Abstract
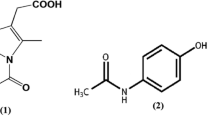
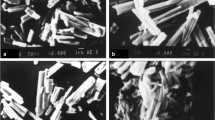
A series of blends of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and indomethacin (IMC), containing 20–80 wt.% IMC were obtained and characterized by differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform–infrared spectroscopy, and powder X-ray diffraction in order to observe the mutual influence of the two components. The main thermal transitions of PDMS remained un-changed. Both the solvent (tetrahydrofuran, THF) and the PDMS influenced the crystalline form of IMC. The blends were subsequently re-dissolved in THF, with or without cross-linking reagents added and precipitated into diluted aqueous solutions of siloxane-based surfactants. The resulted nanoparticles were analyzed by dynamic light scattering and scanning electron microscopy. Most of the particles had diameters between 200 and 300 nm. The surfactants, the IMC content and the cross-linking influenced the particles size and polydispersity, as well as the nanoparticle yield. The maximum drug release from selected aqueous formulations was 30%.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Habal MB. The biologic basis for the clinical application of the silicones. A correlate to their biocompatibility. Arch Surg. 1984;119(7):843–8.
Thomas X. Silicone adhesives in healthcare applications. http://www.dowcorning.com/content/publishedlit/52-1057-01.pdf. Accessed 10 Jan 2013.
Andriot M, Chao SH, Colas A, Cray S, de Buyl F, DeGroot JV, Dupont A, Easton T, Garaud JL, Gerlach E, Gubbels F, Jungk M, Leadley S, Lecomte JP, Lenoble B, Meeks R, Mountney A, Shearer G, Stassen S, Stevens C, Thomas X, Wolf AT. Silicones in industrial applications. In: De Jaeger R, Gleria M, editors. Inorganic Polymers. Nova; 2007. p. 61–161.
European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals. Joint Assessment of Commodity Chemicals JACC 055: Linear Polydimethylsiloxanes CAS No. 63148-62-9 (Second Edition). Brussels. 2011.
Noll W. Chemistry and technology of silicone. New York: Academic; 1968.
Colas A. Silicones in pharmaceutical applications. http://www.dowcorning.com/content/publishedlit/51-993a-01.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2012.
Di Colo G. Controlled drug release from implantable matrices based on hydrophobic polymers. Biomaterials. 1992;13:850–6.
Racles C, Hamaide T, Ioanid A. Siloxane surfactants in polymer nanoparticles formulation. Appl Organomet Chem. 2006;20:235–45.
Racles C, Cazacu M, Hitruc G, Hamaide T. On the feasibility of chemical reactions in the presence of siloxane-based surfactants. Colloid Polym Sci. 2009;287:461–70.
Racles C, Alexandru M, Cazacu M, Ioanid A, Hamaide T. Obtention des elastomeres silicones en nanoreacteurs siloxane-organiques. Rev Roum Chim. 2009;54:583–8.
Hadgraft J, Plessis J, Goosen C. The selection of NSAIDs for dermal delivery. Int J Pharm. 2000;207:31–7.
Cordero J, Camacho M, Obach R, Domenench J, Vila L. In vitro based index of topical anti-inflammatory activity to compare a series of NSAIDs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2001;51:135–42.
Rhee Y, Choi J, Park E, Chi S. Transdermal delivery of ketoprofen using microemulsions. Int J Pharm. 2001;228:161–70.
Kawashima Y. Nanoparticulate systems for improved drug delivery. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2001;47:1–2.
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V. Biodegradable nanoparticle from drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2003;55:329–47.
Petros RA, DeSimone JM. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery. 2010;9:615–27.
Racles C. Siloxane-based surfactants containing tromethamol units. Soft Materials. 2010;8:1–11.
Higuchi T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52:1145–9.
Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm. 1983;15:25–35.
Ritger PL, Peppas NA. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-Fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J Control Release. 1987;5:23–6.
Martena V, Censi R, Hoti E, Malaj L, Di Martino P. Indomethacin nanocrystals prepared by different laboratory scale methods: effect on crystalline form and dissolution behavior. J Nanopart Res. 2012;14:1275. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1275-9.
Taylor LS, Zografi G. Spectroscopic characterization of interactions between PVP and indomethacin in amorphous molecular dispersions. Pharm Res. 1997;14:1691–8.
Yilgor I, McGrath JE. Polysiloxane containing copolymers: a survey of recent developments. Adv Polym Sci. 1988;86:1–87.
Pan X, Julian T, Augsburger L. Quantitative measurement of indomethacin crystallinity in indomethacin-silica gel binary system using differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray powder diffractometry. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006;7(1):11.
Crowley KJ, Zografi G. Cryogenic grinding of indomethacin polymorphs and solvates: assessment of amorphous phase formation and amorphous phase physical stability. J Pharm Sci. 2002;91:492–507.
Greco K, Bogner R. Crystallization of amorphous indomethacin during dissolution: effect of processing and annealing. Mol Pharm. 2010;7:1406–18. doi:10.1021/mp1000197.
Qi C, Xia X, Zhang W, Xie C, Cai S. Indomethacin/Cu/LDPE porous composite for medicated copper intrauterine devices with controlled release performances. Compos Sci Technol. 2012;72:428–34. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.12.004.
Bodmeier R, Chen H. Indomethacin polymeric nanosuspensions prepared by microfluidization. J Contr Release. 1990;12:223–33.
Raval A, Parikha J, Engineer C. Dexamethasone eluting biodegradable polymeric matrix coated stent for intravascular drug delivery. Chem Eng Res Des. 2010;88:1479–84. doi:10.1016/j.cherd.2010.03.007.
Dash AK, Suryanarayanan R. An implantable dosage form for the treatment of bone infections. Pharm Res. 1992;9:993–1002.
Yohe ST, Colson YL, Grinstaff MW. Superhydrophobic materials for tunable drug release: using displacement of air to control delivery rates. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:2016–9. doi:10.1021/ja211148a.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partly supported by a grant of the Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNCS–UEFISCDI, project number PN-II-ID-PCCE-2011-2-0028. The author thanks Dr. V. Cozan and Prof. S. Shova for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Racles, C. Polydimethylsiloxane–Indomethacin Blends and Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 14, 968–976 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9989-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9989-2