Abstract
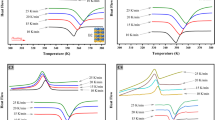
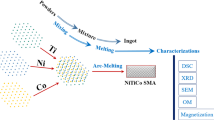
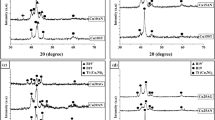
\(\hbox {Ni}_{ 50-x}\hbox {Ti}_{50}\hbox {Cu}_x\) (at.%) \(x=14, 17, 20)\) shape memory alloys were produced using the arc-melting technique. The replacing Cu element into Ti-rich NiTi alloy has been investigated through characterization techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), optical and SEM microscopy. Additionally, various phases and precipitations were determined using EDS measurement. The manufactured alloys showed a single-step austenite \(\leftrightarrow \) martensite phase transformation (B2 \(\leftrightarrow \)\(\hbox {B19}^{\prime }\) ). The DSC results showed that the samples have comparable high-temperature hysteresis in the range of about (30–50 K). The main detected XRD peaks are the monoclinic martensite phase with cubic austenite phases, which their intensities were decreased by increasing copper addition into the alloy. The microhardness results revealed that the second phase of the alloys has higher hardness compared to the matrix phase. It was concluded that NiTiCu can be used in low-temperature shape memory alloys as they illustrate transformation temperature below \(100\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\)
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.N. Qader, M. Kök, F. Dagdelen, Y. Aydogdu, A review of smart materials: researches and applications. El-Cezerî J. Sci. Eng. 6(3), 755–788 (2019). https://doi.org/10.31202/ecjse.562177
S.S. Mohammed, K. Mediha, I.N. Qader, F. Dagdelen, The developments of piezoelectric materials and shape memory alloys in robotic actuator systems. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 17, 1014–1030 (2019). https://doi.org/10.31590/ejosat.653751
M. Geetha, A.K. Singh, R. Asokamani, A.K. Gogia, Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants–a review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 54(3), 397–425 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.06.004
S. Shabalovskaya, J. Anderegg, J. Van Humbeeck, Critical overview of Nitinol surfaces and their modifications for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 4(3), 447–467 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2008.01.013
M.H. Elahinia, M. Hashemi, M. Tabesh, S.B. Bhaduri, Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants: a review. Prog. Mater Sci 57(5), 911–946 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.11.001
D.A. Miller, D.C. Lagoudas, Influence of cold work and heat treatment on the shape memory effect and plastic strain development of NiTi. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 308(1–2), 161–175 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)01982-1
C. Tatar, Z. Yildirim, Phase transformation kinetics and microstructure of NiTi shape memory alloy: effect of hydrostatic pressure. Bull Mater. Sci 40(4), 799–803 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1413-1
T. Goryczka, J. Van Humbeeck, NiTiCu shape memory alloy produced by powder technology. J. Alloys Compd. 456(1–2), 194–200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.094
E. Ercan, F. Dagdelen, I. Qader, Effect of tantalum contents on transformation temperatures, thermal behaviors and microstructure of CuAlTa HTSMAs. J Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139(1), 29–36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.094
F. Dagdelen, M. Aldalawi, M. Kok, I. Qader, Influence of Ni addition and heat treatment on phase transformation temperatures and microstructures of a ternary CuAlCr alloy. Euro. Phys J. Plus 134(2), 66 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12479-3
S.N. Saud, E. Hamzah, T. Abubakar, M. Zamri, M. Tanemura, Influence of Ti additions on the martensitic phase transformation and mechanical properties of Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 118(1), 111–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3953-6
J.-Y. Jang, S.-J. Chun, N.-S. Kim, J.-W. Cho, J.-H. Kim, J.-T. Yeom, J.-I. Kim, T.-H. Nam, Martensitic transformation behavior in Ti-Ni-X (Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Te, Tl, Pb, Bi) ternary alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(12), 5064–5069 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.004
X. He, L. Rong, Effect of deformation on the stress-induced martensitic transformation in (Ni 47 Ti 44) 100–x Nb x shape memory alloys with wide hysteresis. Met. Mater. Int. 12(4), 279–288 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027544
T. Fukuda, T. Kakeshita, M. Kitayama, T. Saburi, Effect of aging on martensitic transformation in a shape memory Ti-40.5 Ni-10Cu alloy. J. Phys. IV, 5(C8), C8-717–C8-722 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4/199558717
T.H. Nam, T. Saburi, Y. Nakata, K.i. Shimizu, Shape memory characteristics and lattice deformation in Ti-Ni-Cu alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 31(12), 1050–1056 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.31.1050
F. Gil, E. Solano, J. Pena, E. Engel, A. Mendoza, J. Planell, Microstructural, mechanical and citotoxicity evaluation of different NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15(11), 1181–1185 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-004-5953-8
