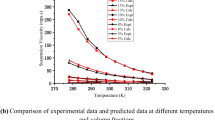
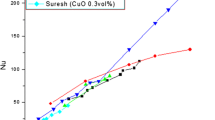
Abstract
Here is the review of experimental and theoretical results on the mechanism of heat transfer in nanofluids. A wide scope of problems related to the technology of nanofluid production, experimental equipment, and features of measurement methods is considered. Experimental data on heat conductivity of nanofluids with different concentrations, sizes, and material of nanoparticles are presented. Results on forced and free convection in laminar, and turbulent flows are analyzed. The available models of physical mechanisms of heat transfer intensification and suppression in nanofluids are presented. There are significant divergences in data of different researchers; possible reasons for this divergence are analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Akoh, Y. Tsukasaki, S. Yatsuya, and A. Tasaki, Magnetic properties of ferromagnetic ultrafine particles prepared by vacuum evaporation on running oil substrate, J. Crystal Growth, 1978, Vol. 45, P. 495–500.
K. Asaka, H. Nakahara, and Y. Saito, Nanowelding of a multiwalled carbon nanotube to metal surface and its electron field emission properties, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, Vol. 92, P. 023114.
M.J. Assael, C.F. Chen, I. Metaxa, and W.A. Wakeham, Thermal conductivity of suspensions of carbon nanotubes in water, Int. J. Thermophysics, 2004, Vol. 25, P. 971–985.
M. Biercuk, M. Llaguno, M. Radosavljevic, J. Hyun, A. Johnson, and J. Fischer, Carbon nanotube composites for thermal management, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, Vol. 80, No. 15, P. 2767–2769.
M. Chandrasekar and S. Suresh, A Review on the mechanisms of heat transfer in nanofluids, Heat Transfer Engng., 2009, Vol. 30, No. 14, P. 1136–1150.
S.U.S. Choi, Nanofluids: A new field of scientific research and innovative applications, Heat Transfer Engng., 2008, Vol. 29, No. 5, P. 429–431.
S.U.S. Choi, Nanofluids: from vision to reality through research, J. Heat Transfer, 2009, Vol. 131, P. 033106-1–033106-9.
S.U.S. Choi, Z.G. Zhang, W. Yu, F.E. Lockwood, and E.A. Grulke, Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nano-tube suspensions, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, Vol. 79, P. 2252–2254.
C.H. Chon and K.D. Kihm, Thermal conductivity enhancement of nanofluids by brownian motion, ASME J. Heat Transfer, 2005, b, Vol. 127, P. 810.
C.H. Chon, K.D. Kihm, S.P. Lee, and S.U.S. Choi, Empirical correlation finding the role of temperature and particle size for nanofluid (Al2O3) thermal conductivity enhancement, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, a, Vol. 87, P. 153107.
M. Chopkar, P.K. Das, and I. Manna, Synthesis and Characterization of Nanofluid for Advanced Heat Transfer Applications, Scr. Mater, 2006, Vol. 55, P. 549–552.
S.K. Das, S.U.S. Choi, and H. Patel, Heat transfer in nanofluids. A Review, Heat Transfer Engng., 2006, Vol. 20, No. 10, P. 3–19.
S.K. Das, S.U.S. Choi, W. Yu, and T. Pradeep, Nanofluids Science and Technology, Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey, 2007, 397 p.
S.K. Das, N. Putra, P. Thiesen, and W. Roetzel, Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids, J. Heat Transfer, 2003, Vol. 125, P. 567–574.
Y.L. Ding, H. Alias, D.S. Wen, and R.A. Williams, Heat transfer of aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes (CNT nanofluids), Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2006, Vol. 49, P. 240–250.
Y.L. Ding, H. Chen, L. Wang, C.-Y. Yang, Y. He, W. Yang, W.P. Lee, L. Zhang, and R. Huo, Heat Transfer Intensification Using Nanofluids, Powder and Particle, 2007, No. 25, P. 23–36.
J.A. Eastman, S.U.S. Choi, Li S., L.J. Thompson, and S. Lee, Enhanced thermal conductivity through the development of nanofluids, in: Proc. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Materials Res. Soc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA, Boston, MA, USA, 1997, Vol. 457, P. 3–11.
