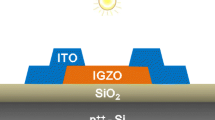
Abstract
Metal oxide optoelectronics is an emerging field that exploits the intriguing properties of the ns orbital-derived isotropic band structure as a replacement for traditional silicon-based electronics in advanced active-matrix information displays. Although the device performance of metal oxide thin film transistors (TFTs) has been substantially improved, the device reliability against external light and gate bias stress remains a critical issue. This paper provides a literature review of light-induced gate bias stress instability in metal oxide TFTs and explain the importance of photo-bias instability in the applications of metal oxide TFTs to optoelectronic device. The rationale of threshold voltage (Vth) instability under the negative bias illumination stress (NBIS) condition is discussed in detail. The charge trapping/injection model, oxygen vacancy photoionization model, and ambient interaction model are described as plausible degradation mechanisms. Finally, the possible approaches to prevent NBIS-induced Vth instability are proposed based on an understanding of the NBIS instability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Matsueda: Required characteristics of TFTs for next generation flat panel display backplanes. Digest of International Transistor Conference, Tokyo, Japan, January 28–29, 2010, p. 314.
W.B. Jackson and M.D. Moyer: Creation of near-interface defects in hydrogenated amorphous silicon-silicon nitride heterojunctions: The role of hydrogen. Phys. Rev. B 36, 6217–6220 (1987).
M.J. Powell: Charge trapping instabilities in amorphous silicon-silicon nitride thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 43, 597–599 (1983).
M. Jahinuzzaman, A. Sultana, K. Sakariya, P. Servati, and A. Nathan: Threshold voltage instability of amorphous silicon thin-film transistors under constant current stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 023502 (2005).
S.D. Theiss and S. Wagner: Amorphous silicon thin-film transistors on steel foil substrates. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 17, 578–580 (1996).
T. Serikawa and F. Omata: High-quality polycrystalline Si TFTs fabricated on stainless-steel foils by using sputtered Si films. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 49, 820–825 (2002).
J.K. Jeong, D.U. Jin, H.S. Shin, H.J. Lee, M. Kim, T.K. Ahn, J. Lee, Y.G. Mo, and H.D. Kim: Flexible full-color AMOLED on ultra-thin metal foil. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28, 389–391 (2007).
J.S. Im, H.J. Kim, and M.O. Thompson: Phase transformation mechanism involved in excimer laser crystallization of amorphous silicon films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 1969–1971 (1993).
E. Fortunato, P. Barquinha, and R. Martins: Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: A review of recent advances. Adv. Mater. 24, 2945–2986 (2012).
J.S. Park, S-J. Maeng, H-S. Kim, and J-S. Park: Review of recent development in amorphous oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor devices. Thin Solid Films 520, 1679–1693 (2012).
J.Y. Kwon, D.J. Lee, and K.B. Kim: Transparent amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film transistor. Electron. Mater. Lett. 7, 1–11 (2011).
T. Kamiya, K. Nomura, and H. Hosono: Present status of amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O thin-film transistors. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 11, 044305_1-23 (2010).
K. Nomura, H. Ohta, A. Takagi, T. Kamiya, M. Hirano, and H. Hosono: Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004).
H. Hosono: Ionic amorphous oxide semiconductors: Material design, carrier transport, and device application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 352, 851–858 (2006).
T. Iwasaki, N. Itagaki, T. Den, H. Kumomi, K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, and H. Hosono: Combinatorial approach to thin-film transistors using multicomponent semiconductor channels: An application to amorphous oxide semiconductors in In-Ga-Zn-O system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 242114_1-3 (2007).
J.K. Jeong, J.H. Jeong, H.W. Yang, J.S. Park, Y.G. Mo, and H.D. Kim: High performance thin film transistors with co-sputtered amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 113505_1–3 (2007).
H.N. Lee, J. Kyung, M.C. Sung, D.Y. Kim, S.K. Kang, S.J. Kim, C.N. Kim, H.G. Kim, and S.T. Kim: Oxide TFT with multilayer gate insulator for backplane of AMOLED device. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 16, 265–272 (2008).
