Abstract
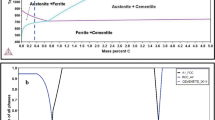
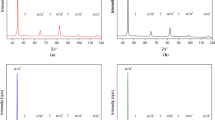
A modified heat treatment process designated quenching–partitioning–tempering (Q–P–T) process is developed based on the quenching and partitioning process proposed by J.G. Speer et al. [Acta Mater.51, 2611 (2003)] and D.K. Matlock et al. [Mater. Sci. Forum426–432, 1089 (2003)]. A Fe–0.485C–1.195Mn–1.185Si–0.98Ni–0.21Nb steel after Q–P–T process satisfies the designed requirement of tensile strength over 2000 MPa and elongation over 10%. The microstructure characterization indicates that this ultrahigh-strength steel consists of nanomicrostructures including lath martensite, filmlike retained austenite, and dispersive Nb-containing carbides. The effect of tempering time on the mechanical properties is analyzed based on microstructures.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Sakuma: Recent achievements in manufacturing and application of high-strength steel sheets for automotive body structure Proc. of International Conference on Advanced High Strength Sheet Steels for Automotive Applications edited by M.A. Baker Association for Iron & Steel Technology Warrendale, PA 2004 11
K. Sugimoto, M. Kobayshi, S. Hashimoto: Ductility and strain-induced transformation in a high strength TRIP-aided dual-phase steel. Metall. Trans. A 23, 3085 1992
W.C. Leslie, G.G. Rauch: Precipitation of carbides in low carbon Fe–Al–C alloys. Metall. Trans. A 9, 343 1978
X.D. Wang, B.X. Huang, Y.H. Rong, L. Wang: Transformation behavior of retained austenite in TRIP steels under stress. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 22, 532 2006
E. Girault, A. Mertens, P. Jacques, Y. Houbaert, B. Verlinden, J. Van Humbeeck: Comparison of the effects of silicon and aluminium on the tensile behaviour of multiphase TRIP-assisted steels. Scr. Mater. 44, 885 2001
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Very strong bainite. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. 8, 251 2004
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, J.A. Mawella, D.G. Jones, P. Brown: Very strong low temperature bainite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 18, 279 2002
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: 52nd Hatfield Memorial Lecture. Large chunks of very strong steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 21, 1293 2005
J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. Cooman, J.G. Schroch: Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater. 51, 2611 2003
D.K. Matlock, V.E. Brautigam, J.G. Speer: Application of the quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process to a medium-carbon, high-Si microalloyed bar steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 426–432, 1089 2003
C.G. Fan, H. Dong, J. Shi, Y.L. Lin, Q.L. Yong, W.J. Hui, M.Q. Wang, Y.Q. Weng: Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2200 MPa grade ultra-high strength low alloy steels. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 29, 31 2006 (in Chinese)
G. Krauss: Deformation and fracture in martensitic carbon steels tempered at low temperatures. Metall. Trans. B 32, 205 2001
N. Zhong, X.D. Wang, B.X. Huang, Y.H. Rong, L. Wang: Microstructures and mechanical property of quenched and partitioned Fe–C–Mn–Si steel. Proc. Third Int. Conf. on Advanced Structural Steels edited by the Committee of ICASS Gyeongju Korea 2006 885
T.Y. Hsu, Z.Y. Xu: Design of structure, composition and heat treatment process for high strength steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 561–565, 2283 2007
X.D. Wang, B.X. Huang, L. Wang, Y.H. Rong: Microstructure and mechanical properties of microalloyed high-strength transformation-induced plasticity steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39, 1 2008
N. Zhong, X.D. Wang, Y.H. Rong, L. Wang: Interface migration between martensite and austenite during quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 22, 751 2006
D.P. Koistinen, R.E. Marburger: A general equation prescribing extend of austenite–martensite transformation in pure Fe–C alloys and plain carbon steels. Acta Metall. 7, 59 1959
J.G. Speer, D.V. Edmonds, F.C. Rizzo, D.K. Matlock: Partitioning of carbon from supersaturated plates of ferrite, with application to steel processing and fundamentals of the bainite transformation. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 8, 219 2004
F.C. Rizzo, D.V. Edmonds, K. He, J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, A. Clarke: Carbon enrichment of austenite and carbide precipitation during the quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process. Solid-solid Phase Transformations in Inorganic Materials edited by J.M. Howe, D.E. Laughlin, J.K. Lee, U. Dahmen, and W.A. Soffa TMS Warrendale, PA 2005 535
D.V. Edmonds, K. He, F.C. Rizzo, B.C. De Cooman, D.K. Matlock, J.G. Speer: Quenching and partitioning martensite—A novel steel heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 438–440, 25 2006
F. Rizzo, A.R. Martins, J.G. Speer, D. Matlock, A. Clarke, B. De Cooman: Quenching and partitioning of Ni-added high strength steels. Mater. Sci. Forum 539–543, 4476 2007
L.C. Zhang, H.B. Lu, C. Mickel, J. Eckert: Ductile ultrafine-grained Ti-based alloys with high yield strength. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 051906 2007
B.V.N. Rao, G. Thomas: Structure-property relations and the design of Fe–4Cr–C base structural steels for high strength and toughness. Metall. Trans. A 11, 441 1980
A.J. Clarke, J.P. Speer, M.K. Miller, R.E. Hackenberg, D.V. Edmonds, D.K. Matlock, F.C. Rizzo, K.D. Clarke, E. De Moor: Carbon partitioning to austenite from martensite or bainite during the quench and partition (Q&P) process: A critical assessment. Acta Mater. 56, 16 2008
L.C. Zhang, J. Das, H.B. Lu, C. Duhamel, M. Calina, J. Eckert: High strength Ti–Fe–Sn ultrafine composites with large plasticity. Scr. Mater. 57, 101 2007
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50771110) and Baosteel Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.D., Zhong, N., Rong, Y.H. et al. Novel ultrahigh-strength nanolath martensitic steel by quenching–partitioning–tempering process. Journal of Materials Research 24, 260–267 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2009.0029
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2009.0029