Abstract
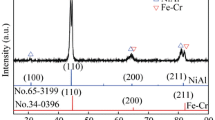
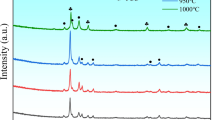
This study aims to investigate the sliding wear behavior of Al0.4FeCrNiCox (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys (HEAs) under oil lubricating conditions at room temperature. Phase and microstructural characterizations of HEAs are performed by utilizing X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The compressive yield strength of Al0.4FeCrNiCox (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) HEAs is observed to decrease from 1169.35 to 257.63 MPa. Plastic deformation up to 75% is achieved in the case of Al0.4FeCrNiCox =1 HEA. The microhardness of HEA samples is found to decrease from 377 to 199 HV after the addition of cobalt content from x = 0 to 1.0 mol. Thermal analysis is performed using a differential scanning calorimeter. It is confirmed that Al0.4FeCrNiCox (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) HEAs do not undergo any phase change up to 1000 °C. The specific wear rate of Al0.4FeCrNiCox =1 HEA is observed to be highest in all wear conditions. The worn surfaces were analyzed by SEM with attached energy-dispersive spectroscopy, 3D profiling, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004).
B.S. Murty, J.W. Yeh, and S. Ranganathan: High-Entropy Alloys (Elsevier, London, 2014).
C.C. Koch: Nanocrystalline high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. 32, 3435–3444 (2017).
O. Maulik, D. Kumar, S. Kumar, S.K. Dewangan, and V. Kumar: Structure and properties of light weight high entropy alloys: A brief review. Mater. Res. Express 5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aabbca.
A. Munitz, S. Salhov, S. Hayun, and N. Frage: Heat treatment impacts the micro-structure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 221–230 (2016).
Y. Zou: Nanomechanical studies of high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res., 33, 3035–3054 (2018).
T.T. Shun and Y.C. Du: Microstructure and tensile behaviors of FCC Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 479, 157–160 (2009).
Y. Guo, L. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Qi, B. Wang, Z. Zhao, J. Shang, and J. Xiang: A superfine eutectic microstructure and the mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMox high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res., 33, 3258–3265 (2018).
E. Ghassemali, R. Sonkusare, K. Biswas, and N.P. Gurao: In situ study of crack initiation and propagation in a dual phase AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 710, 539–546 (2017).
M. Zhang and L. Zhang: Effect of Nb content on thermal stability, mechanical and corrosion behaviors of hypoeutectic CoCrFeNiNbx high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res., 33, 3276–3286 (2018).
R. Wang, K. Zhang, C. Davies, and X. Wu: Evolution of microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy prepared by direct laser fabrication. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 971–981 (2017).
C.M. Lin and H.L. Tsai: Evolution of microstructure, hardness, and corrosion properties of high-entropy Al0.5CoCrFeNi alloy. Intermetallics 19, 288–294 (2011).
D. Kumar, O. Maulik, V.K. Sharma, Y.V.S.S. Prasad, and V. Kumar: Understanding the effect of tungsten on corrosion behavior of AlCuCrFeMnWx high-entropy alloys in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 4481–4488 (2018).
T.M. Butler and M.L. Weaver: Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 229–244 (2016).
Y.X. Liu, C.Q. Cheng, J.L. Shang, R. Wang, P. Li, and J. Zhao: Oxidation behavior of high-entropy alloys AlxCoCrFeNi (x = 0.15, 0.4) in supercritical water and comparison with HR3C steel. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25, 1341–1351 (2015).
X. Chen, Y. Sui, J. Qi, Y. He, F. Wei, Q. Meng, and Z. Sun: Microstructure of Al1.3CrFeNi eutectic high entropy alloy and oxidation behavior at 1000 °C. J. Mater. Res. 32, 2109–2116 (2017).
Y. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Yang, M. Zhang, and J. Qiao: Effect of nitriding on the tribological properties of Al1.3CoCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 725, 365–372 (2017).
