Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Jelenković, Predrag R.
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2010.
Information ranking and power laws on trees.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
1057.
Jelenković, Predrag R.
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2012.
Implicit Renewal Theory and Power Tails on Trees.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 2,
p.
528.
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2012.
Asymptotics for Weighted Random Sums.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 4,
p.
1142.
Jelenković, Predrag R.
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2012.
Implicit renewal theorem for trees with general weights.
Stochastic Processes and their Applications,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 9,
p.
3209.
Alsmeyer, Gerold
and
Meiners, Matthias
2012.
Fixed points of inhomogeneous smoothing transforms.
Journal of Difference Equations and Applications,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 8,
p.
1287.
Jelenković, Predrag R.
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2013.
Random Matrices and Iterated Random Functions.
Vol. 53,
Issue. ,
p.
159.
Buraczewski, Dariusz
and
Kolesko, Konrad
2014.
Linear stochastic equations in the critical case.
Journal of Difference Equations and Applications,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 2,
p.
188.
Chen, Ningyuan
Litvak, Nelly
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2014.
Algorithms and Models for the Web Graph.
Vol. 8882,
Issue. ,
p.
120.
Jelenković, Predrag R.
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2015.
Maximums on trees.
Stochastic Processes and their Applications,
Vol. 125,
Issue. 1,
p.
217.
Chen, Ningyuan
and
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2015.
Efficient simulation for branching linear recursions.
p.
2716.
Avrachenkov, Konstantin
Kadavankandy, Arun
Ostroumova Prokhorenkova, Liudmila
and
Raigorodskii, Andrei
2015.
Algorithms and Models for the Web Graph.
Vol. 9479,
Issue. ,
p.
151.
Buraczewski, D.
Damek, E.
and
Zienkiewicz, J.
2015.
Precise tail asymptotics of fixed points of the smoothing transform with general weights.
Bernoulli,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 1,
Yang, Yang
Leipus, Remigijus
and
Šiaulys, Jonas
2016.
Asymptotics for randomly weighted and stopped dependent sums.
Stochastics,
Vol. 88,
Issue. 2,
p.
300.
Markovich, Natalia M.
2017.
Analysis of Clusters in Network Graphs for Personalized Web Search.
IFAC-PapersOnLine,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1,
p.
5178.
Yang, Yang
Zhang, Ting
and
Yuen, Kam C.
2017.
Approximations for finite-time ruin probability in a dependent discrete-time risk model with CMC simulations.
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 321,
Issue. ,
p.
143.
Asmussen, Søren
and
Foss, Sergey
2018.
Regular variation in a fixed-point problem for single- and multi-class branching processes and queues.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 50,
Issue. A,
p.
47.
Avrachenkov, Konstantin
Kadavankandy, Arun
and
Litvak, Nelly
2018.
Mean Field Analysis of Personalized PageRank with Implications for Local Graph Clustering.
Journal of Statistical Physics,
Vol. 173,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
895.
Markovich, Natalia M.
Ryzhov, Maxim S.
and
Krieger, Udo R.
2018.
Developments in Language Theory.
Vol. 11088,
Issue. ,
p.
71.
Vial, Daniel
and
Subramanian, Vijay
2019.
A Structural Result for Personalized PageRank and its Algorithmic Consequences.
Proceedings of the ACM on Measurement and Analysis of Computing Systems,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 2,
p.
1.
Olvera-Cravioto, Mariana
2019.
Convergence of the population dynamics algorithm in the Wasserstein metric.
Electronic Journal of Probability,
Vol. 24,
Issue. none,
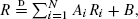 where the Ris are distributed as R. This equation is inspired by the original definition of the PageRank. In particular, N models the number of incoming links to a page, and B stays for the user preference. Assuming that N or B are heavy tailed, we employ the theory of regular variation to obtain the asymptotic behavior of R under quite general assumptions on the involved random variables. Our theoretical predictions show good agreement with experimental data.
where the Ris are distributed as R. This equation is inspired by the original definition of the PageRank. In particular, N models the number of incoming links to a page, and B stays for the user preference. Assuming that N or B are heavy tailed, we employ the theory of regular variation to obtain the asymptotic behavior of R under quite general assumptions on the involved random variables. Our theoretical predictions show good agreement with experimental data.



