Sahelian Zone, Agr. Wat. Manag., 2010, Vol. 97, pp. 707–714.
Zahiri, A. and Eghbali, P., Gene expression programming for prediction of flow discharge in compound channels, J. Civil Eng. Urbanism, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 164–169.
Zanetti, S.S., Sousa, E.F., Oliveira, V.P.S., Almeida, F.T., and Bernardo, S., Estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural network and minimum climatological data, J. Irrig. Drain. Eng., ASCE, 2007, Vol. 133, No. 2, pp. 83–89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yassin, M.A., Alazba, A.A. & Mattar, M.A. Comparison between gene expression programming and traditional models for estimating evapotranspiration under hyper arid Conditions. Water Resour 43, 412–427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807816020172
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807816020172