Abstract
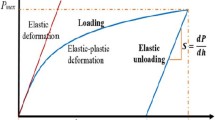
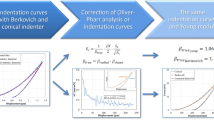
The standard Oliver–Pharr nanoindentation analysis tacitly assumes that the specimen is structurally rigid and that it is both semi-infinite and homogeneous. Many specimens violate these assumptions. We show that when the specimen flexes or possesses heterogeneities, such as free edges or interfaces between regions of different properties, artifacts arise in the standard analysis that affect the measurement of hardness and modulus. The origin of these artifacts is a structural compliance (Cs), which adds to the machine compliance (Cm), but unlike the latter, Cs can vary as a function of position within the specimen. We have developed an experimental approach to isolate and remove Cs. The utility of the method is demonstrated using specimens including (i) a silicon beam, which flexes because it is supported only at the ends, (ii) sites near the free edge of a fused silica calibration standard, (iii) the tracheid walls in unembedded loblolly pine (Pinus taeda), and (iv) the polypropylene matrix in a polypropylene–wood composite.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.C. Oliver G.M. Pharr: Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564 1992
R. Wimmer, B.N. Lucas, T.Y. Tsui W.C. Oliver: Longitudinal hardness and Young’s modulus of spruce tracheid secondary walls using nanoindentation technique. Wood Sci. Technol. 31(2), 131 1997
R. Wimmer B.N. Lucas: Comparing mechanical properties of secondary wall and cell corner middle lamella in spruce wood. IAWA J. 18(1), 77 1997
W. Gindl, H.S. Gupta C. Grunwald: Lignification of spruce tracheid secondary cell walls related to longitudinal hardness and modulus of elasticity using nano-indentation. Can. J. Bot. 80(10), 1029 2002
W. Gindl, H.S. Gupta, T. Schoberl, H.C. Lichtenegger P. Fratzl: Mechanical properties of spruce wood cell walls by nanoindentation. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. 79(8), 2069 2004
W.T.Y. Tze, S. Wang, T.G. Rials, G.M. Pharr S.S. Kelley: Nanoindentation of wood cell walls: continuous stiffness and hardness measurements. Composites Part A: Appl. Sci. 38(3), 945 2007
W. Gindl H.S. Gupta: Cell-wall hardness and Young’s modulus of melamine-modified spruce wood by nano-indentation. Composites Part A: Appl. Sci. 33(8), 1141 2002
W. Gindl, T. Schoberl G. Jeronimidis: The interphase in phenol-formaldehyde and polymeric methylene di-phenyl-di-isocyanate glue lines in wood. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 24(4), 279 2004
J. Konnerth W. Gindl: Mechanical characterisation of wood-adhesive interphase cell walls by nanoindentation. Holzforschung 60(4), 429 2006
G.A. Zickler, T. Schoberl O. Paris: Mechanical properties of pyrolysed wood: a nanoindentation study. Philos. Mag. 86(10), 1373 2006
G.E.L. Franco, D.S. Stone, R.D. Blank: (unpublished work, 2005)
R.B. King: Elastic analysis of some punch problems for a layered medium. Int. J. Solids Struct. 23(12), 1657 1987
D.S. Stone: Elastic rebound between an indenter and a layered specimen. I. Model.: J. Mater. Res. 13(11), 3207 1998
D.S. Stone, K.B. Yoder W.D. Sproul: Hardness and elastic modulus of TiN based on continuous indentation technique and new correlation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 9(4), 2543 1991
K.B. Yoder, D.S. Stone, R.A. Hoffman J.C. Lin: Elastic rebound between an indenter and a layered specimen. II. Using contact stiffness to help ensure reliability of nanoindentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 13(11), 3214 1998
Y. Choi, K.J. Van Vliet, L. Ju S. Suresh: Size effects on the onset of plastic deformation during nanoindentation of thin films and patterned lines. J. Appl. Phys. 94(9), 6050 2003
Y.M. Soifer, A. Verdyan, M. Kazakevich E. Rabkin: Edge effect during nanoindentation of thin copper films. Mater. Lett. 59(11), 1434 2005
D. Ge, A.M. Minor, E.A. Stach, J.W. Morris Jr. Size effects in the nanoindentation of silicon at ambient temperature. Philos. Mag. 86(25), 4069 2006
