Abstract
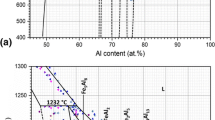
The low-temperature, Fe-rich portion of the Fe-Ni-S phase diagram was determined from Fe-Ni-S alloys (2.5,5,10,20, and 30 wt.% Ni, 10 wt % S, balance Fe) heat treated at 100 °C intervals from 900 to 300 °C. The microstructure and microchemistry of the phases in the heat treated Fe-Ni-S alloys were studied using a high-resolution field-emission gun (FEG) scanning electron microscope (SEM), electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA), and analytical electron microscope (AEM). Tieline compositions were obtained by determining the average phase composition and by measuring compositional profiles across interphase interfaces with the EPMA and AEM. At 600 °C and below, at least one phase was <1 Μm in size requiring the use of the AEM for analysis. The measured α + FeS, γ+ FeS, and α + γ + FeS boundaries in the Fe-rich corner of the Fe-Ni-S isotherms are consistent with previous studies. However, two new phases were observed for the first time coexisting with γ and FeS phases: FeNiγ′′ (∼52 wt.% Ni) at 600 and 500 °C and Ni 3 Fe, ordered Ll 2,γ′ (∼64 wt.% Ni) at 400 °C. New ternary isotherms are given at 600,500, and 400 °C that include the newly determined γ+γ′′ + FeS and the γ + γ′ + FeS three-phase fields. The effects of S on the phase boundaries of the α + γ phase field and the application of the Fe-Ni-S phase diagram to explain the microstructure and microchemistry of the metallic phases of stony meteorites are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Cited References
K. Kaufman and M. Cohen, “The Martensitic Transformation in the Iron-Nickel System,”Trans. AIME, 206, 1394–1401 (1956).
G. Kullerud, “The Fe-Ni-S System,”Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yr. Book, 62, 175 (1963).
A. J. Naldrett, J.R. Craig, and G. Kullerud, “The Central Portion of the Fe-Ni-S System and Its Bearing on Pentlandite Exsolution in Iron-Nickel Sulfide Ores,”Econ. Geol, 62, 826(1967).
J.R. Craig, A. J. Naldrett, and G. Kullerud, “The Fe-Ni-S System,”Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yr. Book, 66, 434–442 (1968).
G. Kullerud, R. A. Yund, and G.H. Moh, “Phase Relations in the Cu-Fe-S, Cu-Ni-S and Fe-Ni-S Systems,”Econ. Geol. Mon. 4, 323–343(1969).
R.W. Shewman and L.A. Clark, “Pentlandite Phase Relations in the Fe-Ni-S System and Notes on the Monosulfide Solid Solution,”Can. J. Earth Sci., 7, 67(1970).
J.R. Craig, “Violante Stability Relations,”Am. Mine., 56, 1303–1311(1971).
J.R. Craig, “Pyrite-Pentlandite Assemblages and Other Low Temperature Relations in the Fe-Ni-S System,”Am. J. Sei, 273A, 496–510(1973).
K.C. Misra and M.E. Fleet, “The Chemical Compositions of Synthetic and Natural Pentlandite Assemblages,”Econ. Geol, 68, 518–539(1973).
G. Cliff and G.W. Lorimer, “The Quantitative Analysis of Thin Specimens,”J. Microscopy, 103, 203–207 (1975).
T. W. Anderson and S. L. Sclove,An Introduction to the Statistical Analysis of Data, Houghton Mifflin Co. (1978).
J.G. Lenz, B.R. Conard, R. Sridhar, and J.S. Warner, “The Liquidus Surface and Tie Lines in the Iron-Nickel-Sulfur System between 1473and 1673K,”’Metall Trans.B, 9B, 459–462(1978).
R.S. Clarke Jr. andE.R.D. Scott, “Tetrataenite-Ordered FeNi, a New Mineral in Meteorites,” Am. Mme. 65, 624–630(1980).
A.D. Romig, “Determination of the Fe-Ni and Fe-Ni-P Phase Diagrams at Low Temperatures (700 to 300°C),”Metall. Trans., 11 A, 1151–1159(1980).
K.C. Hsieh, Y.A. Chang, and T. Zhong, “The Fe-Ni-S System above 700 °C,”Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 3, (2), 165 (1982).
O. Kubaschewski,Iron Binary Phase Diagrams, Springer Verlag, (1982).
G.F. Bastin, F.J.J. van Loo, and H.J.M. Heijligers, “Evaluation of the Use of Gaussian Φ(ρz) Curve in Quantitative Electron Probe Microanalysis: A New Optimization,”X-Ray Spectrom., 13, 91–97 (1984).
J. A. van Beek, P.M.T. De Kok, and F. J. J. van Loo, “Solid-State Displacement Reactions in the Fe-Ni-S and Cu-Ni-S Systems Between 400 °C and 500 °C,”Oxid. Met., 22, 147–160 (1984).
K.C. Hsieh, M.Y. Kao, and Y.A. Chang, “A Thermogravimetric Investigation of the Fe-Ni-S System from 700 °C to 900 °C,Oxid. Met, 27(3/4), 123–141 (1987).
K.C. Hsieh, K.C. Vlach, and Y.A. Chang, “The Fe-Ni-S System: I. AThermodynamic Analysis of the Phase Equilibria and Calculation of the Phase Diagram from 1173 to 1623 K,”High Temp. Sci., 23, 17–38(1987).
D.B. Williams, “Practical Analytical Electron Microscopy in Materials Science,” Electron Optics Publishing Group, Phillips Electronic Instruments Inc., Mahwah, NJ (1987).
J. Zhang, “Phase Decomposition in Fe-Rich Fe-Ni Alloys at Low Temperatures (<450 °C),” Ph.D. Dissertation, Lehigh University, Bethlehem, PA(1991).
J.I. oldstein, A.D Romig, D.E. Newbury, C.E. Lyman, P. Echlin, C. Fiori, D.C. Joy, and E. Lifshin,Scanning Electron Microscopy andX-Ray Microanalysis, Plenum Press, (1992).
E. Makovicky and S. Karup-MØller, “The System Pd-Fe-S at 900 °C, 725 °C, 550 °C, and 400 °C,”Econ. Geol, 88, 1269–1278 (1993).
J. Zhang, D.B. Williams, and J.I. Goldstein, “Decomposition of Fe-Ni Martensite: Implications for the Low-Temperature (≤500 °C) Fe-Ni Phase Diagram,”Metall Trans., 25A, 1626–1737(1994).
L. Ma, D.B. Williams, and J.I. Goldstein, “Phase Decomposition in the Iron-Rich Iron-Nickel-Sulfur System from 900 to 300 °C-Application to Meteoritic Metall,”Meteoritics, 30, 538–539(1995).
L. Ma, “Phase Decomposition in Fe-Rich Fe-Ni-S Alloys at 300 °C to 900 °C,” Ph.D. Thesis, Lehigh University (1996).
C.W. Yang, D.B. Williams, and J.I. Goldstein, “A Revision of the Fe-Ni Phase Diagram at Low Temperatures (<400 °C),”J. Phase Equilibria, 17, 522–531 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Williams, D.B. & Goldstein, J.I. Determination of the Fe-rich portion of the Fe-Ni-S phase diagram. JPE 19, 299–309 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1361/105497198770342030
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105497198770342030