J.K. Jeong, J.H. Jeong, H.W. Yang, T.K. Ahn, M. Kim, K.S. Kim, B.S. Gu, H.J. Chung, J.S. Park, Y.G. Mo, H.D. Kim, and H.K. Chung: 12.1-in. WXGA AMOLED display driven by InGaZnO thin-film transistors. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 17, 95–100 (2009).
M. Kim, J.H. Jeong, H.J. Lee, T.K. Ahn, H.S. Shin, J.S. Park, J.K. Jeong, Y.G. Mo, and H.D. Kim: High mobility bottom gate InGaZnO thin-film transistors with SiOx etch stopper. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 212114_1–3 (2007).
A. Sato, K. Abe, R. Hayashi, H. Kumomi, K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, M. Hirano, and H. Hosono: Amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O coplanar homojunction thin-film transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 133502_1–3 (2009).
N. Morosawa, Y. Ohshima, M. Morooka, T. Arai, and T. Sasaoka: A novel self-aligned top-gate oxide TFT for AM-OLED displays. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers 42, 479–482 (2011).
M. Ito, C. Miyazaki, M. Ishizaki, M. Kon, N. Ikeda, T. Okubo, R. Matsubara, K. Hatta, Y. Ugajin, and N. Sekine: Application of amorphous oxide TFT to electrophoretic display. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354(19–25), 2777–2782 (2008).
J.H. Lee, D.H. Kim, D.J. Yang, S.Y. Hong, K.S. Yoon, P.S. Hong, C.O. Jeong, H.S. Park, S.Y. Kim, S.K. Lim, and S.S. Kim: World’s largest (15-inch) XGA AMLCD panel using IGZO TFT. SID International Symposium Digest Technical Papers 39, 625–628 (2008).
OLED. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OLEDwiki/OLED.
J-H. Shin, J-S. Lee, C-S. Hwang, S-H.K. Park, W-S. Cheong, M. Ryu, C-W. Byun, J-I. Lee, and H.Y. Chu: Light effects on the bias stability of transparent ZnO thin film transistors. ETRI J. 31, 62–64 (2009).
J.K. Jeong: The status and perspectives of metal oxide thin film transistors for active matrix flexible displays. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 26, 034008_1–10 (2011).
R.B.M. Cross and M.M. De Souza: Investigating the stability of zinc oxide thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 263513_1–3 (2006).
A. Suresh and J.F. Muth: Bias stress stability of indium gallium zinc oxide channel based transparent thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 033502_1–3 (2008).
K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, H. Yanagi, E. Ikenaga, K. Yang, K. Kobayashi, M. Hirano, and H. Hosono: Subgap states in transparent amorphous oxide semiconductor, In-Ga-Zn-O, observed by bulk sensitive x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 202117_1–3 (2008).
K. Ghaffazadeh, A. Nathan, J. Roberson, S. Kim, S. Jeong, C. Kim, U-I. Chung, and J.H. Lee: Instability in threshold voltage and subthreshold behavior in Hf-In-Zn-O thin film transistors induced by bias-and light-stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 113504_1–3 (2010).
D.A. Neamen: Semiconductor Physics and Devices: Basic Principles, 3rd ed. (McGraw Hill, New York, 2003), Chap. 14.
S. Kim, S. Kim, C. Kim, J. Park, I. Song, S. Jeon, S-E. Ahn, J-S. Park, and J.K. Jeong: The influence of visible light on gate bias instability of In-Ga-Zn-O thin film transistors. Solid-State Electron. 62, 77–81 (2011).
Y.J. Chung, J.H. Kim, U.K. Kim, D-Y. Cho, H.S. Jung, J.K. Jeong, and C.S. Hwang. Direct observation of a hole current in amorphous oxide semiconductor under illumination. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 14, G35–G37 (2011).
K.H. Ji, J-I. Kim, H.Y. Jung, S.Y. Park, R. Choi, U.K. Kim, C.S. Hwang, D. Lee, H. Hwang, and J.K. Jeong: Effect of high-pressure oxygen annealing on negative bias illumination stress-induced instability of InGaZnO thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 103509_1–3 (2011).
B. Ryu, H-K. Noh, E-A. Choi, and K.J. Chang: O-vacancy as the origin of negative bias illumination stress instability in amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 022108_1–3 (2010).
