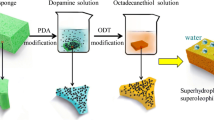
Abstract
The removal of oil spills or oily organic solvents from water surface is a great technological challenge for environmental protection. Here, a facile method to prepare superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponge for fast and selective removal of oils from water surface has been reported. The as-prepared sponge exhibited superhydrophobic property with the water contact angle around 165°, which can be used for the absorption of oil spills or oily organic solvents. Furthermore, the resultant sponge showed good durability toward temperature. This fabrication technique is easy to grasp and to be extended. So we believe that this new functionalized sponge could be realized for the large-scale commercialized production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Yuan, X. Liu, O. Akbulut, J. Hu, S. Suib, J. Kong, and F. Stellacci: Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 332 (2008).
A. Rao, N. Hegde, and H. Hirashima: Absorption and desorption of organic liquids in elastic superhydrophobic silica aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 305, 124 (2007).
Y. Liu, L. Jiang, H. Dong, Z. Tang, and W. Hu: Large-area single-crystalline nanocone arrays of an organic charge-transfer complex: Controlling growth, characterization, and applications. Small 7, 1412 (2011).
D. Ishii, H. Yabu, and M. Shimomura: Novel biomimetic surface based on a self-organized metal-polymer hybrid structure. Chem. Mater. 21, 1799 (2009).
H. Zhu, S. Qiu, W. Jiang, D. Wu, and C. Zhang: Evaluation of electrospun polyvinyl chloride/polystyrene fibers as sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 4527 (2011).
C. Wang, F. Tzeng, H. Chen, and C. Chang: Ultraviolet-durable superhydrophobic zinc oxide-coated mesh films for surface and underwater-oil capture and transportation. Langmuir 28, 10015 (2012).
L. Zhang, J. Wu, Y. Wang, Y. Long, N. Zhao, and J. Xu: Combination of bioinspiration: A general route to superhydrophobic particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 9879 (2012).
X. Liu, Y. Liang, F. Zhou, and W. Liu: Extreme wettability and tunable adhesion: Biomimicking beyond nature? Soft Matter 8, 2070 (2012).
M. Guix, J. Orozco, M. García, W. Gao, S. Sattayasamitsathit, A. Merkoç, A. Escarpa, and J. Wang: Superhydrophobic alkanethiol-coated microsubmarines for effective removal of oil. ACS Nano 6, 4445 (2012).
T. Nguyen, F. Simon, N. Khan, M. Schmutz, and P. Mésini: Formation of reactive aerogels and their reactivity in aqueous media. Wettability induces hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic selectivity. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 7712 (2012).
M. Cheng, Y. Gao, X. Guo, Z. Shi, J. Chen, and F. Shi: A functionally integrated device for effective and facile oil spill cleanup. Langmuir 27, 7371 (2011).
Q. Zhu, Q. Pan, and F. Liu: Facile removal and collection of oils from water surfaces through superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponges. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 17464 (2011).
J. Li, L. Shi, Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, Z. Guo, B. Su, and W. Liu: Stable superhydrophobic coatings from thiol-ligand nanocrystals and their application in oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 9774 (2012).
W. Choi, A. Tuteja, S. Chhatre, J. Mabry, R. Cohen, and G. McKinley: Fabrics with tunable oleophobicity. Adv. Mater. 21, 2190 (2009).
T. Stoebe, Z. Lin, R. Hill, M. Ward, and H. Davis: Superspreading of aqueous films containing trisiloxane surfactant on mineral oil. Langmuir 13, 7282 (1997).
L. Rossi, L. Shi, F. Quina, and Z. Rosenzweig: Stöber synthesis of monodispersed luminescent silica nanoparticles for bioanalytical assays. Langmuir 21, 4277 (2005).
K. Nozawa, H. Gailhanou, L. Raison, P. Panizza, H. Ushiki, E. Sellier, J. Delville, and M.H. Delville: Smart control of monodisperse Stöber silica particles: Effect of reactant addition rate on growth process. Langmuir 21, 151 (2005).
P. Calcagnile, D. Fragouli, I. Bayer, G. Anyfantis, L. Martiradonna, P. Cozzoli, R. Cingolani, and A. Athanassiou: Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano 6, 5413 (2012).
E. Burkarter, C. Saul, F. Thomazi, N. Cruz, L. Roman, and W. Schreiner: Superhydrophobic electrosprayed PTFE. Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 194 (2007).
D. Xu, M. Wang, X. Ge, M. Lam, and X. Ge: Fabrication of raspberry SiO2/polystyrene particles and superhydrophobic particulate film with high adhesive force. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 5784 (2012).
H. Teisala, M. Tuominen, M. Aromaa, M. Stepien, J. Mäkelä, and J. Jarkko: Nanostructures increase water droplet adhesion on hierarchically rough superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 28, 3138 (2012).
R. David and A. Neumann: Computation of the wetting properties of randomly structured superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 2362 (2012).
L. Zhang, R. Dillert, D. Bahnemann, and M. Vormoor: Photo-induced hydrophilicity and self-cleaning: models and reality. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 7491 (2012).
H. Park, S. Yoon, and Y. Do: Superhydrophobicity of 2D SiO2 hierarchical micro/nanorod structures fabricated using a two-step micro/nanosphere lithography. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 14035 (2012).
A. Rawlings, J. Bramble, and S. Staniland: Innovation through imitation: Biomimetic, bioinspired and biokleptic research. Soft Matter 8, 6675 (2012).
G. Gong, J. Wu, J. Liu, N. Sun, Y. Zhao, and L. Jiang: Bio-inspired adhesive superhydrophobic polyimide mat with high thermal stability. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 8257 (2012).
L. Hao, Z. Chen, R. Wang, C. Guo, P. Zhang, and S. Pang: A non-aqueous electrodeposition process for fabrication of superhydrophobic surface with hierarchical micro/nano structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 8970 (2012).
H. Fan, N. Zhao, H. Wang, X. Li, and J. Xu: One step preparation of polyaniline micro/nanohierarchical structures with superhydrophobicity. Mater. Lett. 78, 42 (2012).
L. Wu, Q. Shao, X. Wang, H. Zheng, and C. Wong: Hierarchical structured sol-gel coating by laser textured template imprinting for surface superhydrophobicity. Soft Matter 8, 6232 (2012).
J. Wang, Q. Yang, M. Wang, C. Wang, and L. Jiang: Rose petals with a novel and steady air bubble pinning effect in aqueous media. Soft Matter 8, 2261 (2012).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the Qianjiang Talents Project of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2010R10023), the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, the State Education Ministry (Grant No. 1001603-C), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. Y4100045), Training Foundation for the Excellent Young Talents by the Key Laboratory of Advanced Textile Materials and Manufacturing Technology (ATMT), Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2011QN04), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51133006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, G., Hu, R., Xi, X. et al. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponge for fast removal of oils from water surface. Journal of Materials Research 28, 651–656 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.410
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.410