Abstract
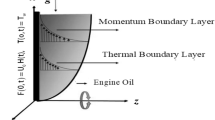
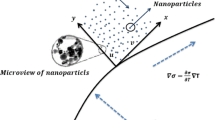
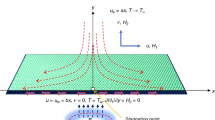
The main target of the present model is to find the idea of magneto-hydrodynamics incompressible nanofluid flow past over an infinite rotating disk. The effect of the magnetic field is existed to check the nanofluid flow. The single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) engine oil can be utilized despite carrier fluid for an unsteady rotating disk. Here, we transform the nonlinear system of differential equations to the dimensionless ordinary differential equation by using similarity transformation. Then, we use the numerical method of lines to solve the nonlinear ODE via the Runge–Kutta technique. The resultant of the velocity, Nusselt number and Skin friction is demonstrated under the effect of several factors. We note that when we increase the velocity of the rotating disk, fluid velocity and temperature are safely increased. Finally, we note that the outcomes obtained demonstrate that the SWCNTs nanofluids improved the heat transfer more than the MWCNTs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, T. Ichihashi, Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 363, 603–605 (1993)
D.S. Bethune, C.H. Kiang, M.S. Devries, G. Gorman, R. Savoy, J. Vazquez et al., Cobalt-catalysed growth of carbon nanotubes with single-atomic-layer walls. Nature 363, 605–607 (1993)
T. Von Karman, Uber laminar and turbulent reibung. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1, 233–235 (1921)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Exact analytical solutions for heat and mass transfer of MHD slip flow in nanofluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 84, 182–187 (2012)
K. Millsaps, K. Pohlhausen, Heat transfer by laminar flow from a rotating plate. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 19(2), 120–126 (1952)
M.M. Rashidi, N. Kavyani, S. Abelman, Investigation of entropy generation in MHD and slip flow over a rotating porous disk with variable properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 70, 892–917 (2014)
N.A. Khan, S. Aziz, N.A. Khan, MHD flow of Powell–Eyring fluid over a rotating disk. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45(6), 2859–2867 (2014)
M.F.L. De Volder et al., Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339, 535–543 (2013)
S.M.S. Murshed, C.A. Nieto de Castro, Superior thermal features of carbon nanotubes-based nano fluids—a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 37, 155–167 (2014)
C. Negin, S. Ali, Q. Xie, Application of nanotechnology for enhancing oil recovery, a review. Petroleum 2, 324–333 (2016)
Z. Zaidi, S.T. Mohyud-din, B.B. Mohsen, Convective heat transfer and MHD analysis of wall jet flow of nanofluids containing carbon nanotubes. Eng. Comput. 343, 1–9 (2017)
R.U. Haq, F. Shahzad, Q.M. Al-Mdallal, MHD pulsatile flow of engine oil based carbon nanotubes between two concentric cylinders. Results Phys. 7, 57–68 (2017)
N. Hordy, D. Rabilloud, J.-L. Meunier, S. Coulombe, A stable carbon nanotube nanofluid for latent heat-driven volumetric absorption solar heating applications. J. Nanomater. 16, 248 (2015)
Q. Xue, Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 368, 302–307 (2005)
A.U. Rehman et al., Effects of single and multi-walled carbon nano tubes on water and engine oil based rotating fluids with internal heating. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 1991–2002 (2017)
R. Ellahi, M. Hassan, A. Zeeshan, Study of natural convection MHD nanofluid by means of single and multiwalled carbon nanotubes suspended in a salt water solution. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 1–10 (2015)
T. Hayat, T. Nasir, M.I. Khan, A. Alsaedi, Non-Darcy flow of water-based single (SWCNTs) and multiple (MWCNTs) walls carbon nanotubes with multiple slip conditions due to rotating disk. Results Phys. 9, 390–399 (2018)
S. Farooq, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, S. Asghar, Mixed convection peristalsis of carbon nanotubes with thermal radiation and entropy generation. J. Mol. Liq. 250, 451–467 (2018)
M. Terrones, Science and technology of the twenty-first century: synthesis, properties, and applications of carbon nanotubes. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 33, 491–501 (2003)
R.I. Hamilton, O.K. Crosser, Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1, 182–191 (1962)
D.J. Jaffery, Conduction through a random suspension of spheres. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 335, 355–367 (1973)
R. Davis, The effective thermal conductivity of a composite material with spherical inclusions. Int. J. Thermophys. 7, 609–620 (1986)
