Abstract.
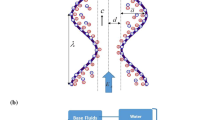
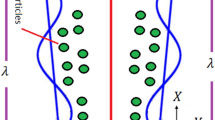
We investigate the velocity slip and thermal slip effects on peristaltically driven thermal transport of nanofluids through the vertical parallel plates under the influence of transverse magnetic field. The wall surface is propagating with sinusoidal wave velocity c. The flow characteristics are governed by the mass, momentum and energy conservation principle. Low Reynolds number and large wavelength approximations are taken into consideration to simplify the non-linear terms. Analytical solutions for axial velocity, temperature field, pressure gradient and stream function are obtained under certain physical boundary conditions. Two types of nanoparticles, SiO2 and Ag, are considered for analysis with water as base fluid. This is the first article in the literature that discusses the SiO2 and Ag nanoparticles for a peristaltic flow with variable viscosity. The effects of physical parameters on velocity, temperature, pressure and trapping are discussed. A comparative study of SiO2 nanofluid, Ag nanofluid and pure water is also presented. This model is applicable in biomedical engineering to make thermal peristaltic pumps and other pumping devices like syringe pumps, etc. It is observed that pressure for pure water is maximum and pressure for Ag nanofluid is minimum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.C., Fung, C.S. Yih, J. Appl. Mech. 35, 669 (1968)
M. Costa, J.B. Furness, Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 294, 47 (1976)
S.B. Benjamin, D.C. Gerhardt, D.O. Castell, Gastroenterology 77, 478 (1979)
L.M. Srivastava, V.P. Srivastava, J. Biomech. 17, 821 (1984)
P.J. Kahrilas, W.J. Dodds, W.J. Hogan, M. Kern, R.C. Arndorfer, A. Reece, Gastroenterology 91, 897 (1986)
T. Morita, I. Wada, H. Saeki, S. Tsuchida, R.M. Weiss, J. Urol. 137, 132 (1987)
J.R. Grider, A.E. Foxx-Orenstein, J.G. Jin, Gastroenterology 115, 370 (1998)
J.R. Roth, Phys. Plasmas 10, 2117 (2003)
M.M. Teymoori, E. Abbaspour-Sani, Sensors Actuators A: Physical 117, 222 (2005)
D. Tripathi, Math. Biosci. 233, 90 (2011)
D. Tripathi, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 51, 91 (2012)
D. Tripathi, J. Bionic Engin. 9, 119 (2012)
W.K.H. Chu, J. Fang, Eur. Phys. J. B 16, 543 (2000)
A.E.H.A. El Naby, I.I.E. El Shamy, Appl. Math. Sci. 1, 2967 (2007)
A. Ebaid, Phys. Lett. A 372, 4493 (2008)
Y. Wang, T. Hayat, M. Oberlack, J. Appl. Mech. 76, 011006 (2009)
S. Srinivas, R. Gayathri, M. Kothandapani, Computer Phys. Commun. 180, 2115 (2009)
R. Ellahi, M. Hameed, Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat & Fluid Flow 22, 24 (2012)
D. Tripathi, Transp. Porous Media 92, 559 (2012)
D. Tripathi, O.A. Bég, J.L. Curiel-Sosa, Comp. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 17, 433 (2014)
N.S. Akbar, S. Nadeem, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 3964 (2012)
N.S. Akbar, S. Nadeem, Z.H. Khan, Appl. NanoSci. 4, 849 (2014)
R. Ellahi, A. Riaz, S. Nadeem, Appl. Nanosci. 4, 753 (2014)
S. Nadeem, A. Riaz, R. Ellahi, N.S. Akbar, Appl. Nanosci. 4, 393 (2014)
A. Ebaid, Comp. Math. Appl. 68, 77 (2014)
D. Tripathi, O.A. Bég, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 70, 61 (2014)
N.S. Akbar, S. Nadeem, Z.H. Khan, Alexandria Engin. J. 53, 191 (2014)
M. Kothandapani, J. Prakash, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 234 (2015)
N.S. Akbar, M. Raza, R. Ellahi, Comp. Methods Prog. Biomed. 130, 22 (2015)
M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, M.Y. Javed, R. Ellahi, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 36 (2015)
B.C. Sarkar, S. Das, R.N. Jana, O.D. Makinde, J. Nanofluids 4, 461 (2015)
M. Kothandapani, J. Prakash, J. Mech. Med. Biol. 15, 1550030 (2015)
R. Ellahi, M.M. Bhatti, A.A. Khan, Wulfenia 22, 248 (2015)
Noreen Sher Akbar, Dharmendra Tripathi, O. Anwar Bég, J. Mech. Med. Biol. 16, 1650088 (2015)
S.E. Ghasemi, M. Vatani, M. Hatami, D.D. Ganji, J. Mol. Liquids 215, 88 (2016)
R. Ellahi, M. Hassan, A. Zeeshan, Asia-Pacific J. Chem. Engin. 11, 179 (2016)
S.U. Rehman, R. Ellahi, S. Nadeem, Q.M. Zaigham Zia, J. Mol. Liquids 218, 484 (2016)
A. Zeeshan, A. Majeed, R. Ellahi, J. Mol. Liquids 215, 549 (2016)
M. Akbarzadeh, S. Rashidi, M. Bovand, R. Ellahi, J. Mol. Liquids 220, 1 (2016)
R. Ellahi, M. Hassan, A. Zeeshan, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 726 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sher Akbar, N., Bintul Huda, A. & Tripathi, D. Thermally developing MHD peristaltic transport of nanofluids with velocity and thermal slip effects. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 332 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16332-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16332-y