Abstract
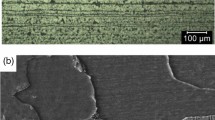
The influence of electropulsing on the damage of 1045 steel was studied. The results show that electropulsing can substantially increase the strength and ductility of the damaged material, with a little decrease of the Martensite hardness. After the treatment of electropulsing, the microstructure around the crack is modified, and the new structure can prevent the crack from growing. The healing effect of electropulsing on crack is discussed. It is thought that the temperature and thermal compressive stress caused by electropulsing are the main factors causing the healing effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S. Qin and B.L. Zhou, Acta Metall. Sinica 32, 1093 (1996).
R.S. Qin and B.L. Zhou, Nanostruct. Mater. 7, 741 (1996).
R.S. Qin and B.L. Zhou, Chin. J. Mater. Res. 11, 69 (1997).
R.S. Qin, H.C. Yan, G.H. He, and B.L. Zhou, Chin. J. Mater. Res. 9, 219 (1995).
J.P. Barnak, A.F. Sprecher, and H. Conrad, Scripta Metall. 32, 879 (1995).
V.H. Wever and W. Seith, Z. Elektrochem. 59, 942 (1955).
C. Bosvieux and J. Friedel, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 23, 123 (1962).
P.S. Ho and T. Kwok, Rep. Prog. Phys. 52, 301 (1989).
A.F. Sprecher, S.L. Mannan, and H. Conrad, Acta Metall. 34, 1145 (1986).
K. Okazaki, M. Kagawa, and H. Conrad, Scripta Metall. 12, 1063 (1978).
H. Conrad and A.F. Sprecher, in Dislocations in Solids, edited by F.R.N. Nabarro (Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989), p. 499.
A.K. Misra, Metall. Trans. 16A, 1354 (1985).
M. Nakada, Y. Shiohara, and M.C. Flemings, ISIJ Int. 30, 27 (1990).
J.M. Li, S.L. Li, J. Li, and H.T. Liu, Scripta Metall. 31, 1691 (1994).
Z.H. Lai, H. Conrad, Y.S. Chao, S.Q. Wang, and J. Sun, Scripta Metall. 23, 305 (1989).
H. Mizubayashi and S. Okuda, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 40, 8057 (1989).
Y.S. Chao, Z.H. Lai, K.H. He, and H.R. Er, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 181–182, 982 (1994).
W.F. Jr. Brown and J.E. Srawley, ASTM STP 410 (1967).
R.S. Qin, S.X. Su, J.D. Guo, G.H. He, and B.L. Zhou, Biomimetics 4, 121 (1996).
D.W. Tang, B.L. Zhou, H. Cao, and G.H. He, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 3749 (1993).
X.N. Guo, Y.F. Shen, Y.Z. Zhou, G.H. He, and B.L. Zhou, Chin. J. Mater. Res. 13, 73 (1999).
F.R.N. Nabarro, Theory of Crystal Dislocations (Clarendon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1967), p. 529.
V.I. Alshits and V.L. Indenbom, Dislocations in Solids, edited by F.R.N. Nabarro (North-Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986), p. 43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Qin, R., Xiao, S. et al. Reversing effect of electropulsing on damage of 1045 steel. Journal of Materials Research 15, 1056–1061 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2000.0152
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2000.0152