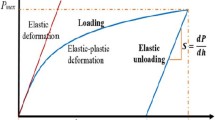
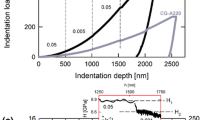
Abstract
The influence of applied stress on the measurement of hardness and elastic modulus using nanoindentation methods has been experimentally investigated using special specimens of aluminum alloy 8009 to which controlled stresses could be applied by bending. When analyzed according to standard methods, the nanoindentation data reveal changes in hardness with stress similar to those observed in conventional hardness tests. However, the same analysis shows that the elastic modulus changes with stress by as much as 10%, thus suggesting that the analysis procedure is somehow deficient. Comparison of the real indentation contact areas measured optically to those determined from the nanoindentation data shows that the apparent stress dependence of the modulus results from an underestimation of the contact area by the nanoindentation analysis procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kokubo, Science Reports of the Tohoku Imperial University 21, 256 (1932).
G. Sines and R. Carlson, ASTM Bulletin 180, 35 (1952).
G. U. Oppel, Exp. Mech. 21, 135 (1964).
F. H. Vitovec, in Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering, ASTM STP 889, edited by P.J. Blau and B.R. Lawn (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1986), p. 175.
T. R. Simes, S. G. Mellor, and D. A. Hills, J. Strain Analysis 19, 135 (1984).
P. A. Blain, Metal. Progress, 99 (1957).
P. A. Blain, Sheet Metal Ind. 26, 135 (1949).
J. O. Almen, Product Engineering, 121 (1950).
W. R. LaFontaine, C. A. Paszkiet, M.A. Korhonen, and Che-Yu Li, J. Mater. Res. 6, 2084 (1991).
M.A. Korhonen, W.R. LaFontaine, C.A. Paszkiet, R. D. Black, and Che-Yu Li, in Thin Films: Stresses and Mechanical Properties II, edited by M.F. Doerner, W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, and F.R. Brotzen (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 188, Pittsburgh, PA, 1990), p. 159.
W. R. LaFontaine, B. Yost, and Che-Yu Li, J. Mater. Res. 5, 776 (1990).
M. F. Doerner, D. S. Gardner, and W. D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 845 (1986).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
G. M. Pharr, W. C. Oliver, and F. R. Brotzen, J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
G. M. Pharr and W. C. Oliver, MRS Bull. XVII, 28 (1992).
W. C. Oliver, MRS Bull. XI, 15 (1986).
M. F. Doerner and W. D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
I. N. Sneddon, Int. J. Engng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
A. Bolshakov, W. C. Oliver, and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 11, 760 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsui, T.Y., Oliver, W.C. & Pharr, G.M. Influences of stress on the measurement of mechanical properties using nanoindentation: Part I. Experimental studies in an aluminum alloy. Journal of Materials Research 11, 752–759 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1996.0091
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1996.0091