A. Hodzic, Z.H. Stachurski J.K. Kim: Nano-indentation of polymer-glass interfaces. I. Experimental and mechanical analysis. Polymer 41(18), 6895 2000
T.D. Downing, R. Kumar, W.M. Cross, L. Kjerengtroen J.J. Kellar: Determining the interphase thickness and properties in polymer matrix composites using phase imaging atomic force microscopy and nanoindentation. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 14(14), 1801 2000
S-H. Lee, S. Wang, G.M. Pharr H. Xu: Evaluation of interphase properties in a cellulose fiber-reinforced polypropylene composite by nanoindentation and finite element analysis. Composites Part A: Appl. Sci. 38(6), 1517 2007
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: Critical review of analysis and interpretation of nanoindentation test data. Surf. Coat. Tech. 200(14), 4153 2006
W.C. Oliver G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 3 2004
M. Troyon S. Lafaye: About the importance of introducing a correction factor in the Sneddon relationship for nanoindentation measurements. Philos. Mag. 86(33), 5299 2006
M.F. Doerner W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1(4), 601 1986
D.L. Joslin W.C. Oliver: New method for analyzing data from continuous depth-sensing microindentation tests. J. Mater. Res. 5(1), 123 1990
W. Gindl T. Schoberl: The significance of the elastic modulus of wood cell walls obtained from nanoindentation measurements. Composites Part A: Appl. Sci. 35(11), 1345 2004
A.E. Slaughter: Design and Fatigue of a Structural Wood–Plastic Composite Washington State University Pullman, WA 2004
R. Hull: Properties of Crystalline Silicon IEE 1999 xxvi+1016
N.A. Stillwell D. Tabor: Elastic recovery of conical indentations. Proc. Phys. Soc. 78(2), 169–179 1961
M. Sakai Y. Nakano: Elastoplastic load–depth hysteresis in pyramidal indentation. J. Mater. Res. 17(8), 2161 2002
O.L. Warren, A. Dwivedi, T.J. Wyrobek, O.O. Famodu I. Takeuchi: Investigation of machine compliance uniformity for nanoindentation screening of wafer-supported libraries. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76(6), 62209 2005
S.E. Grillo, M. Ducarroir, M. Nadal, E. Tournie J.P. Fauriel: Nanoindentation of Si, GaP, GaAs and ZnSe single crystals. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36(1), 5 2003
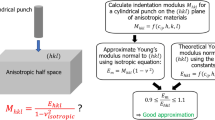
J.J. Vlassak W.D. Nix: Measuring the elastic properties of anisotropic materials by means of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42(8), 1223 1994
J.J. Hall: Electronic effects in the elastic constants of n-type silicon. Phys. Rev. 161(3), 756 1967
S. Cramer, D. Kretschmann, R. Lakes T. Schmidt: Earlywood and latewood elastic properties in loblolly pine. Holzforschung 59(5), 531 2005
J.E. Jakes, J.C. Hermanson D.S. Stone: Nanoindentation of the interphase region of a wood-reinforced polypropylene composite in Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Woodfiber-Plastic Composites, (Madison WI, 21–23 May, 2007), pp. 197–203
C.E. Gerber: Contact Problems for the Elastic Quarter-Plane and for the Quarter Space Stanford University Palo Alto, CA 1968 100
M. Hetenyi: Method of solution for elastic quarter-plane. Trans. ASME Series E, J. Appl. Mech. 27(2), 289 1960
M. Hetenyi: A general solution for the elastic quarter space. Trans. ASME Series E, J. Appl. Mech. 37(1), 70 1970
L.M. Keer, J.C. Lee T. Mura: Contact problem for the elastic quarter space. Int. J. Solids Struct. 20(5), 513 1984
G.Y. Popov: An exact solution of the mixed elasticity problem in a quarter-space. Mech. Solids 38(6), 23 2003
N. Schwarzer, I. Hermann, T. Chudoba F. Richter: Contact Modelling in the Vicinity of an Edge Elsevier San Diego, CA 2001 371–377
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jakes, J., Frihart, C., Beecher, J. et al. Experimental method to account for structural compliance in nanoindentation measurements. Journal of Materials Research 23, 1113–1127 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2008.0131
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2008.0131