S. Yang, D-H. Cho, M.K. Ryu, S-H.K. Park, C-S. Hwang, J. Jang, and J.K. Jeong: Improvement in the photon-induced bias stability of Al-Sn-Zn-In-O thin film transistors by adopting AlOx passivation layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 213511_1–3 (2010).
D.L. Staebler and C.R. Wronski: Optically induced conductivity changes in discharge-produced hydrogenated amorphous silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 3262–3268 (1980).
M. Stutzmann, W.B. Jackson, and C.C. Tsai: Light-induced metastable defects in hydrogenated amorphous silicon: A systematic study. Phys. Rev. B 32, 23–47 (1985).
C.R. Kagan and P. Andry: Thin Film Transistors (Dekker, New York, 2003), Chap. 3, p. 104.
E.A. Douglas, A. Scheurmann, R.P. Davies, B.P. Gila, H. Cho, V. Craciun, E.S. Lambers, S.J. Pearton, and F. Ren: Measurement of SiO2/InZnGaO4 heterojunction band offsets by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 242110_1–3 (2011).
Y-K. Moon, S. Lee, W-S. Kim, B-W. Kang, C-O. Jeong, D-H. Lee, and J-W. Park: Improvement in the bias stability of amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide thin-film transistors using an O2 plasma-treated insulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 013507_1–3 (2009).
K.H. Ji, J-I. Kim, Y-G. Mo, J.H. Jeong, S. Yang, C-S. Hwang, S-H.K. Park, M-K. Ryu, S-Y. Lee, and J.K. Jeong; Comparative study on light-induced bias stress instability of IGZO transistors with SiNx and SiO2 gate dielectrics. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 1404–1406 (2010).
K.H. Ji, J-I. Kim, H.Y. Jung, S.Y. Park, Y-G. Mo, J.H. Jeong, J-Y. Kwon, M-K. Ryu, S.Y. Lee, R. Choi, and J.K. Jeong: The effect of density-of-state on the temperature and gate bias-induced instability of InGaZnO thin film transistor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, H983–H986 (2010).
Y-N. Tan, W-K. Chim, B.J. Cho, and W-K. Choi: Over-erase phenomenon in SONOS-type flash memory and its minimization using a hafnium oxide charge storage layer. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 51, 1143–1145 (2004).
A. Janotti and C.G. Van de Walle: Oxygen vacancies in ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 122102_1–3 (2005).
S. Lany and A. Zunger: Anion vacancies as a source of persistent photoconductivity in II-VI and chalcopyrite semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 72, 035215_1–13 (2005).
A. Janotti and C.G. Van de Walle: Native point defects in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 76, 165202_1–22 (2007).
A. Janotti and C.G. Van de Walle: Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 126501_1–27 (2009).
K. Ghaffazadeh, A. Nathan, J. Roberson, S. Kim, S. Jeong, C. Kim, U-I. Chung, and J.H. Lee: Persistent photoconductivity in Hf-In-Zn-O thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 143510_1–3 (2010).
M.D.H. Chowdhury, P. Migliorato, and J. Jang: Light induced instabilities in amorphous indium-gallium-zinc-oxide thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 173506_1–3 (2010).
H. Omura, H. Kumomi, K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, M. Hirano, and H. Hosono: First-principles study of native point defects in crystalline indium gallium zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 093712_1–8 (2009).
H. Oh, S-M. Yoon, M.K. Ryu, C-S. Hwang, S. Yang, and S-H.K. Park: Photon-accelerated negative bias instability involving subgap states creation in amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O thin film transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 183502_1–3 (2010).
H. Oh, S-H.K. Park, C-S. Hwnag, S. Yang, and M.K. Ryu: Enhanced bias illumination stability of oxide thin film transistor through insertion of ultrathin positive charge barrier into active material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 022105_1–3 (2011).
S. Oh, B.S. Yang, Y.J. Kim, M.S. Oh, M. Jang, H. Yang, J.K. Jeong, C.S. Hwang, and H.J. Kim: Anomalous behavior of negative bias illumination stress instability in an indium zinc oxide transistor: A cation combinatorial approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 092107_1–5 (2012).
