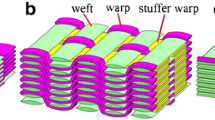
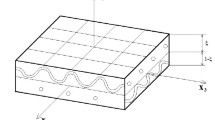
Abstract
A procedure for predicting the in-plane and out-of-plane thermal conductivities of woven fabric composites through a combined approach of the representative volume element method and heat transfer analyses via finite element is presented. The representative volume element method was implemented using two unit cells established at different length scales with periodic boundary conditions. The procedure was exemplified on a plain weave glass fabric reinforced epoxy resin matrix composite. Sensitivity studies were conducted to quantify the influence of fiber volume fraction and thermal conductivity of the constituent phases on the effective thermal conductivities of the composite. The procedure, which can be implemented into commercial finite element codes, is an efficient tool for the design of woven fabric composites.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.D. Tang, J.D. Whitcomb, Y.M. Li, and H.J. Sue: Microme-chanics modeling of moisture diffusion in woven composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 817 (2005).
S. Li: General unit cells for micromechanical analyses of unidirectional composites. Composites Part A 32, 815 (2001).
S.G. Li and A. Wongsto: Unit cells for micromechanical analyses of particle-reinforced composites. Mech. Mater. 36, 543 (2004).
H.Z. Li, S. Li, Y.C. Wang, E. Kandare, B.K. Kandola, P. Myler, and A.R. Horrocks: Micromechanical finite element analyses of woven fabric composites at elevated temperatures using unit cells at multiple length scales (to be submitted).
A. Dasgupta, R.K. Agarwal, and S.M. Bhandarkar: Three-dimensional modeling of woven-fabric composites for effective thermo-mechanical and thermal properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 56, 209 (1996).
A. Dasgupta and R.K. Agarwal: Orthotopic thermal conductivity of plain-weave fabric composites using a homogenization technique. J. Compos. Mater. 26, 2736 (1992).
D. Bigaud, J.M. Goyheneche, and P. Hamelin and: A global-local nonlinear modelling of effective thermal conductivity tensor of textile-reinforced composites. Composites Part A 32, 1443 (2001).
K. Woo and N.S. Goo: Thermal conductivity of carbon-phenolic 8-harness satin weave composites. Compos. Struct. 66, 521 (2004).
J.K. Farooqi and M.A. Sheikh: Finite element modelling of thermal transport in ceramic-matrix composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 37, 361 (2006).
J. Schuster, D. Heider, K. Sharp, and M. Glowania: Thermal conductivities of three-dimensionally woven fabric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 2085 (2008).
N. Ahuja and B.J. Schachter: Pattern Models (Wiley, New York, 1983).
ABAQUS Analysis User’s Manual, version 6.5 (ABAQUS Inc., Providence, RI, 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Li, S. & Wang, Y. Prediction of effective thermal conductivities of woven fabric composites using unit cells at multiple length scales. Journal of Materials Research 26, 384–394 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.51
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.51