Abstract
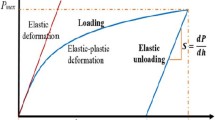
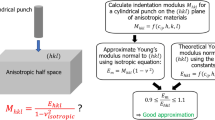
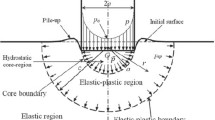
We previously proposed a method for estimating Young’s modulus from instrumented nanoindentation data based on a model assuming that the indenter had a spherical-capped Berkovich geometry to take account of the bluntness effect. The method is now further improved by releasing the constraint on the tip shape, allowing it to have a much broader arbitrariness to range from a conical-tipped shape to a flat-ended shape, whereas the spherical-capped shape is just a special case in between. This method requires two parameters to specify a tip geometry, namely, a volume bluntness ratio Vr and a height bluntness ratio hr. A set of functional relationships correlating nominal hardness/reduced elastic modulus ratio (Hn/Er) and elastic work/total work ratio (We/W) were established based on dimensional analysis and finite element simulations, with each relationship specified by a set of Vr and hr. Young’s modulus of an indented material can be estimated from these relationships. The method was shown to be valid when applied to S45C carbon steel and 6061 aluminum alloy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Pethica, R. Hutchings W.C. Oliver: Hardness measurement at penetration depth as small as 20 nm. Philos. Mag. A 48, 593 1983
J.L. Loubet, J.M. Georges, O. Marchesini G. Meille: Vickers indentation curves of magnesium oxide (MgO). J. Tribol. 106, 43 1984
D. Newey, M.A. Wilkens H.M. Pollock: An ultra-low-load penetration hardness tester. J. Phys. E.: Sci. Instrum. 15, 119 1982
W.C. Oliver G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 1992
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver F.R. Brotzen: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 1992
W.C. Oliver G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 2004
Y-T. Cheng C.M. Cheng: Scaling, dimension analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 91 2004
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: Nanoindentation Springer-Verlag New York 2004 39
J. Malzbender G. de With: Indentation load-displacement curve, plastic deformation, and energy. J. Mater. Res. 17, 502 2002
T.A. Venkatesh, K.J. Van Vliet, A.E. Giannakopoulos S. Suresh: Determination of elasto-plastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation: Guidelines for property extraction. Scr. Mater. 42, 833 2000
A.E. Giannakopoulos S. Suresh: Determination of elasto-plastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation. Scr. Mater. 40, 1191 1999
Y-T. Cheng C-M. Cheng: Relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 1998
C-M. Cheng Y-T. Cheng: On the initial unloading slope in indentation of elastic-plastic solids by an indenter with an axisymmetric smooth profile. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 2623 1997
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng, C.M. Chen D.S. Grummon: An energy-based method for analyzing instrumented spherical indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 19, 149 2004
D. Ma, C.W. Ong, S.F. Wong J. He: New method for determining Young’s modulus by non-ideally sharp indentation. J. Mater. Res. 20, 1498 2005
D. Ma, C.W. Ong S.F. Wong: New relationship between Young’s modulus and nonideally sharp indentation parameters. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2144 2004
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K.J. Van Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3899 2001
M. Lichinchi, C. Lenardi, J. Haupt R. Vitali: Simulation of Berkovich nanoindentation experiments on thin films using finite element method. Thin Solid Films 312, 240 1998
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: Use of combined elastic modulus in depth-sensing indentation with a conical indenter. J. Mater. Res. 18, 1043 2003
ABAQUS Version 6.2 Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc. Pawtucket, RI 2001
A. Bolshakov G.M. Pharr: Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1049 1998
J.J. Vlassak W.D. Nix: Measuring the elastic properties of anisotropic materials by means of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42, 1223 1994
J.J. Vlassak W.D. Nix: Indentation modulus of elastically anisotropic half spaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 67, 1045 1993
J.J. Vlassak, M. Ciavarella, J.R. Barber X. Wang: The indentation modulus of elastically anisotropic materials for indenters of arbitrary shape. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51, 1701 2003
J.P. Hirth J. Lothe: Elastic Constants in Theory of Dislocations Krieger Publishing Company Malabar, FL 1982 837
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 10672185, 10432050, and 10572142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Ong, C.W. & Zhang, T. An improved energy method for determining Young’s modulus by instrumented indentation using a Berkovich tip. Journal of Materials Research 23, 2106–2115 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0257
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0257