Y. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Yang, M. Zhang, S. Ma, and J. Qiao: Microstructure and wear properties of nitrided AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys., 210, 233–239 (2018).
S. Yadav, A. Kumar, and K. Biswas: Wear behavior of high entropy alloys containing soft dispersoids (Pb, Bi). Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 222–232 (2018).
S. Kumar, D. Kumar, O. Maulik, A.K. Pradhan, V. Kumar, and A. Patnaik: Synthesis and air jet erosion study of AlxFe1.5CrMnNi0.5 (x = 0.3, 0.5) high-entropy alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 49, 5607–5618 (2018).
D. Kumar, O. Maulik, S. Kumar, Y.V.S.S. Prasad, and V. Kumar: Phase and thermal study of equiatomic AlCuCrFeMnW high entropy alloy processed via spark plasma sintering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 71–77 (2017).
O. Maulik and V. Kumar: Synthesis of AlFeCuCrMgx (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.7) alloy powders by mechanical alloying. Mater. Charact. 110, 116–125 (2015).
O. Maulik, D. Kumar, S. Kumar, D.M. Fabijanic, and V. Kumar: Structural evolution of spark plasma sintered AlFeCuCrMgx (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.7) high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 77, 46–56 (2016).
Y. Zhang, Z.P. Lu, S.G. Ma, P.K. Liaw, Z. Tang, Y.Q. Cheng, and M.C. Gao: Guidelines in predicting phase formation of high-entropy alloys. MRS Commun. 4, 57–62 (2014).
J.W. Qiao, S.G. Ma, E.W. Huang, C.P. Chuang, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang: Microstructural characteristics and mechanical behaviors of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at ambient and cryogenic temperature. Mater. Sci. Forum 688, 419–425 (2011).
Z. Wang, M.C. Gao, S.G. Ma, H.J. Yang, Z.H. Wang, M.Z. Moroz, and J.W. Qiao: Effect of cold rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.25CoCrFe1.25Ni1.25 High-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 645, 163–169 (2015).
W. Chen, Z. Fu, S. Fang, H. Xiao, and D. Zhu: Alloying behavior microstructure and mechanical properties in a FeNiCrCo0.3Al0.7 high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 51, 854–860 (2013).
S. Fang, W. Chen, and Z. Fu: Microstructure and mechanical properties of twinned Al0.5CrFeNiCo0.3C0.2 high entropy alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 54, 973–979 (2014).
G. Qin, W. Xue, C. Fan, R. Chen, L. Wang, Y. Su, H. Ding, and J. Guo: Effect of Co content on phase formation and mechanical properties of (AlCoCrFeNi)100−xCox high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 710, 200–205 (2018).
Y. Zhao, H. Cui, M. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Zhang, and C. Wang: The microstructures and properties changes induced by Al:Co ratios of the AlxCrCo2−xFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 733, 153–163 (2018).
C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, and T.T. Shun: Wear resistance and high-temperature compression strength of Fcc CuCoNiCrAl0.5Fe alloy with boron addition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35, 1465–1469 (2004).
C.J. Tong, M.R. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, S.J. Lin, and S.Y. Chang: Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 1263–1271 (2005).
M.R. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, and M.H. Chuang: Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1363–1369 (2006).
H. Duan, Y. Wu, M. Hua, C. Yuan, D. Wang, J. Tua, H. Kou, and J. Li: Tribological properties of AlCoCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy in hydrogen peroxide solution and in oil lubricant. Wear 297, 1045–1051 (2013).
Y. Yu, W.M. Liu, T.B. Zhang, J.S. Li, J. Wang, H.C. Kou, and J. Li: Microstructure and tribological properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy in hydrogen peroxide solution. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 201–207 (2014).
Y. Yu, J. Wang, J. Li, J. Yang, H. Kou, and W. Liu: Tribological behavior of AlCoCrFeNi(Ti0.5) high entropy alloys under oil and MACs lubrication. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 470–476 (2016).
