Abstract
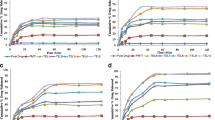
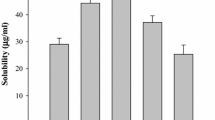
This article investigates enhancement of the dissolution profile of valdecoxib using solid dispersion with PVP. The article also describes the preparation of fast-dissolving tablets of valdecoxib by using a high amount of superdisintegrants. A phase solubility method was used to evaluate the effect of various water-soluble polymers on aqueous solubility of valdecoxib. Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K-30) was selected and solid dispersions were prepared by the method of kneading. Dissolution studies, using the USP paddle method were performed for solid dispersions of valdecoxib. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and x-ray diffractometry (XRD) were performed to identify the physicochemical interaction between drug and carrier, hence its effect on dissolution. Tablets were formulated containing solid dispersion products and compared with commercial products. IR spectroscopy, XRD, and DSC showed no change in the crystal structure of valdecoxib. Dissolution of valdecoxib improved significantly in solid dispersion products (<85% in 5 minutes). Tablets containing solid dispersion exhibited better dissolution profile than commercial tablets. Thus, the solid dispersion technique can be successfully used for improvement of dissolution of valdecoxib.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Medical Economics Company.Physician’s Desk Reference. 57th ed. Stamford, CT: Thomson Healthcare; 2003.
Chiou WL, Riegelman S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems.J Pharm Sci. 1971; 60: 1281–1302.
Babu GV, Kumar NR, Himasankar K, Seshasayana A, Murthy KV. Nimesulide-modified gum karaya solid mixtures: preparation, characterization and formulation development.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003; 29: 855–864.
Rogers JA, Anderson AJ. Physical characteristics and dissolution profiles of ketoprofen-urea solid dispersions.Pharm Acta Helv. 1982; 57: 276–281.
El-Gazayerly ON. Characterization and evaluation of tenoxicam coprecipitates.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000; 26: 925–930.
Vippagunta SR, Maul KA, Tallavajhala S, Grant DJW. Solid-state characterization of nifedipine solid dispersions.Int. J. Pharm. 2002; 236: 111–123.
Murali Mohan Babu GV, Prasad CHDS, Ramana Murthy KV. Evaluation of modified gum karaya as carrier for the dissolution enhancement of poorly water soluble drug nimodipines.Int J Pharm. 2002; 234: 1–17.
Okonogi S, Yonemochi E, Oguchi T, Puttipipatkhachorn S, Yamamoto K. Enhanced dissolution of urosodeocholic acid from the solid dispersion.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1997;23:1115–1121.
Torrado S, Torrado S, Torrado JJ, Cadorniga R. Preparation, dissolution and characterization of albendazole solid dispersions.Int J Pharm. 1996; 140: 247–250.
Margarit MV, Rodrýguez IC, Cerezo A. Physical characteristics and dissolution kinetics of solid dispersions of ketoprofen and polyethylene glycol 6000.Int J Pharm. 1994; 108: 101–107.
Yagi N, Terashima Y, Kenmotsu H, Sekikawa H, Takada M. Dissolution behavior of probucol from solid dispersion systems of probucol-polyvinylpyrrolidone.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1996; 44:241–244.
Kushida I, Ichikawa M, Asakawa N. Improvement of dissolution and oral absorption of ER-341 22, a poorly water soluble dual 5-lipoxygenase/ cyclooxygenase inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity by preparing solid dispersion.J Pharm Sci. 2002;91:258–266.
Danjo K, Nakata T, Otsuka A. Preparation and dissolution behavior of ethenzamide solid dispersions using various sugars as dispersion carriers.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1997; 45: 1840–1844.
Arias MJ, Ginés JM, Moyano JR, Pérez-Martínez JI, Rabasco AM. Influence of preparation method of solid dispersion on dissolution rate: study of triammterene-D-mannitol. system.Int J Pharm. 1995; 123: 25–31.
Tros de Ilarduya MC, Martín C, Goñi MM, Martinez-Ohárriz MC. Solubilization and interaction of sulindac with polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 in the solid state and in aqueous solution.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1998; 24: 295–300.
Sheu MT, Yeh CM, Sokoloski TD. Characterization and dissolution of fenofibrate solid dispersion systems.Int J Pharm. 1994; 103: 137–146.
Yamashita K, Nakate T, Okimoto KA, et al. Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus.Int J Pharm. 2003; 267: 79–91.
Marin MT, Margarit MV, Salcedo GE. Characterization and solubility study of solid dispersions of flunarizine and polyvinylpyrrolidone.Farmaco. 2002; 57: 723–727.
Khan KA. The concept of dissolution efficiency.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1975; 27: 48–49.
Ford JL. The current status of solid dispersions.Pharm Acta Helv. 1986; 61: 69–88.
Mura P, Manderioli A, Bramanti G, Ceccarelli L. Properties of solid dispersions of naproxen in various polyethylene glycols.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1996; 22: 909–916.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: August 18, 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modi, A., Tayade, P. Enhancement of dissolution profile by solid dispersion (kneading) technique. AAPS PharmSciTech 7, 68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070368
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070368