Abstract
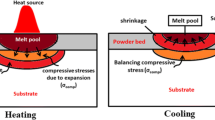
Heat-transfer- and thermocapillary-convection macroprocesses observed during direct laser metal deposition (DLMD) with coaxial powder injection are examined. The study is performed using the 3D mathematical model incorporating self-consistent equations for free surface evolution, heat transfer, and hydrodynamics, which allow for powder-particle embedding into the thermocapillary convection zone under DLMD. The processes under consideration refer to the main ones underlying additive laser technologies, which determine the microstructural properties and quality of synthesized parts. The convection-diffusion equations are numerically solved using the final volume method. Calculations are carried out for the thermocapillary convection of H13 steel powder. The influence of laser-radiation characteristics (power, scanning rate, intensity distribution in the beam) and the powder-mass flow velocity on temperature fields, the structure of convective melt flow (including a maximum melt velocity), and the geometric characteristics (height and width) of the object formed is investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Ya. Panchenko, V. S. Golubev, V. V. Vasil’tsov, et al., Laser Technologies for Materials Processing: Modern Problems on Fundamental Researches and Applied Developments, Ed. by V. Ya. Panchenko (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
I. V. Shishkovskii, Laser Synthesis of Functional Mesostructures and Volumetric Units (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
G. G. Gladush and I. Smurov, Physics of Laser Materials Processing: Theory and Experiment (Springer, Berlin, 2011).
L. Han, F. W. Liou, and K. M. Phatak, Metall. Trans. B 35, 1139 (2004).
A. Frenk, M. Vandyoussefi, J.-D. Wagniere, et al., Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28, 501 (1997).
V. G. Niz’ev, F. Kh. Mirzade, V. Ya. Panchenko, et al., Math. Models Comput. Simul. 4 (2), 163 (2012).
B. Ollier, N. Pirch, E. W. Krentz, and H. Schluter, in Proc. European Conference on Laser Treatment of Materials ECLAT’92, Ed. B. L. Mordike (Gottigen, 1992), p. 687
S.-L. Wang, R. F. Sekerka, A. A. Wheeler, et al., Phys. D (Amsterdam, Neth.) 69, 189 (1993).
J. A. Warren and W. J. Boettinger, Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 689 (1995).
Z. Bi and R. F. Sekerka, Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.) 261, 95 (1998).
O. Penrose and P. C. Fife, Phys. D (Amsterdam, Neth.) 3, 44 (1990).
F. Kh. Mirzade, Zhurn. Prikl. Spektr. 83 (6–16), 559 (2016) [in Russian].
S. Osher and J. A. Sethian, J. Comput. Phys. 79, 12 (1998).
E. Olsson and G. Kreiss, J. Comput. Phys. 210, 225 (2005).
C. Hirt and B. Nichols, J. Comput. Phys. 39, 201 (1981).
J. Choi, L. Han, and Y. Hua, J. Heat Transfer 127 (9), 978 (2005).
Z. Fan, J. K. Stroble, J. Ruan, et al., in Proc. ASME 2007 Int. Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference (Atlanta, GA, 2007), p.37.
D. V. Bedenko, O. B. Kovalev, I. Smurov, and A. V. Zaitsev, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 95, 902 (2016).
F. Kh. Mirzade, Proc. SPIE 10330, 10330 (2017).
W. D. Bennon and F. P. Incropera, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 30, 2161 (1987).
A. Albadawi, D. B. Donoghue, A. J. Robinson, et al., Int. J. Multiphase Flow 53, 11 (2013).
K. Yokoi, J. Comput. Phys. 278, 221 (2014).
V. R. Voller and C. R. Swaminathan, Numer. Heat Transfer, Part B 19, 175 (1991).
H. Qi, J. Mazumder, and H. Ki, J. Appl. Phys. 100 (2), 024903 (2006).
S. Morville, M. Carin, P. Peyre, et al., J. Laser Appl. 24 (3), 032008 (2012).
H. O. Zhang, F. R. Kong, G. L. Wang, and L. F. Zeng, J. Appl. Phys. 100 (12), 123522 (2006).
J. Mazumder, A. Schifferer, and J. Choi, Mater. Res. Innovations 3 (3), 118 (1999).
J. T. Hofman, B. Pathiraj, J. Van Dijk, et al., J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212 (11), 2455 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Dubrov, F.Kh. Mirzade, V.D. Dubrov, V.Ya. Panchenko, 2018, published in Poverkhnost’, 2018, No. 1, pp. 65–75.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubrov, A.V., Mirzade, F.K., Dubrov, V.D. et al. Heat Transfer and Thermocapillary Convection during the Laser Deposition of Metal Powders Implemented in Additive Technologies. J. Surf. Investig. 12, 54–63 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451018010081
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451018010081