Abstract
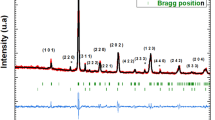
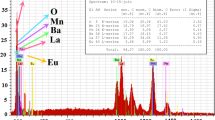
The solid solutions CeO2–(Sm,Nd)2O3 have been prepared by the solid-phase synthesis. The microstructure, density, and electrical conductivity of ceramic samples obtained by rolling with an organic binder, followed by sintering in air at a temperature of 1600°C have been investigated. The contributions to the total conductivity from the grain volume and grain boundaries in the temperature range of 250–700°C have been separated using impedance spectroscopy. The impedance spectroscopy data have revealed a significant effect of grain boundaries on the transport properties of the solid electrolyte with a Sm dopant as compared to the electrolyte with Nd. The optical properties of the polycrystalline electrolytes Ce1–x Nd x O2–δ and Ce0.8Sm0.2O2–δ have been studied using Raman spectroscopy. In the spectrum of the ceramic samples, there are two modes: a mode of CeO2 at a frequency of 465 cm–1 and an additional mode at a frequency of ~550 cm–1 due to vibrations associated with oxygen vacancies, the intensity of which depends on the dopant concentration and the energy of the dopant cation–oxygen vacancy bond. The binding energy of oxygen vacancies in the fluorite structure correlates with the behavior of bulk conductivity, and the solid solutions with samarium exhibit the highest bulk conductivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Inaba and H. Tagawa, Solid State Ionics 1, 1 (1996).
M. Mogensen, N. M. Sammers, and G. A. Tompsett, Solid State Ionics 1, 63 (2000).
B. C. H. Steele, J. Mater. Sci. 1, 1053 (2001).
V. V. Kharton, F. M. Figuiredo, L. Navarro, E. N. Naumovich, A. V. Kovalevsky, A. A. Yaremchenko, A. P. Viskup, A. Carneiro, F. M. B. Marques, and J. Frade, J. Mater. Sci. 1, 1105 (2001).
A. I. Leonov, High-Temperature Chemistry of Cerium Oxygen Compounds (Nauka, Leningrad, 1969), p. 205 [in Russian].
D.-J. Kim, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1, 1415 (1989).
E. Yu. Pikalova, V. G. Bamburov, A. A. Murashkina, A. D. Neuimin, A. K. Demin, and S. V. Plaksin, Russ. J. Electrochem. 1 (6), 690 (2011).
H. Yahiro, K. Eguchi, and H. Arai, Solid State Ionics 1, 71 (1989).
E. Pikalova, V. Bamburov, I. Rukavishnikova, A. Demin, and A. Kolchugin, Energy Production and Management in the 21st Century (WIT Press, Southampton, United Kingdom, 2014), p. 261.
E. G. Vaganov, V. P. Gorelov, N. M. Bogdanovich, I. V. Korzun, and V. A. Kazantsev, Russ. J. Electrochem. 1 (6), 663 (2007).
Y. Wang, T. Mori, J.-G. Li, and Y. Yajima, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 1, 229 (2003).
R. Peng, Ch. Xia, Q. Fu, G. Meng, and D. Peng, Mater. Lett. 1, 1043 (2002).
J. Van herle, T. Horita, T. Kawada, N. Sakai, H. Yokokawa, and M. Dokiya, Solid State Ionics 86–1, 1255 (1996).
G. B. Balazs and R. S. Glass, Solid State Ionics 1, 155 (1995).
H. Yahiro, Y. Eguchi, K. Eguchi, and H. Arai, J. Appl. Electrochem. 1, 527 (1988).
H. Yoshida, H. Deguchi, K. Miura, M. Horiguchi, and T. Inagaki, Solid State Ionics 1, 191 (2001).
D. A. Andersson, S. I. Simak, N. V. Skorodumova, I. A. Abrikosov, and B. Johansson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1, 3518 (2006).
S. Omar, E. D. Wachsman, and J. C. Nino, Solid State Ionics 1, 1890 (2008).
E. Yu. Pikalova, A. A. Murashkina, V. I. Maragou, A. K. Demin, V. N. Strekalovsky, and P. E. Tsiakaras, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1, 6175 (2011).
D. Medvedev, E. Pikalova, V. Maragou, A. Demin, and P. Tsiakaras, J. Power Sources 1, 217 (2013).
D. Medvedev, E. Yu. Pikalova, A. Demin, A. Podias, I. Korzun, B. Antonov, and P. Tsiakaras, J. Power Sources 1, 269 (2014).
Y. Ikuma, E. Shimada, and N. Nakomura, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1, 419 (2005).
H. L. Tuller and A. S. Nowick, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1, 255 (1975).
V. N. Chebotin and M. V. Perfil’ev, Electrochemistry of Solid Electrolytes (Khimiya, Moscow, 1978), p. 312 [in Russian].
C. M. Kleinlogel and L. J. Gauckleryu, J. Electroceram. 1, 231 (2000).
X.-M. Lin, L.-P. Li, G.-Sh. Li, and W.-H. Su, Mater. Chem. Phys. 1, 236 (2001).
G.-B. Jung, T.-J. Huang, and C.-L. Chang, J. Solid State Electrochem. 1, 225 (2002).
E. Yu. Pikalova, A. A. Murashkina, and D. A. Medvedev, Russ. J. Electrochem. 1 (6), 681 (2011).
P.-S. Cho, S. B. Lee, D.-S. Kim, J.-H. Lee, D.-Y. Kim, and H.-M. Park, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 9, A399 (2006).
J. R. McBride, K. C. Hass, B. D. Poindexter, and W. H. Weber, J. Appl. Phys. 1, 2435 (1994).
T. Sato and S. Tateyama, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 1, 2257 (1982).
Z. D. Doh evi-Mitrovi, M. Radovi, M. Šepanovi, M. Gruji-Brojin, and Z. V. Popovi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 1, 203118 (2007).
S. A. Acharya, V. M. Gaikwad, V. Sathe, and S. K. Kulkarni, Appl. Phys. Lett. 1, 113508 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Sal’nikov, E.Yu. Pikalova, 2015, published in Fizika Tverdogo Tela, 2015, Vol. 57, No. 10, pp. 1895–1903.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sal’nikov, V.V., Pikalova, E.Y. Raman and impedance spectroscopic studies of the specific features of the transport properties of electrolytes based on CeO2 . Phys. Solid State 57, 1944–1952 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415100261
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415100261