Abstract
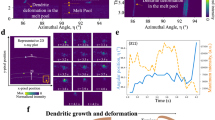
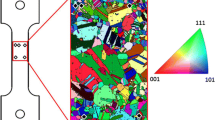
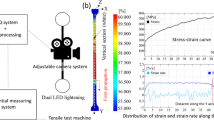
This paper examines the onset and progression of dynamic recrystallization (DRX) phenomena under shear deformation conditions characterized by strains >1 and strain rates >102/s by purposing large strain machining (LSM) as a test of microstructure response. To accomplish this, samples are created using LSM while characterizing the deformation using digital image correlation and infrared thermography. Microstructural consequences resulting from the characterized thermomechanical conditions are examined using electron backscattered diffraction. The progression of DRX is measured by identifying the threshold of grain orientation spread demarcating the onset of recrystallization and utilizing this threshold to segregate the microstructure and quantify the extent of DRX. A model for the onset of DRX as a function of thermomechanics of deformation is presented. This characterization can help understand surface microstructures resulting from shear-based manufacturing processes, such as turning, milling, shaping, etc., that are created under analogous thermomechanical conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mishra, B.K. Kad, F. Gregori, and M.A. Meyers: Microstructural evolution in copper subjected to severe plastic deformation: Experiments and analysis. Acta Mater. 55(1), 13 (2007).
R.Z. Valiev and T.G. Langdon: Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51(7), 881 (2006).
M. Kawasaki, B. Ahn, and T.G. Langdon: Microstructural evolution in a two-phase alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 58(3), 919 (2010).
R. Kuzel, M. Janecek, Z. Matej, J. Cizek, M. Dopita, and O. Srba: Microstructure of equal-channel angular pressed Cu and cu-Zr samples studied by different methods. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41(5), 1174 (2010).
M.R. Shankar, B.C. Rao, S. Lee, S. Chandrasekar, A.H. King, and W.D. Compton: Severe plastic deformation (SPD) of titanium at near-ambient temperature. Acta Mater. 54(14), 3691 (2006).
Y. Amouyal, S.V. Divinski, L. Klinger, and E. Rabkin: Grain boundary diffusion and recrystallization in ultrafine grain copper produced by equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 56(19), 5500 (2008).
X. Molodova, G. Gottstein, M. Winning, and R.J. Hellmig: Thermal stability of ECAP processed pure copper. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 460-461(15), 204 (2007).
G. Gottstein: Physikalische Grundlagen der Metallkunde, 2nd ed. (Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2001).
R.W. Cahn and P. Haasen: Physical Metallurgy, Part 2, 3rd ed. (Physics Publishing, North Holland, 1983).
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed. (Elsevier Science Ltd, London, 2002).
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas: Overview no. 35 dynamic recrystallization: Mechanical and microstructural considerations. Acta Metall. 32(2), 189 (1984).
F. Montheillet and J. Le Coze: Influence of purity on the dynamic recrystallization of metals and alloys. Phys. Status Solidi A 189(1), 51 (2002).
U. Andrade, M.A. Meyers, K.S. Vecchio, and A.H. Chokshi: Dynamic recrystallization in high-strain, high-strain-rate plastic deformation of copper. Acta Metall. Mater. 42(9), 3183 (1994).
T. Nicholas: Tensile testing at high rates of strain. Exp. Mech. 21, 177 (1981).
S. Lindholm, A. Nagy, G.R. Johnson, and J.M. Hoegfeldt: Large strain, high strain rate testing of copper. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 102(4), 376 (1980).
G.T. GrayIII: Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, 10th ed. (ASM Handbook, Ohio, 2000).
H.J. McQueen and S. Bergerson: Dynamic recrystallization of copper during hot torsion. Met. Sci. 6, 25 (1972).
H.J. McQueen: Materials Technology (An Inter-American Approach ASME, New York, 1968), pp. 379, 388.
J.J. Jonas, C.M. Sellars, and W.J.McG. Tegart: Strength and structure under hot-working conditions. Metall. Rev. 14, 1 (1969).
C.M. Sellars and W.J.McG. Tegart: On the mechanism of hot deformation. Acta Metall. 14(9), 1136 (1966).
J.P. Sah, G.J. Richardson, and C.M. Sellars: Recrystallization during hot deformation of Nickel. J. Aust. Inst. Met. 14, 292 (1969).
J.A. Hines and K.S. Vecchiot: Recrystallization kinetics within adiabatic shear bands. Acta Mater. 45(2), 635 (1997).