J.A. Eastman, S.U.S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu, and L.J. Thomson, Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, Vol. 78, P. 718–720.
J.A. Eastman, S.R. Phillpot, S.U.S. Choi, and P. Keblinski, Thermal transport in nanofluids, Ann. Rev. Mater. Res., 2004, Vol. 34, P. 219–246.
A.V. Eletskii, Transport properties of carbon nanotubes, Physics Uspekhi, 2009, Vol. 179, No. 3, P. 209–223.
W. Evans, J. Fish, and P. Keblinski, Role of Brownian motion hydrodynamics on nanofluids thermal conductivity, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, Vol. 88, P. 093116.
W. Evans, R. Prasher, J. Fish, P. Meakin, and P. Phelan, Effect of aggregation and interfacial thermal resistance on thermal conductivity of nanocomposites and colloidal nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2008, Vol. 51, P. 1431–1438.
J.E. Fischer and A.T. Johnson, Electronic properties of carbon nanotubes, Current Opinition in Solid State and Material Sci., 1999, Iss. 1, P.28–33.
L. Gao, X. Zhou, and Y.L. Ding, Effective thermal and electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube composites, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2007, Vol. 434, P. 297–300.
R.L. Hamilton and O.K. Crosser, Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems, I & EC Fundamentals, 1962, Vol. 1, No. 3, P. 187–191.
Y.R. He, Y. Jin, H.S. Chen, Y.L. Ding, D.Q. Cang, and H.L. Lu, Heat transfer and flow behaviour of aqueous suspensions of TiO2 nanoparticles (nanofluids) flowing upward through a vertical pipe, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2007, Vol. 50, P. 2272–2281.
J. Hone, M. Whitney, C. Pisconi, and A. Zett, Thermal conductivity of single-walled carbon nanotubes, Phys. Rev., B 25, 1999, P. R2514–R2516.
K.S. Hong, T.K. Hong, and H.S. Yang, Thermal Conductivity of Fe Nanofluids Depending on Cluster Size of Nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, Vol. 88, P. 031901.
T.-K. Hong, H.-S. Yang, and C.J. Choi, Study of the enhanced thermal conductivity of Fe nanofluids, J. Appl. Phys., 2005, Vol. 97, No. 6, P. 1–4.
S. Jana, A. Salehi-Khojin, and W.-H. Zhong, Enhancement of fluid thermal conductivity by the addition of single and hybrid nano-additives, Thermochim. Acta., 2007, Vol. 462, No. 1–2, P. 45–55.
H.U. Kang and S.H. Kim, Estimation of thermal conductivity of nanofluid using experimental effective particle volume, Exp.Heat Transfer, 2006, Vol. 19, P. 181–191.
P. Keblinski, S.R. Phillpot, S.U.S. Choi, and J.A. Eastman, Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids), Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2002, Vol. 45, P. 855–863.
P. Keblinski, J.A. Eastman, and D.G. Cahill, Nanofluids for thermal transport, Materials Today, 2005, June Iss., P. 36–44.
P. Keblinski, R. Prasher, and J. Eapen, Thermal conductance of nanofluids: is the controversy over? J. Nanoparticle Research, 2008, Vol. 10, No. 7, P. 1089–1097.
P. Kim, L. Shi, A. Majumdar, and P.L. McEuen, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2001, Vol. 87, P. 215502.
S.H. Kim, S.R. Choi, and D. Kim, Thermal conductivity of metal ? oxide nanofluids: particle size dependence and effect of laser irradiation, ASME J. Heat Transfer, 2007, Vol. 129, P. 298–307.
D.H. Kumar, H.E. Patel, V.R.R. Kumar, T. Sundararajan, T. Pradeep, and S.K. Das, Model for heat conduction in nanofluids, Physical Review Letter, 2004, Vol. 93, P. 144301.
S. Lee, S. Choi, S. Li, and J. Eastman, Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles, J. Heat Transfer, 1999, Vol. 121, P. 280–289.
C.H. Li and G.P. Peterson, Experimental investigation of temperature and volume fraction variations on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions (nanofluids), J. Appl. Phys., 2006, Vol. 99, P. 084314.