P. Migliorato, M.D.H. Chowdhury, J.G. Um, M. Seok, and J. Jang: Light/negative bias stress instabilities in indium gallium zinc oxide thin film transistors explained by creation of a double donor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 123502_1–5 (2012).
H-H. Nahm, Y-S. Kim, and D.H. Kim: Instability of amorphous oxide semiconductors via carrier-mediated structural transition between disorder and peroxide state. Phys. Status Solidi B 249, 1277–1281 (2012).
D.H. Lee, K. Kawamura, K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, and H. Hosono: Large photoresponse in amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O and origin of reversible and slow decay semiconductor devices, materials, and processing. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 13, H324–H327 (2010).
M.D.H. Chowdhury, P. Migliorato, and J. Jang: Time-temperature dependence of positive gate bias stress and recovery in amorphous indium-gallium-zinc-oxide thin-film-transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 153511_1–3 (2011).
J. Xu, Q. Pan, Y. Shun, and Z. Tian: Grain size control and gas sensing properties of ZnO gas sensor. Sens. Actuators, B 66(1–3), 277–279 (2000).
S.T. Shishiyanu, T.S. Shishiyanu, and O.I. Lupan: Sensing characteristics of tin-doped ZnO thin films as NO2 gas sensor. Sens. Actuators, B 107, 379–386 (2005).
D. Kang, H. Lim, C. Kim, I. Song, J. Park, Y. Park, and J. Chung: Amorphous gallium indium zinc oxide thin film transistors: Sensitive to oxygen molecules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 192101_1–3 (2007).
J.K. Jeong, H.W. Yang, J.H. Jeong, Y.G. Mo, and H.D. Kim: Origin of threshold voltage instability in indium-gallium-zinc oxide thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 123508_1–3 (2008).
Y.C. Chen, T.C. Chang, H.W. Li, S.C. Chen, J. Lu, W.F. Chung, Y.H. Tai, and T.Y. Tseng: Bias-induced oxygen adsorption in zinc tin oxide thin film transistors under dynamic stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 262104_1-3 (2010).
S.Y. Sung, J.H. Choi, U.B. Han, C.K. Lee, J.H. Lee, J.J. Kim, W. Lim, S.J. Pearton, D.P. Norton, and Y.W. Heo: Effects of ambient atmosphere on the transfer characteristics and gate-bias stress stability of amorphous indium-gallium-zinc oxide thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 102107_1–3 (2010).
W. Göpel: Chemisorption and charge transfer at ionic semiconductor surfaces: Implication in designing gas sensors. Prog. Surf. Sci. 20, 9–103 (1985).
W. Göpel: Initial steps of interface formation: Surface states and thermodynamics. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 16, 1229–1235 (1979).
P. Gorrn, T. Riedl, and W. Kowalsky: Encapsulation of zinc tin oxide based thin film transistors. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 11126–11130 (2009).
K-H. Lee, J.S. Jung, K.S. Son, J.S. Park, T.S. Kim, R. Choi, J.K. Jeong, J-Y. Kwon, B. Koo, and S. Lee: The effect of moisture on the photon-enhanced negative bias thermal instability in Ga-In-Zn-O thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 232106_1–3 (2009).
S. Yang, D-H. Cho, M.K. Ryu, S-H.K. Park, C-S. Hwang, J. Jang, and J.K. Jeong: High performance Al-Sn-Zn-In-O thin film transistors: Impact of passivation layer on device stability. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 144–146 (2010).
J-Y. Kwon, J.S. Jung, K.S. Son, K-H. Lee, J.S. Park, T.S. Kim, J-S. Park, R. Choi, J.K. Jeong, B. Koo, and S. Lee: The impact of gate dielectric materials on the light-induced bias instability in Hf-In-Zn-O thin film transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 183503_1–3 (2010).
J.H. Kim, U.K. Kim, Y.J. Chung, and C.S. Hwang: Improvement in the negative bias illumination temperature stress instability of In-Ga-Zn-O thin film transistors using an Al2O3 buffer layer. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 5(5–6), 178–180 (2011).