Y.B. Xu, W.L. Zhong, Y.J. Chen, L.T. Shen, Q. Liu, Y.L. Bai, and M.A. Meyers: Shear localization and recrystallization in dynamic deformation of 8090 Al–Li alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 299, 287 (2001).
M. Meyers: Dynamic Behavior of Materials (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1994).
M.A. Meyers, G. Subhash, B.K. Kad, and L. Prasad: Evolution of microstructure and shear-band formation in α-hcp titanium. Mech. Mater. 17, 175 (1994).
A.H. Chokshi and M.A. Meyers: The prospects for superplasticity at high strain rates: Preliminary considerations and an example. Scr. Metall. Mater. 24, 605 (1990).
S. Shekhar, J. Cai, S. Basu, S. Abolghasem, and M.R. Shankar: Effect of strain-rate in severe plastic deformation on microstructure refinement and stored energies. J. Mater. Res. 26, 395 (2011).
G.H. Akbari, C.M. Sellars, and J.A. Whiteman: Microstructural development during warm rolling of an if steel. Acta Mater. 45(12), 5047 (1997).
G.J. Baxter, D. Dulv, P.L. Orsetti Rossi, C.M. Sellars, J.A. Whiteman, H.R. Shercliff, and M.F. Ashby: Microstructural and crystallographic aspects of recrystallization. In 16th Riso International Symposium on Material Science, Microstructural and Crystallographic Aspects of Recrystallization, edited by N. Hansen, Y.L. Liu, D.J. Jensen, and B. Ralph (RISO National Laboratory, Roskilde, 1995), p. 267.
I. Haessner and S. Hofmann: Recrystallization of Metallic Materials (Riederer Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany, 1978).
P. Gerber, J. Tarasiuk, T. Chauveau, and B. Bacroix: A quantitative analysis of the evolution of texture and stored energy during annealing of cold rolled copper. Acta Mater. 51(20), 6359 (2003).
S. Mitsche, P. Poelt, and C. Sommitsch: Recrystallization behaviour of the nickel-based alloy 80 A during hot forming. J. Microsc. 227(3), 267 (2007).
J. Tarasiuk, P. Gerber, and B. Bacroix: Estimation of recrystallized volume fraction from EBSD data. Acta Mater. 50, 1467 (2002).
P. Poelt, C. Sommitsch, S. Mitsche, and M. Walter: Dynamic recrystallization of Ni-base alloys—experimental results and comparisons with simulations. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 420, 306 (2006).
F.J. Humphreys: Review grain and subgrain characterisation by electron backscatter diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 3833 (2001).
T.R. McNelley, A.P. Zhilyaev, S. Swaminathan, J. Su, and E. Sarath Menon: Application of EBSD methods to severe plastic deformation (SPD) and related processing methods. Chapter in Electron Backscatter Diffraction in Materials Science, edited by A.J. Schwartz, M. Kumar, B.L. Adams and D.P. Field (Kluwer Academic Plenum Publishers, New York, 2000).
S. Cheong and H. Weiland: Understanding a microstructure using GOS (grain orientation spread) and its application to recrystallization study of hot deformed Al-Cu-Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 558-559, 153 (2007).
C.V.S. Lim: Length scale effect on the microstructure evolution of Cu Layers in a Roll-Bonded CuNb composite, Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 2008.
M.H. Alvi, B.S. El-Dasher, and A.D. Rollett: Hot deformation of aluminum alloys III. ed. Z. Jin, A. Beaudoin, T. Bieler, and B. Radhakrishnan (TMS, Warrendale, PA (2003)), p. 3, 12.
R.A. Vandermeer and D. Juul Jensen: Recrystallization in hot vs cold deformed commercial aluminum: A microstructure path comparison. Acta Mater. 51, 3005 (2003).
M.H. Alvi, S. Cheong, H. Weiland, and A.D. Rollett: 1st International Symposium of Metallurgical Modelling of Aluminum Alloys, Pittsburgh, PA, 2003; p. 183.
M.H. Alvi, S. Cheong, H. Weiland, and A.D. Rollett: Recrystallization and texture development in hot rolled 1050 aluminum. Mater. Sci. Forum 467-470, 357 (2004).
S. Mitsche, P. Poelt, C. Sommitsch, and M. Walter: Quantification of the recrystallized fraction in a nickel-base-alloy from EBSD-data. Microsc. Microanal. 9, 344 (2003).
