Abstract
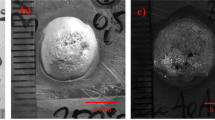
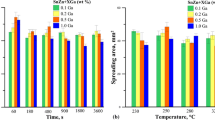
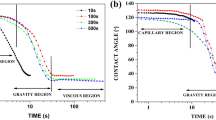
Wetting properties of lead-free solders, Sn–0.7 wt.% Cu and Sn–3.5 wt.% Ag, pure Sn, and conventional Sn–40 w.t% Pb on Ni, Cu, and Ag substrates at 250 and 240 °C were determined by using a wetting balance technique. Wetting times and wetting forces were determined directly from the wetting curves, and surface tensions of molten solders were calculated from the wetting force measurements. A statistic tool, analysis of variance (ANOVA), was used to analyze the experimental results. By using the wetting time as an indication, it was found that Sn–Pb exhibited the best wetting followed by Sn–Ag, Sn–Cu, and Sn, in that order. A very significant but frequently ignored issue is that most solders react with substrates, and the molten solders are not in contact with the original substrates but rather with intermetallic compounds. On the basis of theoretical analysis and experimental observations, it was concluded that the withdrawing forces and the surface tensions of the molten solders determined by the present technique are not significantly affected by the interfacial reactions if the interfacial reactions are not too excessive. However, wetting times are strong functions of both solders and substrates and the interfacial reactions between them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Jin, JOM 45(7), 13 (1993).
P.T. Vianco and D.R. Frear, JOM 45(7), 14 (1993).
J.W. Morris, Jr., J.L. Goldstein, and Z. Mei, JOM 45(7), 25 (1993).
C. Melton, JOM 45(7), 33 (1993).
M. McCormack and S. Jin, JOM 45(7), 36 (1993).
J. Glazer, Int. Mater. Rev. 40, 63 (1995).
J.C. Berg, Wettability (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1993), Chap. 2.
F.G. Yost, E.J. O’Toole, P.A. Sackinger, and T.P. Swiler, Sandia Report (Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM, 1998), pp. 1–7.
F.G. Yost, The Metal Science of Joining, edited by M.J. Cieslak, J.H. Perepezko, S. Kang, and M.E. Glicksman (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992) pp. 49–59.
W.J. Boettinger, C.A. Handwerker, and L.C. Smith, The Metal Science of Joining edited by M.J. Cieslak, J.H. Perepezko, S. Kang, and M.E. Glicksman (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992), pp. 183–189.
F.G. Yost and A.D. Romig, Jr. in Electronic Packaging Materials Science II, edited by R.C. Sundahl, R. Jaccodine, and K.A. Jackson (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 108, Pittsburgh, PA, 1988), pp. 385–390.
I.A. Aksay, C.E. Hoge, and J.A. Pask, J. Phys. Chem. 78, 1178 (1974).
W.J. Boettinger, C.A. Handwerker, and U.R. Kattner, in The Mechanics of Solder Alloy Wetting and Spreading, edited by F.G. Yost, F.M. Hosking, and D.R. Frear (Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1993), pp. 103–140.
K. Landry, C. Rado, R. Voitovich, and N. Eustathopoulos, Acta Mater. 45, 3079 (1997).
P.T. Vianco, F.M. Hosking, and J.A. Rejent, in Proceedings of the Conference Nepcon West (1992), pp. 1730–1738.
S. Green, D. Lea, and C. Hunt, NPL Report CMMT(A)213 (NPL, Teddington, Middlesex, U.K., 1999), pp. 1–10.
J-I. Lee, S-W. Chen, H-Y. Chang, and C-M. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 117 (2003).
J.Y. Park, J.S. Ha, C.S. Kang, K.S. Shin, M.I. Kim, and J.P. Jung, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1145 (2000).
J.Y. Park, C.S. Kang, and J.P. Jung, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 1256 (1999).
M. Abtew and G. Selvaduray, Mater. Sci. Eng. 27, 95 (2000).
I. Artaki, A.M. Jackson, and P.T. Vianco, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 757 (1994).
P.T. Vianco and P.M. Mizik, International SAMPE Electronics Conference (1994), Vol. 7, pp. 366–380.
A.M. Jackson, I. Artaki, and P.T. Vianco, International SAMPE Electronics Conference (1994), Vol. 7, pp. 381–393.
T. Takemoto and M. Miyazaki, Mater. Trans. 42, 745 (2001).
M.K. Choi, C.Y. Lee, and C.J. Shur, J. Electron. Manuf. 8, 235 (1998).
D.C. Montgomery, Design and Analysis of Experiments (Wiley, New York, 1997).
S-W. Chen and Y-W. Yen, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1133 (2001).
C-Y. Huang and S-W. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 152 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Hy., Chen, Sw., Wong, D.Sh. et al. Determination of reactive wetting properties of Sn, Sn–Cu, Sn–Ag, and Sn–Pb alloys using a wetting balance technique. Journal of Materials Research 18, 1420–1428 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0195
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0195