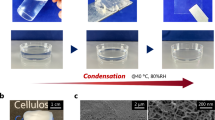
Abstract
We present a time-resolved investigation of the natural drying process of microbial cellulose (MC) by means of simultaneous small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), intermediate-angle neutron scattering (IANS) and weighing techniques. SANS was used to elucidate the microscopic structure of the MC sample. The coherent scattering length density of the water penetrating amorphous domains varied with time during the drying process to give a tunable scattering contrast to the water-resistant cellulose crystallites, thus the contrast variation was automatically performed by simply drying. IANS and weighing techniques were used to follow the macroscopic structural changes of the sample, i.e., the composition variation and the loss of the water. Thus, both the structure and composition changes during the whole drying process were resolved. In particular, the quantitative crosscheck of composition variation by IANS and weighing provides a full description of the drying process. Our results show that: i) The natural drying process could be divided into three time regions: a 3-dimensional shrinkage in region I, a 1-dimensional shrinkage along the thickness of the sample in region II, and completion in region III; ii) the further crystallization and aggregation of the cellulose fibrils are observed in both the rapid drying and natural drying methods, and the rapid drying even induces obvious structural changes in the length scale of 7-125nm; iii) the amount of “bound water”, which is an extremely thin layer of water surrounding the surfaces of cellulose fibrils, was estimated to be ∼ 0.35 wt% by the weighing measurement and was verified by the quantitative analysis of SANS results.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Nishi, M. Uryu, S. Yamanaka, K. Watanabe, N. Kitamura, M. Iguchi, S. Mitsuhashi, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 2997 (1990).
S.M. Keshk, Bioproces. Biotechniq. 4, 1000150 (2014).
M. Shoda, Y. Sugano, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 10, 1 (2005).
S. Koizumi, Y. Zhao, Y. Tomita, T. Kondo, H. Iwase, D. Yamaguchi, T. Hashimoto, Eur. Phys. J. E 26, 137 (2008).
S. Koizumi, Y. Tomita, T. Kondo, T. Hashimoto, Macromol. Symp. 279, 110 (2009).
R.L. Legge, Biotechnol. Adv. 8, 303 (1990).
P. Ross, R. Mayer, M. Benziman, Microbial. Rev. 55, 35 (1991).
K. Watanabe, M. Tabuchi, Y. Morinaga, F. Yashinaga, Cellulose 5, 187 (1998).
J. Shah, R.M. Brown, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 66, 352 (2005).
B.R. Evans, H.M. O’Neill, V.P. Malyvanh, I. Lee, J. Woodward, Biosens. Bioelectron. 18, 917 (2003).
M. Iguchi, S. Yamanaka, A. Budhiono, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 261 (2000).
D. Klemm, U. Udhardt, S. Marsch, D. Schumann, Polymer News 24, 377 (1999).
D. Klemm, D. Schumann, U. Udhardt, S. Marsch, Prog. Polym. Sci. 26, 1561 (2001).
O.M. Alvarez, M. Patel, J. Booker, L. Markowitz, Wounds-Compend. Clin. Res. Pract. 16, 224 (2004).
J.D. Fontana, A.M. Desouza, C.K. Fontana, I.L. Torriani, J.C. Moreschi, B.J. Gallotti, S.J. Desouza, G.P. Narcisco, J.A. Bichara, F.X. Farah, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 24, 253 (1990).
J.D. Fontana, C.G. Joerker, M. Baron, M. Maraschin, A.G. Ferreira, I. Torriani, A.M. Souza, M.B. Soares, M.A. Fontana, M.F. Guimaraes, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 63, 327 (1997).
R. Jonas, L.F. Farah, Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 59, 101 (1998).
P.L. Park, J.Y. Je, H.G. Byun, S.H. Moon, S.K. Kim, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14, 317 (2004).
A.M. Sokolnicki, R.J. Fisher, T.P. Harrah, D.L. Kaplan, J. Membr. Sci. 272, 15 (2006).
US 4655758, Microbiol Polysaccharide articles and methods of production (1987).
C. Clasen, B. Sultanova, T. Wilhelms, P. Heisig, W.M. Kulicke, Macromol. Symp. 244, 48 (2006).
C. Zhang, L. Wang, J. Zhao, P. Zhu, Adv. Mater. Res. 239-242, 2667 (2011).
P. Ramanen, P.A. Penttila, K. Svedstrom, S.L. Maumu, R. Serimaa, Cellulose 19, 901 (2012).
M. Schramm, S. Hestrin, Biochem. J. 56, 163 (1954).
M. Schramm, S. Hestrin, J. Gen. Microbiol. 11, 123 (1954).
S. Bielecki, A. Krystynowicz, M. Turkiewicz, A. Kalinowska, Bacterial Cellulose, Biopolymers Online (2005), DOI:10.1002/3527600035.bpol5003.
C.Q. Sun, J. Pharm. Sci. 94, 2132 (2005).
S. Koizumi, H. Iwase, J. Suzuki, T. Oku, R. Motokawa, H. Sasao, H. Tanaka, D. Yamaguchi, H. Shimizu, T. Hashimoto, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, s474 (2007).
D. Yamaguchi, S. Koizumi, R. Morokawa, T. Kumada, K. Aizawa, T. Hashimoto, Physica B. 385-386, 1190 (2006).
S. Koizumi, Y. Zhao, Y. Tomita, D. Yamaguchi, H. Iwase, R. Motokawa, T. Hashimoto, T. Kondo, Soft Matter, submitted.
R.J. Roe, Methods of X-ray and Neutron Scattering in Polymer Science (Oxford University Press, New York, 2000).
J.S. Higgins, H.C. Benoit, Polymers and Neutron Scattering (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1994).
H.F. Jakob, D. Fengel, S.E. Tschegg, P. Fratzl, Macromolecules 28, 8782 (1995).
M. Muller, C. Czihak, G. Vogl, P. Fratzl, H. Schober, C. Riekel, Macromolecules 31, 3953 (1998).
C.H. Haigler, P.J. Weimer (Editors), Biosynthesis and Biodegradation of Cellulose (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1991).
N. Lavoine, I. Desloges, A. Dufresne, J. Bras, Carbohydr. Polym. 90, 735 (2012).
J. Haase, R. Hosemann, B. Renwanz, Colloid Polym. Sci. 252, 712 (1974).
H.P. Fink, D. Hofmann, H. Purz, J. Acta Polym. 41, 131 (1990).
H.F. Jakob, P. Fratzl, S.E. Tschegg, J. Struct. Biol. 113, 13 (1994).
T. Nomura, T. Yamada, Wood Res. 52, 1 (1972).
S. Andersson, R. Serimaa, T. Paakkari, P. Saranpää, E. Pesonen, J. Wood Sci. 49, 531 (2003).
G. Porod, Kolloid Z. 124, 83 (1951).
A. Okiyama, H. Shirae, H. Kano, S. Yamanka, Food Hydrocolloids 6, 471 (1992).
A. Okiyama, M. Motoki, S. Yamanaka, Food Hydrocolloids 6, 503 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Koizumi, S., Yamaguchi, D. et al. Hierarchical structure in microbial cellulose: What happens during the drying process. Eur. Phys. J. E 37, 129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2014-14129-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2014-14129-7