S. Mitsche, C. Sommitsch, P. Pölt, and S. Kleber: Recrystallization Behaviour of the Nickel based alloy 80 A during hot forming (Proc. 13th Conf. And Workshop on electron backscatter diffraction, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, Royal Microscopical Society (RMS), 2006).
S. Abolghasem, S. Basu, S. Shekhar, J. Cai, and M.R. Shankar: Mapping subgrain sizes resulting from severe simple shear deformation. Acta Mater. 60, 376 (2012).
D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf: A critical test on theories of work-hardening for the case of drawn iron wire. Met. Trans. 1, 3173 (1970).
D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf: Work hardenning in tension and fatigue, in edited by A.W. Thompson (The Metallurgical Society of AIME: New York, 1977).
E. Nes: Modeling of work hardening and stress saturation in FCC metals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 41, 129 (1998).
P.L.B. Oxley and W.F. Hasting: Predicting the strain rate in the zone of intense shear in which the chip is formed in machining from the dynamic flow stress properties of the work material and the cutting conditions. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 356, 395 (1977).
S. Lee, J. Hwang, M.R. Shankar, S. Chandrasekar, and W.D. Compton: Large strain deformation field in machining. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1633 (2006).
D. Raybould and T. Sheppard: Axisymmetric extrusion: The effect of temperature rise and strain rate on the activation enthalpy and material constants of some aluminum alloys and their relation to recrystallization, substructure and subsequent mechanical properties. J. Inst. Met. Mar. 101, 65 (1973).
S. Swaminathan, M.R. Shankar, B.C. Rao, W.D. Compton, S. Chandrasekar, A.H. King, and K.P. Trumble: Severe plastic deformation (SPD) and nanostructured materials by machining. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 1529 (2007).
C.E. Campbell, L.A. Bendersky, W.J. Boettinger, and R. Ivester: Microstructural characterization of Al-7075-T651 chips and work pieces produced by high-speed machining. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 430, 15 (2006).
E.K. Cerreta, I.J. Frank, G.T. GrayIII, C.P. Trujillo, D.A. Korzekwa, and L.M. Dougherty: The influence of microstructure on the mechanical response of copper in shear. Mater. Sci. Eng. 501(1), 207 (2009).
A.H. Adibi-Sedeh, V. Madhavan, and B.J. Bahr: Extension of oxley’s analysis of machining to use different material models. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 125, 656 (2003).
S. Shekhar, J. Cai, S. Basu, S. Abolghasem, and M.R. Shankar: Effect of severe plastic deformation in machining elucidated via rate-strain-microstructure mappings. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 134, 31008–31011 (2012).
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon: Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel. J. Appl. Phys. 15, 22 (1944).
W.S. Zhao, N.R. Tao, J.Y. Guo, Q.H. Lu, and K. Lu: High density nano-scale twins in Cu induced by dynamic plastic deformation. Scr. Mater. 53, 745 (2005).
Z.Y. Ma and S.C. Tjong: High temperature creep behavior of in-situ TiB2 particulate reinforced copper-based composite. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 284, 70 (2000).
V. Randle and O. Engler: Introduction to texture analysis: Macrotexture, microtexture and orientation mapping (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 2000).
H. Gao and Y. Huang: Geometrically necessary dislocation and size-dependent plasticity. Scr. Mater. 48, 113 (2003).
S.I. Wright: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Textures. Montreal, Canada (1999), p. 104, 109.
M.H. Alvi: Recrystallization kinetics and microstructural evolution in hot rolled aluminum alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 2005.
H. Jazaeri and F.J. Humphreys: Quantifying recrystallization by electron backscatter diffraction. J. Microsc. 213, 241 (2003).
O. Engler and M. Huh: Evolution of the cube texture in high purity aluminum capacitor foils by continuous recrystallization and subsequent grain growth. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 271, 371 (1999).
H. Jazaeri and F.J. Humphreys: The effect of initial grain size on transition from discontinuous to continuous recrystallization in a highly cold rolled Al–Fe–Mn alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 396, 551 (2002).
H. Ahlborn, E. Hornbogen, and U. Koster: Recrystallisation mechanism and annealing texture in aluminium-copper alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 4, 944 (1969).
H. Abrams: Grain size measurement by the intercept method. Metallography 4, 59 (1971).
Acknowledgments
Support from the National Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 0927410 and 0856626) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers, whose thorough reviews helped improve the paper and the analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abolghasem, S., Basu, S. & Shankar, M.R. Quantifying the progression of dynamic recrystallization in severe shear deformation at high strain rates. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2056–2069 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.201
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.201