Abstract
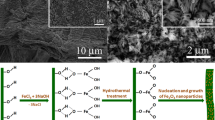
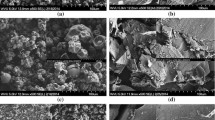
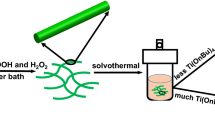
Microsized tubes and fibers of iron(III) oxide are obtained by the sol-gel method using cotton cellulose as template. The influence of the electrokinetic properties of the surface of cotton cellulose and sols of nanoparticles, as well as the calcination temperature on morphology and the properties of ceramic fibers, is studied. It is noted that the use of sol with a strongly acidic dispersion medium leads to the formation of microtubes, fully repeating the features of the structure of the original cellulose fiber. The mechanism of the formation of fibers and tubes based on electrostatic interactions is proposed. With an increase of the calcination temperature from 600 to 1200°C, there is an increase in the size of the α-Fe2O3 particles, a reduction of the inner diameter of the tubes, and an increase of their mechanical strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grashchenkov, D.V., Balinova, Yu.A., and Tinyakova, E.V., Aluminum oxide ceramic fibers and materials based on them, Glass Ceram., 2012, vol. 69, no. 3, pp. 130–133.
Umnov, P.P., Kurakova, N.V., Molokanov, V.V., Sevost’yanov, M.A., Kolmakov, A.G., and Kovneristyi, Yu.K., Effect of processing factors on the quality of the surface of a composite wire coated with amorphous metal, Deform. Razrushenie Mater., 2006, no. 12, pp. 38–42.
Martakov, I.S., Krivoshapkin, P.V., Torlopov, M.A., and Krivoshapkina, E.F., Application of chemically modified celluloses as templates for obtaining of alumina materials, Fibers Polym., 2015, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 975–981.
Cheng, Y., Zou, B., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Fan, X., Zhu, L., Wang, Y., Ma, H., and Cao, X., Formation mechanism of Fe2O3 hollow fibers by direct annealing of the electrospun composite fibers and their magnetic, electrochemical properties, Cryst. Eng. Commun., 2011, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 2863–2870.
Maslennikova, T.P., Korytkova, E.N., Drozdova, I.A., and Gusarov, V.V., Interaction of potassium chloride aqueous solution Mg3Si2O5(OH)4 with the nanotubes based on magnesium hydrosilicate, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2009, vol. 82, no. 3, p. 352–355.
Perez, J.M., Iron oxide nanoparticles: Hidden talent, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2007, vol. 2, pp. 535–536.
Sitnikov, P.A., Kuchin, A.V., Ryazanov, M.A., Belykh, A.G., Vaseneva, I.N., Fedoseev, M.S., and Tereshatov, V.V., Influence of acid-base properties of oxides surface on their reactivity towards epoxy compounds, Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2014, vol. 84, no. 5, pp. 810–815.
Rajala, J.W., Shin, H.U., Lolla, D., and Chase, G.G., Core-shell electrospun hollow aluminum oxide ceramic fibers, Fibers, 2015, vol. 3, pp. 450–462.
Ermolenko, I.N, Ul’yanova, T.M., Vityaz’, P.A., and Fedorova, I.L., Voloknistye vysokotemperaturnye materialy (Fibrous High-Temperature Materials), Minsk: Nauka i Tekhnika, 1991.
Yuan, R., Fu, X., Wang, X., Liu, P., Wu, L., Xu, Y., Wang, X., and Wang, Z., Template synthesis of hollow metal oxide fibers with hierarchical architecture, Chem. Mater., 2006, vol. 18, no. 19, pp. 4700–4705.
Li, Q. and Zhang, C., Preparation of Fe2O3 microtubules and the effect of a surfactant on their properties, J. Ceram. Process. Res., 2010, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 331–334.
Jirgensons, B. and Straumanis, M.E., A Short Textbook of Colloid Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, 1962.
Khamova, T.V., Shilova, O.A., and Golikova, E.V., Investigation of the structuring in the sol–gel systems based on tetraethoxysilane, Glass Phys. Chem., 2006, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 448–459.
Oshima, H.J., Healy, T.W., and White, L.R., Improvement on Hogg–Healy–Fuerstenau formulas for the interaction on dissimilar double layers, Thin Solid Films, 1982, vol. 89, no. 2, pp. 484–493.
Elimelech, M., Gregory, J., Jia, X., and Williams, R.A., Particle Deposition and Aggregation Measurement, Modelling and Simulation, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1995.
Lu, S., Pugh, R.J., and Forssberg, E., Interfacial Separation of Particles, Studies in Interface Science, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005, vol.20.
Bergstrom, L., Stemme, S., Dahlfors, T., Arwin, H., and Odberg, L., Spectroscopic ellipsometry characterization and estimation of the Hamaker constant of cellulose, Cellulose, 1999, vol. 6, pp. 1–13.
Krivoshapkin, P.V., Krivoshapkina, E.F., and Dudkin, B.N., Evaluation of surface forces and structure formation in water–organic dispersed systems of aluminum oxide, Glass Phys. Chem., 2012, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 449–454.
Liu, H.H., Lanphere, J., Walker, S., and Cohen, Y., Effect of hydration repulsion on nanoparticle agglomeration evaluated via a constant number Monte-Carlo simulation, Nanotecnology, 2015, vol. 26, no. 4, p. 045708. doi 10.1088/0957-4484/26/4/045708
Israelachvili, J.N., Intermolecular and Surface Forces, New York: Academic, 1992.
Baturenko, D.Yu., Chernoberezhskii, Yu.M., Lorentsson, A.V., and Zhukov, A.N., Effect of pH on the aggregation stability of microcrystalline cellulose dispersions in aqueous 0.1 M NaCl solutions, Colloid J., 2003, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 666–671.
WWW-MINCRYST, Crystallographic and Crystallochemical Database for Minerals and their Structural Analogues. http://database.iem.ac.ru/mincryst.
Nanoscience: Colloidal and Interfacial Aspects, Starov, V.M., Ed., Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010.
Cornell, R.M. and Schwertmann, U., The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses, Weinheim: Wiley, 2003.
Kruk, M. and Jaroniec, M., Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic–inorganic nanocomposite materials, Chem. Mater., 2001, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 3169–3183.
Smolin, A.S., Shabiev, R.O., and Yakkola, P., A study of the zeta potential and cationic need of semi-finished fiber products, Khim. Rastit. Syr’ya, 2009, no. 1, pp. 177–184.
Mosur, P.M., Chernoberezhskii, Yu.M., and Lorenstson, A.V., Electrosurface properties of microcrystalline cellulose dispersions in aqueous solutions of aluminum chloride, nitrate, and sulfate, Colloid J., 2008, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 462–465.
Herrington, T.M. and Midmore, B.R., Adsorption of ions at the cellulose/aqueous electrolyte interface. Part 1. Charge/pH isotherms, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1984, vol. 80, no. 6, pp. 1525–1537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.I. Mikhailov, E.F. Krivoshapkina, Yu.I. Ryabkov, P.V. Krivoshapkin, 2016, published in Fizika i Khimiya Stekla.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikhailov, V.I., Krivoshapkina, E.F., Ryabkov, Y.I. et al. Influence of the electrokinetic properties of cellulose on the morphology of iron(III) oxide upon template synthesis. Glass Phys Chem 42, 582–589 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659616060158
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659616060158