S. Lu, H. Lin, Effective conductivity of composites containing aligned spherical inclusions of finite conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 6761–6769 (1998)
V.J. Rossow, On flow of electrically conducting fluids over a flat plate in the presence of a transverse magnetic field. Technical Report. Arch. & Image Lib. (1958)
H. Alfvén, Existence of electromagnetic-hydrodynamic waves. Nature 150(3805), 405 (1942)
M. Ramzan, N. Ullah, J.D. Chung, D. Lu, U. Farooq, Buoyancy effects on the radiative magneto Micropolar nanofluid flow with double stratification, activation energy and binary chemical reaction. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 12901 (2017)
D. Lu et al., On three-dimensional MHD Oldroyd-B fluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and homogeneous–heterogeneous reaction. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40(8), 387 (2018)
M.I. Khan, T. Hayat, M. Waqas, A. Alsaedi, M.I. Khan, Effectiveness of radiative heat flux in MHD flow of Jeffrey-nanofluid subject to Brownian and thermophoresis diffusions. J. Hydrodyn. 31, 421–427 (2019)
Z. Yan, J. Jiang, Y. Bai, MHD flow and heat transfer analysis of fractional Oldroyd-B nanofluid between two coaxial cylinders. Comput. Math. Appl. 78(10), 3408–3421 (2019)
N. Kelson, A. Desseaux, Note on porous rotating disk flow. ANZIAM J. 42, 837–855 (2000)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Nanofluid flow and heat transfer due to a rotating disk. Comput. Fluids 94, 139–146 (2014)
J.A. Khan, M. Mustafa, T. Hayat et al., A revised model to study the MHD nanofluid flow and heat transfer due to rotating disk: numerical solutions. Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 957–964 (2018)
V.K. Joshi, P. Ram, R.K. Sharma et al., Porosity effect on the boundary layer Bodewadt flow of a magnetic nanofluid in the presence of geothermal viscosity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 254 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11511-0
N. Acharya, K. Das, P. Kumar Kundu, Fabrication of active and passive controls of nanoparticles of unsteady nanofluid flow from a spinning body using HPM. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11629-y
A.M. Salem, G. Ismail, R. Fathy, Unsteady MHD boundary layer stagnation point flow with heat and mass transfer in nanofluid in the presence of mass fluid suction and thermal radiation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15113-6
C.S.K. Raju, S.U. Mamatha, P. Rajadurai et al., Nonlinear mixed thermal convective flow over a rotating disk in suspension of magnesium oxide nanoparticles with water and EG. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 196 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12552-y
A.Y. Sayed, M.S. Abdel-wahed, Entropy analysis for an MHD nanofluid with a microrotation boundary layer over a moving permeable plate. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00181-6
U. Shankar, N.B. Naduvinamani, Magnetized impacts of Cattaneo–Christov double-diffusion models on the time-dependent squeezing flow of Casson fluid: a generalized perspective of Fourier and Fick’s laws. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12715-x
R. Dhanai, P. Rana, L. Kumar, Multiple solutions in MHD flow and heat transfer of Sisko fluid containing nanoparticles migration with a convective boundary condition: critical points. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16142-3
P.M. Krishna, N. Sandeep, R.P. Sharma, Computational analysis of plane and parabolic flow of MHD Carreau fluid with buoyancy and exponential heat source effects. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11469-9
M. Khan, J. Ahmed, L. Ahmad, Chemically reactive and radiative von Kármán swirling flow due to a rotating disk. Appl. Math. Mech. 39, 1295–1310 (2018)
N. Bachok, A. Ishak, I. Pop, Flow and heat transfer over a rotating porous disk in a nanofluid. Phys. B 406(9), 1767–1772 (2011)
F. Saba, N. Ahmed, U. Khan, S.T. Mohyud-Din, A novel coupling of (CNT-Fe3O4/H2O) hybrid nanofluid for improvements in heat transfer for flow in an asymmetric channel with dilating/squeezing walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 136, 186–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12315-4
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to the Referees and Editors for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baleanu, D., Sadat, R. & Ali, M.R. The method of lines for solution of the carbon nanotubes engine oil nanofluid over an unsteady rotating disk. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 788 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00763-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00763-4