Abstract
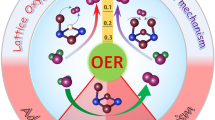
Due to the special crystal structures and electron configurations, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) are expected to have favorable activities for electrocatalytic reactions. In this paper, a set of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) criteria are applied for the HEA-based electrocatalyst design. Specifically, FeNiMnCrCu HEA is predicted to have a better OER performance than the baseline FeCoNiCrAI HEA. To demonstrate this design approach, both FeNiMnCrCu and FeCoNiCrAI samples are prepared and tested. Their crystal structures and electrocatalytic performance are examined. This paper demonstrates the potential of using finely tuned HEAs for OER applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Stojić, M.P. Marčeta, S.P. Sovilj, and Š.S. Miljanić: Hydrogen generation from water electrolysis—possibilities of energy saving. J. Power Sources 118, 315 (2003).
Y. Lee, J. Suntivich, K.J. May, E.E. Perry, and Y. Shao-Horn: Synthesis and activities of rutile IrO2 and RuO2 nanoparticles for oxygen evolution in acid and alkaline solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 399 (2012).
M.S. Faber and S. Jin: Earth-abundant inorganic electrocatalysts and their nanostructures for energy conversion applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3519 (2014).
A. Liu, Z. Chen, X. Wei, W. Xiao, and J. Ding: Economical Fe-doped Ta2O5 electrocatalyst toward efficient oxygen evolution: a combined experimental and first-principles study. MRS Commun. 7, 563 (2017).
L. Fei, Z. Min, Z. Yuxue, and Z. Xianghua: First-row transition metal based catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction under alkaline conditions: basic principles and recent advances. Small 13, 1701931 (2017).
B. Zhang, Y. Mu, M.C. Gao, W.J. Meng, and S.M. Guo: On single-phase status and segregation of an as-solidified septenary refractory high entropy alloy. MRS Commun. 7, 78 (2017).
J. Wang, Y. Zhang, S.Z. Niu, W.Y. Wang, H.C. Kou, J.S. Li, S.Q. Wang, and E. Beaugnon: Formation of a hexagonal closed-packed phase in Al0.5CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. MRS Commun. 7, 879 (2017).
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov: A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 122, 448 (2017).
Z. Wang, W. Qiu, Y. Yang, and C.T. Liu: Atomic-size and lattice-distortion effects in newly developed high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements. Intermetallics 64, 63 (2015).
T. Bak, J. Nowotny, N.J. Sucher, and E. Wachsman: Effect of crystal imperfections on reactivity and photoreactivity of TiO2 (rutile) with oxygen, water, and bacteria. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 15711 (2011).
Z.Y. Lv, X.J. Liu, B. Jia, H. Wang, Y. Wu, and Z.P. Lu: Development of a novel high-entropy alloy with eminent efficiency of degrading azo dye solutions. Sci. Rep. 6, 34213 (2016).
J.K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J.R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard, and H. Jónsson: Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 17886 (2004).
J.M. Thomas and J.W. Thomas (Eds). Principles and Practice of Heterogeneous Catalysis. 2nd ed. 2015. ISBN: 978-3-527-31458-4.
X. Cui, W. Xu, Z. Xie, J.A. Dorman, M.T. Gutierrez-Wing, and Y. Wang: Effect of dopant concentration on visible light driven photocatalytic activity of Sn1-xAgxS2. Dalton Trans. 45, 16290 (2016).
I.D. Brown and R.D. Shannon: Empirical bond-strength–bond-length curves for oxides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 29, 266 (1973).
J.A. Mejias, V. Staemmler, and H.J. Freund: Electronic states of the Cr 2 O 3 (0001) surface from ab initio embedded cluster calculations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11, 7881 (1999).
L.S. Caputi, S.L. Jiang, A. Amoddeo, and R. Tucci: Oxygen-nickel bond length in Ni(111)-O determined by electron-energy-loss fine-structure spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 41, 8513 (1990).
X. Cui, B. Zhang, C. Zeng, H. Wen, H. Yao, and S. Guo: Laser processed Ni-Fe alloys as electrocatalyst toward oxygen evolution reaction. Mater. Res. Express 5, 066527 (2018).
H.-P. Chou, Y.-S. Chang, S.-K. Chen, and J.-W. Yeh: Microstructure, thermophysical and electrical properties in AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x≤2) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 163, 184 (2009).
Y.F. Ye, C.T. Liu, and Y. Yang: A geometric model for intrinsic residual strain and phase stability in high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 94, 152 (2015).
T. Egami: Atomic level stresses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 56, 637 (2011).
W. Ji, Z. Fu, W. Wang, H. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, and F. Zhang: Mechanical alloying synthesis and spark plasma sintering consolidation of CoCrFeNiAl high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 589, 61 (2014).
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, and J. Shi: Microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiTiAlx high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 508, 214 (2009).
T. Zhou, Z. Cao, P. Zhang, H. Ma, Z. Gao, H. Wang, Y. Lu, J. He, and Y. Zhao: Transition metal ions regulated oxygen evolution reaction performance of Ni-based hydroxides hierarchical nanoarrays. Sci. Rep. 7, 46154 (2017).
E. Fabbri, A. Habereder, K. Waltar, R. Kotz, and T.J. Schmidt: Developments and perspectives of oxide-based catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 4, 3800 (2014).
X. Cui, W. Xu, Z. Xie, and Y. Wang: High-performance dye-sensitized solar cells based on Ag-doped SnS2 counter electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 1908 (2016).
X. Cui, Z. Xie, and Y. Wang: Novel CoS2 embedded carbon nanocages by direct sulfurizing metal-organic frameworks for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 11984 (2016).
D.V. Franco, L.M. Da Silva, W.F. Jardim, and J.F.C. Boodts: Influence of the electrolyte composition on the kinetics of the oxygen evolution reaction and ozone production processes. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 17, 746 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This publication is based upon the work supported by NSF-Consortium for innovation in manufacturing and materials (CIMM) program (grant number # OIA-1541079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Zhang, B., Zeng, C. et al. Electrocatalytic activity of high-entropy alloys toward oxygen evolution reaction. MRS Communications 8, 1230–1235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.111