Abstract
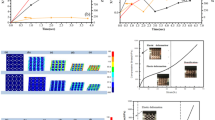
Porous Pd42.5Cu30Ni7.5P20 bulk glassy alloy rods with porosities up to 71% were successfully prepared by water quenching in a 15 MPa hydrogen atmosphere, followed by heat treatment in a supercooled liquid state. Pores with sizes up to 80 μm were homogeneously distributed over the whole cross-sectional area. Under compressive deformation, the porous alloys with porosities exceeding 41% did not show macroscopic fracture in a wide compressive strain range up to 0.6. Mechanical tests with porous alloy rods whose pores are anisotropically oriented indicate that the plasticity of the porous alloy is strongly affected by stress concentration factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Ashby, A.G. Evans, N.A. Fleck, L.J. Gibson, J.W. Hutchinson, H.N.G. Wadley: Metal Foams: A Design Guide (Butterworth–Heinemann, Boston, 2000).
L.J. Gibson, M.F. Ashby: Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties, 2nd ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997).
J. Banhart: Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 559 (2001).
A. Inoue, A. Kato, T. Zhang, S.G. Kim, T. Masumoto: Mg-Cu-Y amorphous alloys with high mechanical strengths produced by a metallic mold casting method. Mater. Trans. JIM. 32, 609 (1991).
A. Inoue, T. Zhang, T. Masumoto: Production of amorphous cylinder and sheet of La55Al25Ni20 alloy by a metallic mold casting method. Mater. Trans. JIM. 31, 425 (1990).
A. Inoue, T. Zhang, T. Masumoto: Preparation of bulky amorphous Zr-Al-Co-Ni-Cu alloys by copper mold casting and their thermal and mechanical properties. Mater. Trans. JIM. 36, 391 (1995).
A. Pecker, W.L. Johnson: A highly processable metallic glass: Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 2342 (1993).
A. Inoue, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, K. Kurosaka: Thermal and mechanical properties of Cu-based Cu-Zr-Ti bulk glassy alloys. Mater. Trans. 42, 1149 (2001).
A. Inoue, N. Nishiyama, T. Matsuda: Preparation of bulk glassy Pd40Ni10Cu30P20 alloy of 40 mm in diameter by water quenching. Mater. Trans. JIM. 37, 181 (1996).
A. Inoue, A. Murakami, T. Zhang, A. Takeuchi: Thermal stability and magnetic properties of bulk amorphous Fe-Al-Ga-P-C-B-Si alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM. 38, 189 (1997).
A. Inoue, B. Shen, H. Koshiba, H. Kato, A.R. Yavari: Cobalt-based bulk glassy alloy with ultrahigh strength and soft magnetic properties. Nat. Mater. 2, 661 (2003).
A. Inoue: Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 48, 279 (2000).
W.L. Johnson: Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys: Science and technology. MRS Bull. 24, 42 (1999).
J. Schroers, C. Veazey, W.L. Johnson: Amorphous metallic foam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 370 (2003).
T. Wada, A. Inoue: Fabrication, thermal stability and mechanical properties of porous bulk glassy Pd-Cu-Ni-P alloys. Mater. Trans. 44, 2228 (2003).
T. Wada, A. Inoue: Formation of porous Pd-based bulk glassy alloys by a high hydrogen pressure melting-water quenching method and their mechanical properties. Mater. Trans. 45, 2761 (2004).
T. Wada, A. Inoue, A.L. Greer: Enhancement of room-temperature plasticity in a bulk metallic glass by finely dispersed porosity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 251907 (2005).
A.H. Brothers, D.C. Dunand: Syntactic bulk metallic glass foam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1108 (2004).
A.H. Brothers, R. Scheunemann, J.D. DeFouw, D.C. Dunand: Processing and structure of open-celled amorphous metal foams. Scripta Mater. 52, 335 (2005).
A.H. Brothers, D.C. Dunand: Ductile bulk metallic glass foams. Adv. Mater. 17, 484 (2005).
A. Inoue, K. Amiya, A. Katsuya, T. Masumoto: Mechanical properties and thermal stability of Ti- and Al-based amorphous wires prepared by a melt extraction method. Mater. Trans. JIM 36, 858 (1995).
R.D. Conner, W.L. Johnson, N.E. Paton, W.D. Nix: Shear bands and cracking of metallic glass plates in bending. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 904 (2003).
J.N. Goodier: Concentration of stress around spherical and cylindrical inclusion and flaws. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 1, 39 (1933).
R.H. Edwards: Stress concentrations around spheroidal inclusion and cavities. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 19, 18 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, T., Kinaka, M. & Inoue, A. Effect of volume fraction and geometry of pores on mechanical properties of porous bulk glassy Pd42.5Cu30Ni7.5P20 alloys. Journal of Materials Research 21, 1041–1047 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0127
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0127