Abstract.
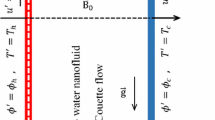
The onset of nanofluid convection in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field is investigated numerically based on the non-homogeneous Buongiorno’s mathematical model. In this study, we use the latest experimental correlations and powerful analytical models for expressing the thermo-physical properties of some electrically conducting nanofluids, such as copper-water, sliver-water and gold-water nanofluids, in which the Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects on slip flow in nanofluids are taken into account in this model (i.e., two-phase transport model). In this paper, we assume that the nanofluid has Newtonian behavior, confined horizontally between two infinite impermeable boundaries and heated from below, in such a way that the nanoparticles tend to concentrate near the upper wall. Considering the basic state of the nanofluidic system, the linear stability theory has been successfully applied to obtain the principal stability equations, which are solved numerically for an imposed volumetric fraction of nanoparticles and no-slip impermeable conditions at the isothermal walls bounding the nanofluid layer. The linear boundary-value problem obtained in this investigation is converted into a pure initial-value problem, so that we can solve it numerically by the fourth-fifth-order Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method. The generalized Buongiorno’s mathematical model proposed in this study allows performing a highly accurate computational analysis. In addition, the obtained results show that the stability of the studied nanofluidic system depends on several parameters, namely, the magnetic Chandrasekhar number Q , the reference value for the volumetric fraction of nanoparticles \( \phi_0\) and the size of nanoparticles \( d_p\) . In this analysis, the thermo-hydrodynamic stability of the studied nanofluid is controlled through the critical thermal Rayleigh number \( R_{ac}\) , which characterizes the onset of convection cells, whose size is \( L_c=2\pi/a_c\) . Furthermore, the effects of various pertinent parameters on the critical stability parameters \( R_{ac}\) and \( a_c\) are discussed in more detail through graphical and tabular illustrations, for three types of nanofluids including copper-water, sliver-water, and gold-water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.U.S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, in Proceedings of the 1995 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vol. 231 (ASME, 1995) pp. 99--105
J. Buongiorno, J. Heat Transf. 128, 240 (2006)
P.G. Siddheshwar, C. Kanchana, Y. Kakimoto, A. Nakayama, J. Heat Transf. 139, 012402 (2017)
A. Wakif, Z. Boulahia, R. Sehaqui, Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 7, 299 (2016)
A. Wakif, Z. Boulahia, R. Sehaqui, J. Nanofluids 6, 136 (2017)
B.S. Bhadauria, S. Agarwal, A. Kumar, Transp. Porous Media 90, 605 (2011)
B.S. Bhadauria, P. Kiran, M. Belhaq, MATEC Web Conf. 16, 09003 (2014)
D. Yadav, C. Kim, J. Lee, H.H. Cho, Comput. Fluids 121, 26 (2015)
T. Hayat, T. Muhammad, S.A. Shehzad, A. Alsaedi, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 111, 274 (2017)
A. Wakif, Z. Boulahia, M. Zaydan et al., Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 14, 1048 (2016)
A. Wakif, Z. Boulahia, R. Sehaqui, Results Phys. 7, 2134 (2017)
S. Chandrasekhar, Hydrodynamic and hydromagnetic stability (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1961)
D.A. Nield, A.V. Kuznetsov, Eur. J. Mech. 29, 217 (2010)
D. Yadav, J. Lee, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 162 (2015)
D. Yadav, J. Wang, R. Bhargava et al., Appl. Therm. Eng. 103, 1441 (2016)
G.S. McNab, A. Meisen, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 44, 339 (1973)
M. Corcione, Energy Convers. Manag. 52, 789 (2011)
T. Armaghani, A. Kasaeipoor, N. Alavi, M.M. Rashidi, J. Mol. Liq. 223, 243 (2016)
M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, M. Gorji-Bandpy, S. Soleimani, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45, 795 (2014)
K. Mehmood, S. Hussain, M. Sagheer, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 109, 397 (2017)
J.C.M. Garnett, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. A 203, 385 (1904)
A.H. Sihvola, I.V. Lindell, Effective permeability of mixtures (Helsinki University of Technology, 1989)
D. Yadav, R. Bhargava, G.S. Agrawal, J. Eng. Math. 80, 147 (2013)
A. Wakif, Z. Boulahia, R. Sehaqui, Results Phys. (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.01.066
J.F. Schenck, Med. Phys. 23, 815 (1996)
P.G. Siddheshwar, N. Meenakshi, Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 3, 271 (2017)
T. Hayat, B. Ahmed, F.M. Abbasi, A. Alsaedi, J. Mol. Liq. 234, 324 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakif, A., Boulahia, Z., Mishra, S.R. et al. Influence of a uniform transverse magnetic field on the thermo-hydrodynamic stability in water-based nanofluids with metallic nanoparticles using the generalized Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133, 181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12037-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12037-7