Abstract
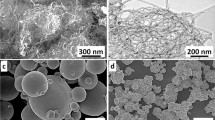
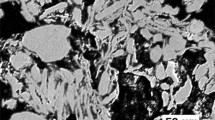
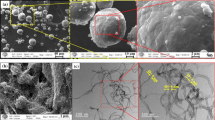
Carbon nanotube (CNT)-reinforced aluminum composite powders were synthesized by cryogenic milling. The effects of different milling parameters and CNT contents on the structural characteristics and mechanical properties of the resulting composite powders were studied. Detailed information on powder morphology and the dispersion and structural integrity of the CNTs is crucial for many powder consolidation methods, particularly cold spray, which is increasingly utilized to fabricate metal-based nanocomposites. While all of the produced composite powders exhibited particle sizes suitable for spray applications, it was found that with increasing CNT content, the average particle size decreased and the size distribution became narrower. The dispersion of CNTs improved with milling time and helped to maintain a small Al grain size during cryogenic milling. Although extensive milling allowed for substantial grain size reduction, the process caused notable CNT degradation, leading to a deterioration of the mechanical properties of the resulting composite.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Suryanarayana: Non-Equilibrium Processing of Materials (Elsevier, 1999).
A.A.A. Baker, S. Dutton, D. Kelly, and D.W. Kelly: Composite Materials for Aircraft Structures (AIAA, New York, NY, 2004).
A. Ramasamy, A-M. Hill, A. Hepper, A. Bull, and J. Clasper: Blast mines: Physics, injury mechanisms and vehicle protection. J. R. Army Med. Corps 155(4), 258 (2009).
J.P. Salvetat, J.M. Bonard, N. Thomson, A. Kulik, L. Forro, W. Benoit, and L. Zuppiroli: Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 69(3), 255 (1999).
H. Dai: Carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, integration, and properties. Acc. Chem. Res. 35(12), 1035 (2002).
W.K. Hong, C. Lee, D. Nepal, K.E. Geckeler, K. Shin, and T. Lee: Radiation hardness of the electrical properties of carbon nanotube network field effect transistors under high-energy proton irradiation. Nanotechnology 17(22), 5675 (2006).
M. Treacy, T. Ebbesen, and J. Gibson: Exceptionally high Young’s modulus observed for individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 381, 678 (1996).
E.W. Wong, P.E. Sheehan, and C.M. Lieber: Nanobeam mechanics: Elasticity, strength, and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. Science 277(5334), 1971 (1997).
S.R. Bakshi, D. Lahiri, and A. Agarwal: Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites-a review. Int. Mater. Rev. 55(1), 41 (2010).
P. Ajayan: Nanotubes from carbon. Chem. Rev. 99(39), 1787 (1999).
T. Kuzumaki, K. Miyazawa, H. Ichinose, and K. Ito: Processing of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composite. J. Mater. Res. 13(9), 2445 (1998).
A. Esawi and K. Morsi: Dispersion of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in aluminum powder. Composites, Part A 38(2), 646 (2007).
L. Wang, H. Choi, J-M. Myoung, and W. Lee: Mechanical alloying of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and aluminium powders for the preparation of carbon/metal composites. Carbon 47(15), 3427 (2009).
I. Sridhar and K.R. Narayanan: Processing and characterization of MWCNT reinforced aluminum matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 44(7), 1750 (2009).
T. Yamamoto, Y. Miyauchi, J. Motoyanagi, T. Fukushima, T. Aida, M. Kato, and S. Maruyama: Improved bath sonication method for dispersion of individual single-walled carbon nanotubes using new triphenylene-based surfactant. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 47(4), 2000 (2008).
J. Lee and K. Rhee: Silane treatment of carbon nanotubes and its effect on the tribological behavior of carbon nanotube/epoxy nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9(12), 6948 (2009).
Y. Chen, M. Conway, and J. Fitzgerald: Carbon nanotubes formed in graphite after mechanical grinding and thermal annealing. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 76(4), 633 (2003).
T. Garosshen and G. McCarthy: Low temperature carbide precipitation in a nickel base superalloy. Metall. Trans. A 16(7), 1213 (1985).
A.J.E. Welch: The reaction of crystal lattice discontinuities to mineral dressing. In Developments in Mineral Dressing (IMM, London, UK, 1953); p. 387.
N. Pierard, A. Fonseca, J.F. Colomer, C. Bossuot, J.M. Benoit, G. Van Tendeloo, J.P. Pirard, and J. Nagy: Ball milling effect on the structure of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 42(8), 1691 (2004).
Á. Kukovecz, T. Kanyó, Z. Kónya, and I. Kiricsi: Long-time low-impact ball milling of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 43(5), 994 (2005).
