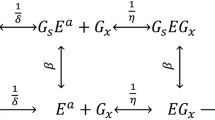Abstract
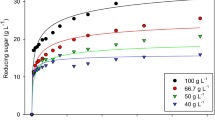
The kinetics of exoglucanase (Cel7A) from Trichoderma reesei was investigated in the presence of cellobiose and 24 different enzyme/Avicel ratios for 47 h, in order to establish which of the eight available kinetic models best explained the factors involved. The heterogeneous catalysis was studied and the kinetic parameters were estimated employing integrated forms of Michaelis-Menten equations through the use of nonlinear least squares. It was found that cellulose hydrolysis follows a model that takes into account competitive inhibition by cellobiose (final product) with the following parameters: K m=3.8 mM, K ic=0.041 mM, k cat=2 h−1 (5.6×10−4 s−1). Other models, such as mixed type inhibition and those incorporating improvements concerning inhibition by substrate and parabolic inhibition, increased the modulation performance very slightly. The results support the hypothesis that nonproductive enzyme substrate complexes, parabolic inhibition, and enzyme inactivation (Selwyn test) are not the principal constraints in enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Under our conditions, the increment in hydrolysis was not significant for substrate/enzyme ratios <6.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E :
-
free enzyme
- EI :
-
enzyme inhibitor complex
- EII :
-
enzyme inhibitor complex for second inhibitor molecule
- EIS :
-
enzyme substrate inhibitor complex
- ES :
-
enzyme substrate complex (nonproductive)
- Et :
-
total enzyme
- f 0.95 :
-
point of Fp ApB (F distribution) curve with area 0.95 (to its left)
- k cat :
-
catalytic constant (h−1)
- K ic :
-
competitive inhibition constant (mM)
- K ip :
-
parabolic inhibition constant (mM)
- K is :
-
substrate inhibition constant (mM)
- K iu :
-
uncompetitive inhibition constant (mM)
- K m :
-
Michaelis constant (mM)
- n :
-
experimental points
- p A′ pB :
-
parameters
- P :
-
product (µg/mL) (cellobiose)
- P 0 :
-
initial product
- P t :
-
product at time t (min)
- R 2 :
-
determination coefficient
- S :
-
substrate (%) (cellulose)
- SSE :
-
sum of squares error
- t :
-
time (min)
- V max :
-
maximum velocity
- w :
-
quotient used to test significance of improvement of different models that are interconvertible by addition or elimination of parameters in comparison with F value
References
Ladisch, M. R. and Svarczkopf, J. A. (1991), Bioresour. Technol. 36, 83–95.
Kurakake, M., Shirasawa, T., Ooshima, H., Converse, A. O., and Kato, J. (1995), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 50, 231–241.
Howell, J. A. and Mangat, M. (1978), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 20, 847–863.
Nidetzky, B., Steiner, W., Hayn, M., and Esterbauer, H. (1993), Bioresour. Technol. 44, 25–32.
Lee, Y.-H. and Fan, L. T. (1982), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24, 2383–2406.
Pereira, A. N. (1987), PhD thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN.
Kim, D. W., Kim, T. S., Jeong, Y. K., and Lee, J. K. (1992), J. Ferment. Bioeng. 73(6), 461–466.
Nidetzky, B., Hayn, M., Macarron, R., and Steiner, W. (1993), Biotechnol. Lett. 15(1), 71–76.
Eriksson, T., Karlsson, J., and Tjerneld, F. A. (2002), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 101, 41–60.
Howell, J. A. and Stuck, J. D. (1975), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 17, 873–893.
Bader, J., Bellgardt, K.-H., Singh, A., Kumar, P. K. R., and Schügerl, K. (1992), Bioprocess Eng. 7, 235–240.
Maglione, G., Russel, J. B., and Wilson, D. B. (1997), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63(2), 665–669.
Schülein, M. J. (1997), Biotechnology 57(1–3), 71–81.
Bezerra, R. M. (1995), PhD thesis, Universidade de Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro, Vila Real, Portugal.
Hsu, T.-A. (1979), PhD thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN.
Lee, Y.-H. and Fan, L. T. (1983), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 939–966.
Beldman, G., Leeuwen, S.-V., Rombouts, F. M., and Voragen, F. G. J. (1985), Biochem. J. 146, 301–308.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. (1951), J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Wood, T. M. and Bhat, K. M. (1988), Methods Enzymol. 160, 87–113.
Klyosov, A. A. and Rabinovitch, M. L. (1980), in Enzyme Engineering Future Directions, Wingard, L. B. Jr., Berezine, I. V., and Klyosov, A. A., eds., Plenum, New York, pp. 83–165.
Nidetzky, B., Steiner, W., and Claeyssens, M. (1994), Biochem. J. 303, 817–823.
Väljamäe, P., Petterson, G., and Johansson, G. (2001), Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 4520–4526.
Harjunpää, V., Teleman, A., Koivula, A., Ruohonen, L., Teeri, T. T., Teleman, O., and Drakenberg, T. (1998), Eur. J. Biochem. 240, 584–591.
Segel, H. I. (1993), in Enzyme Kinetics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 18–89.
Fujii, M., Homma, T., Ooshima, K., and Taniguchi, M. (1991), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 28/29, 145–156.
Fernly, H. N. (1974), Eur. Biochem. J. 43, 377, 378.
Yun, S.-L. and Suelter, C. H. (1977), Biochim. Biophys. Acta 480, 1–13.
Mangat, M. N. and Howell, J. A. (1978), Food Pharm. Bioeng. 74(172), 77–81.
Ladisch, M. R., Lin, K. W., Voloch, M., and Tsao, G. T. (1983), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 5(2), 81–102.
Ghose, T. K., Roychoudhury, P. K., and Ghosh, P. (1984), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26, 377–381.
Golovchenko, N. P., Kataeva, I. A., and Akimenko, V. K. (1992), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 14, 327–331.
Orgeret, C., Seillier, E., Gautier, C., Defaye, J., and Driguez, H. (1992), Carbohydr. Res. 224, 29–40.
Lee, Y.-H. and Fan, L. T. (1983), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 939–966.
Holtzapple, M., Cognata, M., Shu, Y., and Hendrickson, C. (1990), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36, 275–287.
Duggleby, R. G. (1995), Methods Enzymol. 249, 61–90.
Selwyn, M. J. (1965), Biochim. Biophys. Acta 105, 193–195.
Ralston, M. L. and Jennrich, R. I. (1978), Technometrics 20(1), 7–14.
Mannervik, B. (1982), Methods Enzymol. 87C, 370–391.
Igarashi, K., Samejima, M., and Eriksson K.-E. L. (1998), Eur. J. Biochem. 253, 101–106.
Henriksson, H., Ståhlberg, J., Isaksson, R., and Pettersson, G. (1996), FEBS Lett. 390, 339–344.
Ladisch, M. R., Hong, J., Voloch, M., and Tsao, G. T. (1981), in Trends in the Biology of Fermentations for Fuels and Chemicals, Hollaender, A., Rabson, R., Pietro, R., and Wolfe, eds., Plenum, New York, pp. 55–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezerra, R.M.F., Dias, A.A. Discrimination among eight modified michaelis-menten kinetics models of cellulose hydrolysis with a large range of substrate/enzyme ratios. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 112, 173–184 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:112:3:173
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:112:3:173