Abstract
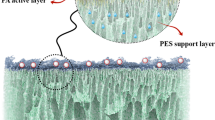
Hybrid zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) reverse osmosis membranes were synthesized by incorporating Linde type A (LTA)-type zeolite molecular sieve nanocrystals in the interfacial polymerization reaction used to form polyamide thin films. Nanocrystals were prepared with two different mobile cations (Na+ and Ag+) exchanged within the LTA crystal matrix. Incorporation of molecular sieve nanocrystals into polyamide thin films during interfacial polymerization was verified by infrared spectroscopy. Both TFN membranes exhibited higher water permeability, while maintaining similar salt rejection to pure polyamide thin film composite membranes. Nanocomposite thin films containing LTA nanocrystals in the silver form (AgA) produced a greater increase in water permeability than those in the sodium form (NaA). Furthermore, AgA-TFN membranes exhibited more hydrophilic and smooth interfaces, which appeared to inhibit adhesion of bacteria cells onto the membranes. The AgA nanocrystals exhibited significant bactericidal activity; however, when encapsulated within polyamide thin films the antimicrobial activity was significantly reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Elimelech: The global challenge for adequate and safe water. J. Water Supply Res Technol. Aqua 55, 3 (2006).
N. Savage and M.S. Diallo: Nanomaterials and water purification: Opportunities and challenges., J. Nanopart. Res. 7, 331 (2005).
E.M.V. Hoek and A.K. Ghosh: Nanotechnology-based Membranes for Water Purification, Nanotechnology Applications: Solutions for Improving Water Quality (Elsevier, Atlanta, GA, 2008).
H.S. Lee, S.J. Im, J.H. Kim, H.J. Kim, J.P. Kim, and B.R. Min: Polyamide thin-film nanofiltration membranes containing TiO2nanoparticles. Desalination 219, 48 (2008).
B.H. Jeong, E.M.V. Hoek, Y.S. Yan, A. Subramani, X.F. Huang, G. Hurwitz, A.K. Ghosh, and A. Jawor: Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: A new concept for reverse osmosis membranes., J. Membr. Sci. 294, 1 (2007).
A.K. Ghosh, B.H. Jeong, X.F. Huang, and E.M.V. Hoek: Impacts of reaction and curing conditions on polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane properties., J. Membr. Sci. 311, 34 (2008).
E.M. Vrijenhoek, S. Hong, and M. Elimelech: Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 188, 115 (2001).
S. Wang, G. Guillen, and E.M.V. Hoek: Direct observation of microbial adhesion to mermbranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 6461 (2005).
A. Subramani and E.M.V. Hoek: Direct observation of initial microbial deposition onto reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes., J. Membr. Sci. 319, 111 (2008).
S.T. Kang, A. Subramani, E.M.V. Hoek, M.A. Deshusses, and M.R. Matsumoto: Direct observation of biofouling in cross-flow microfiltration: Mechanisms of deposition and release., J. Membr. Sci. 244, 151 (2004).
M. Pasmore, P. Todd, S. Smith, D. Baker, J. Silverstein, D. Coons, and C.N. Bowman: Effects of ultrafiltration membrane surface properties on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm initiation for the purpose of reducing biofouling., J. Membr. Sci. 194, 15 (2001).
Y. Li, T.S. Chung, and S. Kulprathipanja: Novel Ag+-zeolite/polymer mixed matrix membranes with a high CO2/CH4 selectivity. AIChE J. 53, 610 (2007).
S. Kim and E.M.V. Hoek: Interactions controlling biopolymer fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 202, 333 (2007).
P.S. Singh, S.V. Joshi, J.J. Trivedi, C.V. Devmurari, A.P. Rao, and P.K. Ghosh: Probing the structural variations of thin film composite RO membranes obtained by coating polyamide over polysulfone membranes of different pore dimensions. J. Membr. Sci. 278, 19 (2006).
A.P. Rao, S.V. Joshi, J.J. Trivedi, C.V. Devmurari, and V.J. Shah: Structure-performance correlation of polyamide thin film composite membranes: Effect of coating conditions on film formation. J. Membr. Sci. 211, 13 (2003).
M.W. Urban: Vibrational Spectroscopy of Molecules and Macro-molecules on Surfaces (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1993).
T. Kyotani, N. Shimotsuma, and S. Kakui: FTIR-ATR study of the surface of a tubular zeolite NaA membrane ultrasonically reacted with water and acetic acid. Anal. Sci. 22, 325 (2006).
S. Alfaro, C. Rodriguez, M.A. Valenzuela, and P. Bosch: Aging time effect on the synthesis of small crystal LTA zeolites in the absence of organic template. Mater. Lett. 61, 4655 (2007).
G.J. Zhao and S.E. Stevens: Multiple parameters for the comprehensive evaluation of the susceptibility of Escherichia coli to the silver ion. Biometals 11, 27 (1998).
I. Sondi and B. Salopek-Sondi: Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 275, 177 (2004).
A.M.P. McDonnell, D. Beving, A.J. Wang, W. Chen, and Y.S. Yan: Hydrophilic and antimicrobial zeolite coatings for gravity-independent water separation. Adv. Fund. Mater. 15, 336 (2005).
T.A. Ostomel, P.K. Stoimenov, P.A. Holden, H.B. Alam, and G.D. Stucky: Host-guest composites for induced hemostasis and therapeutic healing in traumatic injuries. J. Thromb. Thromboly-sis 22, 55 (2006).
S.Y. Kwak, S.H. Kim, and S.S. Kim: Hybrid organic/inorganic reverse osmosis (RO) membrane for bactericidal anti-fouling. 1. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2388 (2001).
C.Y.Y. Tang, Y.N. Kwon, and J.O. Leckie: Probing the nano- and micro-scales of reverse osmosis membranes: A comprehensive characterization of physiochemical properties of uncoated and coated membranes by XPS, TEM, ATR-IR, and streaming potential measurements. J. Membr. Sci. 287, 146 (2007).
H.C. Flemming, G. Schaule, T. Griebe, J. Schmitt, and A. Tamachkiarowa: Biofouling: The Achilles heel of membrane processes. Desalination 113, 215 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Articles in this section are based on presentations that were selected by MRS Meeting Symposium Organizers as outstanding papers. Upon selection, authors are invited to submit their research results to Journal of Materials Research. These papers are subject to the same peer review and editorial standards as all other JMR papers. This is another way by which the Materials Research Society recognizes high quality papers presented at its meetings.
This paper was selected as an Outstanding Symposium Paper for the 2007 MRS Fall Meeting, Symposium V.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lind, M.L., Jeong, BH., Subramani, A. et al. Effect of mobile cation on zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes. Journal of Materials Research 24, 1624–1631 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0189
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0189