D. Poirier, R. Gauvin, and R.A. Drew: Structural characterization of a mechanically milled carbon nanotube/aluminum mixture. Composites, Part A 40(9), 1482 (2009).
A.M.K. Esawi, K. Morsi, A. Sayed, A.A. Gawad, and P. Borah: Fabrication and properties of dispersed carbon nanotube–aluminum composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 508(1), 167 (2009).
C.L. DeCastro and B.S. Mitchell: Nanoparticles from mechanical attrition. In Synthesis, Functionalization, and Surface Treatment of Nanoparticles (American Scientific Publishers, Stevenson Ranch, 2002); pp. 1–15.
H. Kwon, M. Estili, K. Takagi, T. Miyazaki, and A. Kawasaki: Combination of hot extrusion and spark plasma sintering for producing carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Carbon 47(3), 570 (2009).
J. Stein, B. Lenczowski, N. Fréty, and E. Anglaret: Mechanical reinforcement of a high-performance aluminium alloy AA5083 with homogeneously dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 50, 2264 (2012).
S. Ko, B. Kim, Y. Kim, T. Kim, K. Kim, B. McKay, and J. Shin: Manufacture of CNTs-Al Powder Precursors for Casting of CNTs-Al Matrix Composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 765, 353 (2013).
E. Lamotte, K. Phillips, A. Perry, and H. Killias: Continuously cast aluminium-carbon fibre composites and their tensile properties. J. Mater. Sci. 7(3), 346 (1972).
A. Baker, D. Braddick, and P. Jackson: Fatigue of boron-aluminium and carbon-aluminium fibre composites. J. Mater. Sci. 7(7), 747 (1972).
S. Dong, J. Tu, and X. Zhang: An investigation of the sliding wear behavior of Cu-matrix composite reinforced by carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 313(1), 83 (2001).
M.A. Meyers and K.K. Chawla: Mechanical Behavior of Materials, 2nd ed. (Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge, UK, 2009), p. 345.
M. Hüller, G.G. Chernik, E.L. Fokina, and N.I. Budim: Mechanical alloying in planetary mills of high accelerations. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 18, 366 (2008).
J. Wu, H. Fang, S. Yoon, H. Kim, and C. Lee: Measurement of particle velocity and characterization of deposition in aluminum alloy kinetic spraying process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(5), 1368 (2005).
B. Jodoin, L. Ajdelsztajn, E. Sansoucy, A. Zúñiga, P. Richer, and E.J. Lavernia: Effect of particle size, morphology, and hardness on cold gas dynamic sprayed aluminum alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201(6), 3422 (2006).
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1976).
C. Suryanarayana: Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46(1), 1 (2001).
E. Lavernia, B. Han, and J. Schoenung: Cryomilled nanostructured materials: Processing and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 493(1), 207 (2008).
B. Han, J. Ye, F. Tang, J. Schoenung, and E. Lavernia: Processing and behavior of nanostructured metallic alloys and composites by cryomilling. J. Mater. Sci. 42(5), 1660 (2007).
D. Witkin and E.J. Lavernia: Synthesis and mechanical behavior of nanostructured materials via cryomilling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51(1), 1 (2006).
J. Lee, T. Jeong, J. Heo, S.H. Park, D.H. Lee, J.B. Park, H.S. Han, Y.N. Kwon, I. Kovalev, and S.M. Yoon: Short carbon nanotubes produced by cryogenic crushing. Carbon 44(14), 2984 (2006).
D. Woo, B. Sneed, F. Peerally, F. Heer, L. Brewer, J. Hooper, and S. Osswald: Synthesis of nanodiamond-reinforced aluminum metal composite powders and coatings using high-energy ball milling and cold spray. Carbon 63, 404 (2013).
T. Buchheit and T. Vogler: Measurement of ceramic powders using instrumented indentation and correlation with their dynamic response. Mech. Mater. 42(6), 599 (2010).
H.J. Fecht: Nanostructure formation by mechanical attrition. Nanostruct. Mater. 6(1), 33 (1995).
H-T. Wang, C-J. Li, G-J. Yang, C-X. Li, Q. Zhang, and W-Y. Li: Microstructural characterization of cold-sprayed nanostructured FeAl intermetallic compound coating and its ball-milled feedstock powders. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 16(5), 669 (2007).
H. Kaftelen and M. Öveçoğlu: Microstructural characterization and wear properties of ultra-dispersed nanodiamond (UDD) reinforced Al matrix composites fabricated by ball-milling and sintering. J. Compos. Mater. 46(13), 1521 (2012).