H. Sehitoglu, I. Karaman, X. Zhang, H. Kim, Y. Chumlyakov, I. Kireeva, H.J. Maier, Deformation of NiTiCu shape memory single crystals in compression. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32(3), 477–489 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0064-3
J. Uchil, K. Mahesh, K.G. Kumara, Dilatometric study of martensitic transformation in NiTiCu and NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mater Sci 36(24), 5823–5827 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012908222409
R. Bricknell, K. Melton, O. Mercier, The structure of NiTiCu shape memory alloys. Metall. Trans. A 10(6), 693–697 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658390
A. Biscarini, B. Coluzzi, G. Mazzolai, A. Tuissi, F. Mazzolai, Extraordinary high damping of hydrogendoped NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 355(1–2), 52–57 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(03)00267-6
T. Goryczka, J. Van Humbeeck, Characterization of a NiTiCu shape memory alloy produced by powder technology. J Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 17(1–2), 65–68 (2006)
S. Shiva, I. Palani, S. Mishra, C. Paul, L. Kukreja, Investigations on the influence of composition in the development of Ni-Ti shape memory alloy using laser based additive manufacturing. Opt. Laser Technol. 69, 44–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2014.12.014
M. Kök, I.N. Qader, S.S. Mohammed, E. ÖNER, F. Dağdelen, Y. Aydogdu, Thermal stability and some thermodynamics analysis of heat treated quaternary CuAlNiTa shape memory alloy. Mater. Res. Express 7, 015702 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5bef
T. Elrasasi, M. Dobróka, L. Daróczi, D. Beke, Effect of thermal and mechanical cycling on the elastic and dissipative energy in CuAl (11.5 wt%) Ni (5.0 wt%) shape memory alloy. J Alloys Compd. 577, S517–S520 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.06.108
S. Ozgen, C. Tatar, Thermoelastic transition kinetics of a gamma irradiated CuZnAl shape memory alloy. Met. Mater. Int 18(6), 909–916 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-6001-8
J. Ortin, A. Planes, Thermodynamic analysis of thermal measurements in thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Acta Metall. 36(8), 1873–1889 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(88)90291-X
M. Kök, H.S.A. Zardawi, I.N. Qader, M.S. Kanca, The effects of cobalt elements addition on Ti2Ni phases, thermodynamics parameters, crystal structure and transformation temperature of NiTi shape memory alloys. Euro. Phys J. Plus 134(5), 197 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12570-9
F. Dagdelen, M. Kok, I. Qader, Effects of Ta content on thermodynamic properties and transformation temperatures of shape memory NiTi alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 25(6), 1420–1427 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00298-z
F. Dagdelen, T. Gokhan, A. Aydogdu, Y. Aydogdu, O. Adigüzel, Effects of thermal treatments on transformation behaviour in shape memory Cu-Al-Ni alloys. Mater. Lett. 57(5–6), 1079–1085 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00934-5
F. Dagdelen, E. Balci, I.N. Qader, E. Ozen, M. Kok, M.S. Kanca, S.S. Abdullah, S.S. Mohammed, Influence of the Nb content on the microstructure and phase transformation properties of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. JOM (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04026-6
M. Kok, A.O.A. Al-Jaf, Z.D. Çirak, I.N. Qader, E. Özen, Effects of heat treatment temperatures on phase transformation, thermodynamical parameters, crystal microstructure, and electrical resistivity of NiTiV shape memory alloy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08788-3
I.N. Qader, M. Kök, F. Dagdelen, Effect of heat treatment on thermodynamics parameters, crystal and microstructure of (Cu-Al-Ni-Hf) shape memory alloy. Phys. B. Condens. Matter 553, 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.10.021
C. Tatar, Z. Yildirim, O. Kaygili, Effect of hydrostatic pressure on thermodynamic properties of NiTi shape memory alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater 62(2), 799–806 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2017-0119
M. Ghadimi, A. Shokuhfar, A. Zolriasatein, H.R. Rostami, Morphological and structural evaluation of nanocrystalline NiTiCu shape memory alloy prepared via mechanical alloying and annealing. Mater. Lett. 90, 30–33 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.09.008
M. Valeanu, M. Lucaci, A. Crisan, M. Sofronie, L. Leonat, V. Kuncser, Martensitic transformation of Ti50Ni30Cu20 alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 509(13), 4495–4498 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.01.154
A. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.56.978
K. Otsuka, X. Ren, Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 50(5), 511–678 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Management Unit of the Scientific Research Projects of Firat University (FUBAP) (Project Numbers: FF.19.01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatar, C., Acar, R. & Qader, I.N. Investigation of thermodynamic and microstructural characteristics of NiTiCu shape memory alloys produced by arc-melting method. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00288-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00288-w