Y.F. Kao, T.J. Chen, S.K. Chen, and J.W. Yeh: Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤x ≤ 2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 488, 57–64 (2009).
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue: Calculation of mixing enthalpy and mismatch entropy for ternary amorphous alloys. Mater. Trans., JIM 41, 1372–1378 (2000).
S. Guo and C.T. Liu: Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 21, 433–446 (2011).
Y. Dong, Y. Lu, L. Jiang, T. Wang, and T. Li: Effects of electro-negativity on the stability of topologically closepacked phase in high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 52, 105–109 (2014).
H. Baker: ASM Handbook: Alloy phase diagrams, Volume 3 (ASM International, Materials Park, 1992).
Y. Chen, Y. Li, S. Kurosu, K. Yamanaka, N. Tang, and A. Chiba: Effects of microstructures on the sliding behavior of hot-pressed CoCrMo alloys. Wear 319, 200–210 (2014).
V. Kukshal, A. Patnaik, and I.K. Bhat: Effect of cobalt on microstructure and properties of AlCr1.5CuFeNi2Cox high entropy alloys. Mater. Res. Express 5, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/377/1/012023.
C. Li, J.C. Li, M. Zhao, and Q. Jiang: Effect of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of multiprincipal elements high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 475, 752–757 (2009).
J. Joseph, T. Jarvis, X. Wu, N. Stanford, P. Hodgson, and D.M. Fabijanic: Comparative study of the microstructures and mechanical properties of direct laser fabricated and arc-melted AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 633, 184–193 (2015).
P. Sperka, I. Krupka, and M. Hartl: The effect of surface grooves on film breakdowns in point contacts. Tribol. Int. 102, 249–256 (2016).
D.S. Wang and J.F. Lin: Effect of surface roughness on elastohydrodynamic lubrication of line contacts. Tribol. Int. 24, 51–62 (1991).
I.M. Hutchings: Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials (Elsevier, London, 1995).
L. Conceicao and A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira: The effect of oxidation on the tribolayer and sliding wear of a Co-based coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 288, 69–78 (2016).
S. Mitrovic, D. Adamovic, F. Zivic, D. Dzunic, and M. Pantic: Friction and wear behavior of shot peened surfaces of 36CrNiMo4 and 36NiCrMo16 alloyed steels under dry and lubricated contact conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 290, 223–232 (2014).
T. Murakami, H. Mano, Y. Hibi, and S. Sasaki: Friction and wear properties of Fe7Mo6-based alloy in ethyl alcohol. Tribol. Int. 43, 2183–2189 (2010).
B. Bhushan: Modern Tribology Handbook (CRC Press, London, U.K., 2001); p. 455–492.
J.K. Mannekote and S.V. Kailas: The effect of oxidation on the tribological performance of few vegetable oils. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 1, 91–95 (2012).
E.M. Nascimento, L.M. Amaral, and A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira: Characterization and wear of oxides formed on CoCr MoSi alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 332, 408–413 (2017).
L. Ma, L. Wang, Z. Nie, F. Wang, Y. Xue, J. Zhou, T. Cao, Y. Wang, and Y. Ren: Reversible deformation-induced martensitic transformation in Al0.6CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy investigated by in situ synchrotron based high-energy X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 128, 12–21 (2017).
ASTM E3-11: Standard Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens, American Society for Testing and Materials (ASM Society, USA, 2011).
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the institute grants for financial support, Advanced Tribology Research Lab for tribology test, and Department of Mechanical Engineering MNIT Jaipur, Material Research Centre, MNIT Jaipur, for carrying out the experimental work. VK also thanks BRNS Project No. 34/20/01/2014-BRNS-0339, Mumbai (India), for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Patnaik, A., Pradhan, A.K. et al. Room temperature wear study of Al0.4FeCrNiCox (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys under oil lubricating conditions. Journal of Materials Research 34, 841–853 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.499
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.499