C.H. Li and G.P. Peterson, Mixing effect on the enhancement of the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions (nanofluids), Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2007, Vol. 50, P. 4668–4677.
M.-S. Liu, Lin M. Ching-Cheng, I.T. Huang, and C.-C. Wang, Enhancement of thermal conductivity with carbon nanotube for nanofluids, Int. Comm. in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, Vol. 32, No. 9, P. 1202–1210.
M.-S. Liu, Lin M. Ching-Cheng, C.Y. Tsai, and C.-C. Wang, Enhance of thermal conductivity with Cu for nanofluids using chemical reduction method, Inter. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2006, Vol. 49, P. 3028–3033.
C.-H. Lo, T.-T. Tsung, and L.-C. Chen, Ni nano-magnetic fluid prepared by submerged arc nanosynthesis system (sanss), JSME Int. J., Ser. B: Fluids and Thermal Engng., 2006, Vol. 48, No. 4, P. 750–755.
C.-H. Lo, T.-T. Tsung, and L.-C. Chen, Shape-controlled synthesis of Cu based nanofluid using submerged arc nanoparticle synthesis system (SANSS), J. Crystal Growth, 2005, Vol. 277, No. 1–4, P. 636–642.
S.M.S. Murshed, K.C. Leong, and C. Yang, Enhanced thermal conductivity of TiO2—water based nanofluids, Int. J. of Thermal Sciences, 2005, Vol. 44, No. 4, P. 367–373.
C.W. Nan, Z. Shi, and Y. Lin, A simple model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, Vol. 375, P. 666–669.
M.A. Pakhomov, M.V. Protasov, V.I. Terekhov, and A.Yu. Varaksin, Experimental and numerical investigation of downward gas-dispersed turbulent pipe flow, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2007, Vol. 50, P. 2107–2116.
H.E. Patel, S.K. Das, T. Sundararajan, N.A. Sreekumaran, B.P. George, and T. Pradeep, Thermal conductivities of naked and monolayer protected metal nanoparticle based nanofluids: manifestation of anomalous enhancement and chemical effects, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, Vol. 83, P. 2931–2933.
R. Prasher, P. Bhattacharya, and P.E. Phelan, Thermal conductivity of nanoscale colloidal solutions (nanofluids), Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, Vol. 94, P. 025901.
R. Prasher, W. Evans, P. Meakin, J. Fish, P. Phelan, and P. Keblinski, Effect of aggregation on thermal conduction in colloidal nanofluids, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, Vol. 89, P. 143119.
P.A. Putnam, D.G. Cahill, P.V. Braun, Z. Ge, and R.G. Shimmin, Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, Vol. 99, P. 084308-1–6.
V.Ya. Rudyak, A.A. Belkin, and G.V. Harlamov, Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoparticles diffusion in dense gases and fluids, J. Aeros. Sci., 2000, Vol. 31, Suppl. 1, P. S432–S433.
S. Shenogin, A. Bodapati, L. Xue, R. Ozisik, and P. Keblinski, Effect of chemical functionalization on thermal transport of carbon nanotube composites, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, a, Vol. 85, P. 2229–2231.
S. Shenogin, L.P. Xue, R. Ozisik, P. Keblinski, and D.G. Cahill, Role of thermal boundary resistance on the heat flow in carbon nanotube composites, J. Appl. Phys., 2004, b, Vol. 95, P. 8136–8144.
A.V. Simakin, V.V. Voronov, and G.A. Shafeev, Formation of nanoparticles at laser ablation of solid bodies in fluids, Trans. Prokhorov Inst. Gen Phys. RAS, 2004, Vol. 60, P. 83–107.
M. Wagener, B.S. Murty, and B. Gunther, Preparation of metal nanosuspensions by high-pressure DC-sputtering on running fluids, S. Komarnenl, J.C. Parker, H.J. Wollenberger (Eds.), Nanocrystalline and Nanocomposite Materials II, Vol. 457, Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1997, P. 149–154.
B.-X. Wang, L.-P. Zhou, and X.-F. Peng, A fractal model for predicting the effective thermal conductivity of fluid with suspension of nanoparticles, Int. J. of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, Vol. 46, P. 2665–2672.
L. Wang and X. Wei, Nanofluids: synthesis, heat conduction, and extension, J. Heat Transfer, 2009, Vol. 131, P. 033102-1–033102-7.