C-K. Lee, H.Y. Jung, S.Y. Park, B.G. Son, C-K. Lee, H.J. Kim, R. Choi, D-H. Kim, J-U. Bae, W-S. Shin, and J.K. Jeong: Suppression in negative bias illumination stress instability of zinc-tin oxide transistor by insertion of thermal TiOx film. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34, 253–255 (2013).
S.Y. Park, K.H. Ji, J-I. Kim, H.Y. Jung, R. Choi, K.S. Son, M.K. Ryu, S. Lee, and J.K. Jeong: Improvement in the device performance of tin-doped indium oxide transistor by oxygen high pressure annealing at 150 °C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 162108_1–4 (2012).
K.S. Son, J.S. Park, T.S. Kim, H-S. Kim, S-J. Seo, S-J. Kim, J-B. Seon, K.H. Ji, J.K. Jeong, M.K. Ryu, and S. Lee: Improvement of photo-induced negative bias stability of oxide TFTs by reducing of sub-gap states related to oxygen vacancies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 122108_1–4 (2013).
S. Yang, K.H. Ji, U.K. Kim, C.S. Hwang, S-H.K. Park, C-S. Hwang, J. Jang, and J.K. Jeong: Suppression in the negative bias illumination instability of Zn-Sn-O transistor using oxygen plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 102103_1–3 (2011).
B.S. Yang, S. Park, S. Oh, Y.J. Kim, J.K. Jeong, C.S. Hwang, and H.J. Kim: Improvement of the photo-bias stability of the Zn-Sn-O field effect transistors by an ozone treatment. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 10994–10998 (2012).
T. Seiyama: Chemical Sensor Technology, Vol. 1 (Kodansha/Elsevier, Tokyo, Japan, 1988).
B.S. Yang, M.S. Huh, S. Oh, U.S. Lee, Y.J. Kim, M.S. Oh, J.K. Jeong, C.S. Hwang, and H.J. Kim: Role of ZrO2 incorporation in the suppression of negative bias illumination-induced instability in Zn-Sn-O thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 122110_1–3 (2011).
I. Barin: Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, Part 2 (VCH, New York, 1989).
T. Kamiya, K. Nomura, and H. Hosono: Origin of definite Hall voltage and positive slope in mobility-donor density relation in disordered oxide semiconductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 122103_1–3 (2010).
K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, H. Ohta, K. Ueda, M. Hirano, and H. Hosono: Carrier transport in transparent oxide semiconductor with intrinsic structural randomness probed using single-crystalline InGaO3(ZnO)5 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1993–1995 (2004).
K. Nomura, T. Kamiya, and H. Hosono: Highly stable amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O thin-film transistors produced by eliminating deep subgap defects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 053505_1–3 (2011).
J.S. Park, T.S. Kim, K.S. Son, K.H. Lee, W.J. Maeng, H.S. Kim, E.S. Kim, K.B. Park, J.B. Seon, W. Choi, M.K. Ryu, and S.Y. Lee: The influence of SiOx and SiNx passivation on the negative bias stability of Hf-In-Zn-O thin film transistors under illumination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 262109_1–3 (2010).
H.J. Kim, S.Y. Park, H.Y. Jung, B.G. Son, C-K. Lee, C-K. Lee, J.H. Jeong, Y.G. Mo, K.S. Son, M.K. Ryu, S. Lee, and J.K. Jeong: Role of incorporated hydrogen on performance and photo-bias instability of indium gallium zinc oxide thin film transistors. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 055104_1–6 (2013).
D.P. Gosain and T. Tanaka: Instability of amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide thin film transistors under light illumination. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 03B018_1–5 (2009).
H. Ohara, T. Sasaki, K. Noda, S. Ito, M. Sasaki, Y. Endo, S. Yoshitomi, J. Sakata, T. Serikawa, and S. Yamazaki: 4.0-inch active-matrix organic light-emitting diode display integrated with driver circuits using amorphous In-Ga-Zn-Oxide thin-film transistors with suppressed variation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 03CD02_1–6 (2010).
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by a Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (Grant No. 2012R1A2A2A02005854), the industrial strategic technology development program (Grant Nos. 10041808, 10041041, and 10035225) funded by MKE/KEIT and Inha University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, J.K. Photo-bias instability of metal oxide thin film transistors for advanced active matrix displays. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2071–2084 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.214
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.214