K. Morsi and A. Esawi: Effect of mechanical alloying time and carbon nanotube (CNT) content on the evolution of aluminum (Al)–CNT composite powders. J. Mater. Sci. 42(13), 4954 (2007).
L. Kumari, T. Zhang, G. Du, W. Li, Q. Wang, A. Datye, and K. Wu: Thermal properties of CNT-alumina nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68(9), 2178 (2008).
S. Cho, K. Kikuchi, T. Miyazaki, K. Takagi, A. Kawasaki, and T. Tsukada: Multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a contributing reinforcement phase for the improvement of thermal conductivity in copper matrix composites. Scr. Mater. 63(4), 375 (2010).
Q. Zhang, G. Chen, S. Yoon, J. Ahn, S. Wang, Q. Zhou, Q. Wang, and J. Li: Thermal conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 66(16), 165440 (2002).
S. Osswald, V. Mochalin, M. Havel, G. Yushin, and Y. Gogotsi: Phonon confinement effects in the Raman spectrum of nanodiamond. Phys. Rev. B 80(7), 075419 (2009).
A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson: Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond–like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A 362(1824), 2477 (2004).
S. Osswald, M. Havel, and Y. Gogotsi: Monitoring oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 38(6), 728 (2007).
P. Delhaes, M. Couzi, M. Trinquecoste, J. Dentzer, H. Hamidou, and C. Vix-Guterl: A comparison between Raman spectroscopy and surface characterizations of multiwall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 44(14), 3005 (2006).
C. Wu, P. Wang, X. Yao, C. Liu, D. Chen, G. Lu, and H. Cheng: Hydrogen storage properties of MgH2/SWNT composite prepared by ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 420(1), 278 (2006).
J.H. Lee, K.Y. Rhee, and S.J. Park: Effects of cryomilling on the structures and hydrogen storage characteristics of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35(15), 7850 (2010).
M. Kozlov, M. Hirabayashi, K. Nozaki, M. Tokumoto, and H. Ihara: Transformation of C60 fullerenes into a superhard form of carbon at moderate pressure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66(10), 1199 (1995).
R. George, K.T. Kashyap, R. Rahul, and S. Yamdagni: Strengthening in carbon nanotube/aluminium (CNT/Al) composites. Scr. Mater. 53(10), 1159 (2005).
L. Ci, Z. Ryu, N.Y. Jin-Phillipp, and M. Rühle: Investigation of the interfacial reaction between multi-walled carbon nanotubes and aluminum. Acta Mater. 54(20), 5367 (2006).
T. Kuzumaki, O. Ujiie, H. Ichinose, and K. Ito: Mechanical characteristics and preparation of carbon nanotube fiber-reinforced Ti composite. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2(7), 416 (2000).
H.H. He: Two-Dimensional X-Ray Diffraction (Wiley Publishing, Hoboken, NJ, 2011).
J. He and J.M. Schoenung: Nanocrystalline Ni coatings strengthened with ultrafine particles. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34(3), 673 (2003).
X. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Narayan, and C. Koch: Evidence for the formation mechanism of nanoscale microstructures in cryomilled Zn powder. Acta Mater. 49(8), 1319 (2001).
P.G. Shewmon: Transformations in Metals (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1969).
F. Zhou, X. Liao, Y. Zhu, S. Dallek, and E. Lavernia: Microstructural evolution during recovery and recrystallization of a nanocrystalline Al-Mg alloy prepared by cryogenic ball milling. Acta Mater. 51(10), 2777 (2003).
J. Weertman: Hall-Petch strengthening in nanocrystalline metals. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 166(1), 161 (1993).
T. Mukai, K. Ishikawa, and K. Higashi: Influence of strain rate on the mechanical properties in fine-grained aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 204(1), 12 (1995).
J. Benjamin: New Materials by Mechanical Alloying Techniques (DGM Informationgesellschaft, Oberursel, Germany, 1989), p. 3.
A.M. Esawi and M.A. El Borady: Carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminium strips. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68(2), 486 (2008).
T. Laha, Y. Chen, D. Lahiri, and A. Agarwal: Tensile properties of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum nanocomposite fabricated by plasma spray forming. Composites, Part A 40(5), 589 (2009).
S-M. Zhou, X-B. Zhang, Z-P. Ding, C-Y. Min, G-L. Xu, and W-M. Zhu: Fabrication and tribological properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced Al composites prepared by pressureless infiltration technique. Composites, Part A 38(2), 301 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Dr. Sarath Menon (NPS) for his assistance with SEM analysis. This work was supported by the Office of Naval Research (Code 30).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, D.J., Hooper, J.P., Osswald, S. et al. Low temperature synthesis of carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum metal composite powders using cryogenic milling. Journal of Materials Research 29, 2644–2656 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.300
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.300