X. Wang, X. Xu, and S.U.S. Choi, Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle — fluid mixture, J. Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 1999, Vol. 13, No. 4, P. 474–480.
X-Q. Wang and A.S. Mujumbar, Heat Transfer Characteristics of Nanofluids: a Review, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 2007, Vol. 46, P. 1–19.
D.S. Wen and Y.L. Ding, Effective thermal conductivity of aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes (carbon nanotube nanofluids), J. Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2004, a, Vol. 18, No. 4, P. 481–485.
D.S. Wen and Y.L. Ding, Experiment investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluids at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2004, b, Vol. 47, P. 5181–5188.
D.S. Wen and Y.L. Ding, Experimental investigation into the pool boiling heat transfer of aqueous based γ-Alumina nanofluids, J. of Nanoparticle Research, 2005, a, No. 7, P. 265–274.
D.S. Wen and Y.L. Ding, Formulation of nanofluids for natural convective heat transfer applications, Int. J. of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2005, b, Vol. 26, P. 855–864.
D.S. Wen and Y.L. Ding, Natural convective heat transfer of suspensions of TiO2 nanoparticles (nanofluids), Transactions of IEEE on Nanotechnology, 2006, No. 5, P. 220–227.
H. Xie, H. Lee, W. Youn, and M. Choi, Nanofluids containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their enhanced thermal conductivities, J. Appl. Phys., 2003, Vol. 94, No. 8, P. 4967–4971.
H. Xie, J. Wang, T. Xi, Y. Liu, F. Ai, and Q. Wu, Thermal conductivity enhancement of suspensions containing nanosized alumina particles, J. of Appl. Phys., 2002, a, Vol. 91, No. 7, P. 4568–4572.
H. Xie, J. Wang, T. Xi, and Y. Liu, Thermal conductivity of suspensions containing nanosized SiC particles, Int. J. Thermophysics, 2002, b, Vol. 23, P. 571–580.
Y. Xuan and Q. Li, Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Fluid Transfer, 2000, Vol. 21, P. 58–64.
L. Xue, P. Keblinski, S.R. Phillpot, S.U.S. Choi, and J.A. Eastman, Effect of fluid layering at the fluid — solid interface on thermal transport, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2004, Vol. 47, No. 19–20, P. 4277–4284.
S. Yatsuya, Y. Tsukasaki, K. Yamauchi, and K. Mihama, Ultrafine particles produced by vacuum evaporation onto a running oil substrate (VEROS) and the modified method, J. Crystal Growth, 1984, Vol. 70, P. 533–535.
W. Yu and S.U.S. Choi, The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: a renovated Maxwell model, J. of Nanoparticle Research, 2003, No. 5, P. 167–171.
W. Yu, D.M. France, S.U.S. Choi, and J.L. Routbort, Review and Assessment of Nanofluid Technology for Transportation and Other Applications, Argonne National Laboratory, ANL/ESD/07-9, 2007, 78 p.
X. Zhang, H. Gu, and M. Fujii, Effective thermal conductivity an thermal diffusivity of nanofluids containing spherical and cylindrical nanoparticles, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, Vol. 100, No. 4, P. 044325.
X. Zhang, H. Gu, and M. Fujii, Effective thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of nanofluids containing spherical and cylindrical nanoparticles, Experimental Thermal and Fluid Sci., 2007, Vol. 31, No. 6, P. 593–599.
H. Zhu, Y. Lin, and Y. Yin, A novel one-step chemical method for preparation of copper nanofluids, J. Colloid and Interface Sci., 2004, Vol. 227, P. 100–103.
K.P. Zol’nikov, R.I. Kadyrov, I.I. Naumov, S.G. Psakh’e, G.E. Rudenskii, and V.M. Kuznetsov, Possible nonlinear heat pulse propagation of s in solids at Debye temperatures, Technical Phys. Lett., 1999, Vol. 25, No. 3, P. 230–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terekhov, V.I., Kalinina, S.V. & Lemanov, V.V. The mechanism of heat transfer in nanofluids: state of the art (review). Part 1. Synthesis and properties of nanofluids. Thermophys. Aeromech. 17, 1–14 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869864310010014
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869864310010014