Abstract
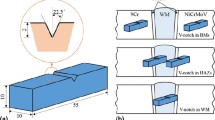
Dissimilar joints of advanced 9Cr/CrMoV have been successfully welded by narrow gap submerged arc welding using multi-layer and multi-pass techniques. The objective of our study is to establish the correlation between impact toughness and microstructural characteristics of the welded joints. Impact toughness tests were conducted in a wide range of temperature from −60 °C to 80 °C for different regions in the dissimilar joints. The fracture appearance transition temperature of base metal of 9Cr, CrMoV and weld metal were tested as 23 °C, −9 °C and −2 °C respectively, which all satisfied the service requirement. Optical microscope and scanning electron microscope revealed that weld metal and base metal of CrMoV comprised martensite and bainite while 9Cr was composed of lath martensite. The low toughness in the latter region arose from large grains with excessive carbide precipitates. Nonuniform microstructure in the heat-affected zone of 9Cr side caused different crack propagation paths and subsequently led to large variations of absorbed energy. When crack propagates along carbon-enriched zone in heat affected zone, the absorbed energy was 48 J. With crack deviating far from carbon-enriched zone, the absorbed energy increased to 147 J. Examination on fracture surfaces revealed the typical brittle fracture appearance in 9Cr and inter-granular fracture mode in heat-affected zone of 9Cr side when crack propagated along carbon-enriched zone.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Poules: Advantages of ultra super critical technology in power generation. Presented at the International Conference on Clean Coal Technologies for our Future CCT, 10, 2005.
X.J. Liu, X.B. Kong, G.L. Hou, and J.H. Wang: Modeling of a 1000 MW power plant ultra super-critical boiler system using fuzzy-neural network methods. Energy Convers. Manage. 65, 518 (2013).
W. Kosman: Thermal analysis of cooled supercritical steam turbine components. Energy 35 (2), 1181 (2010).
W. Huo, J. Li, and X. Yan: Effects of coolant flow rates on cooling performance of the intermediate pressure stages for an ultra-supercritical steam turbine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 62 (2), 723 (2014).
W. Kosman, M. Roskosz, and K. Nawrat: Thermal elongations in steam turbines with welded rotors made of advanced materials at supercritical steam parameters. Appl. Therm. Eng. 29 (16), 3386 (2009).
R. Narula, D. Koza, and H. Wen: Impacts of steam conditions on plant materials and operation in ultra-supercritical coal power plants. In Ultra-Supercritical Coal Power Plants: Materials, Technologies and Optimisation, D. Zhang, ed. (Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2013); p. 23.
L. Helis, Y. Toda, T. Hara, H. Miyazaki, and F. Abe: Effect of cobalt on the microstructure of tempered martensitic 9Cr steel for ultra-supercritical power plants. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 510–511, 88–94 (2009).
P. Verma, G.S. Rao, P. Chellapandi, G. Mahobia, K. Chattopadhyay, N.S. Srinivas, and V. Singh: Dynamic strain ageing, deformation, and fracture behavior of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 621, 39 (2015).
F. Abe, T. Horiuchi, M. Taneike, and K. Sawada: Stabilization of martensitic microstructure in advanced 9Cr steel during creep at high temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 378 (1–2), 299 (2004).
C. Gupta, G.K. Dey, J.K. Chakravartty, D. Srivastav, and S. Banerjee: A study of bainite transformation in a new CrMoV steel under continuous cooling conditions. Scr. Mater. 53 (5), 559 (2005).
E.J. McDonald, K.R. Hallam, W. Bell, and P.E.J. Flewitt: Residual stresses in a multi-pass CrMoV low alloy ferritic steel repair weld. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 325 (1–2), 454 (2002).
D. Meng, F. Lu, H. Cui, Y. Ding, X. Tang, and X. Huo: Investigation on creep behavior of welded joint of advanced 9% Cr steels. J. Mater. Res. 30 (2), 197 (2015).
F. Lu, X. Liu, P. Wang, Q. Wu, H. Cui, and X. Huo: Microstructural characterization and wide temperature range mechanical properties of NiCrMoV steel welded joint with heavy section. J. Mater. Res. 30 (13), 2108 (2015).
W. Liu, X. Liu, F. Lu, X. Tang, H. Cui, and Y. Gao: Creep behavior and microstructure evaluation of welded joint in dissimilar modified 9Cr–1Mo steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 644, 337 (2015).
E.M. El-Banna, M.S. Nageda, and M.M. Abo El-Saadat: Study of restoration by welding of pearlitic ductile cast iron. Mater. Lett. 42 (5), 311 (2000).
H. Furuya, S. Aihara, and K. Morita: A new proposal of HAZ toughness evaluation Method-Part 1: Haz toughness of structural steel in multilayer and single-layer weld joints. Weld. J. 86 (1), 1 (2007).
Q. Wu, F. Lu, H. Cui, X. Liu, P. Wang, and X. Tang: Role of butter layer in low-cycle fatigue behavior of modified 9Cr and CrMoV dissimilar rotor welded joint. Mater. Des. 59, 165 (2014).
Q. Guo, F. Lu, X. Liu, R. Yang, H. Cui, and Y. Gao: Correlation of microstructure and fracture toughness of advanced 9Cr/CrMoV dissimilarly welded joint. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 638 (0), 240 (2015).
Q. Guo, F. Lu, H. Cui, R. Yang, X. Liu, and X. Tang: Modelling the crack propagation behavior in 9Cr/CrMoV welds. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 226, 125 (2015).
M. Taneike, K. Sawada, and F. Abe: Effect of carbon concentration on precipitation behavior of M23C6 carbides and MX carbonitrides in martensitic 9Cr steel during heat treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35, 1255 (2004).
Q. Wu, F. Lu, H. Cui, X. Liu, P. Wang, and Y. Gao: Soft zone formation by carbon migration and its effect on the high-cycle fatigue in 9% Cr–CrMoV dissimilar welded joint. Mater. Lett. 141, 242 (2015).
M.L. Zhu and F.Z. Xuan: Effects of temperature on tensile and impact behavior of dissimilar welds of rotor steels. Mater. Des. 31, 3346 (2010).
A. Shekhter, S. Kim, D.G. Carr, A.B.L. Croker, and S.P. Ringer: Assessment of temper embrittlement in an ex-service 1Cr–1Mo–0.25V power generating rotor by Charpy V-Notch testing, KIc fracture toughness and small punch test. Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping 79 (8–10), 611 (2002).
B. Tanguy, J. Besson, R. Piques, and A. Pineau: Ductile to brittle transition of an A508 steel characterized by Charpy impact test: Part I: Experimental results. Eng. Fract. Mech. 72 (1), 49 (2005).
P. Haušild, C. Berdin, and P. Bompard: Prediction of cleavage fracture for a low-alloy steel in the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature range. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 391 (1–2), 188 (2005).
S.H. Song, H. Zhuang, J. Wu, L.Q. Weng, Z.X. Yuan, and T.H. Xi: Dependence of ductile-to-brittle transition temperature on phosphorus grain boundary segregation for a 2.25Cr1Mo steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 486 (1–2), 433 (2008).
H. Jeong, S-H. Nahm, K-Y. Jhang, and Y-H. Nam: Evaluation of fracture toughness degradation of CrMoV rotor steels based on ultrasonic nonlinearity measurements. KSME Int. J. 16 (2), 147 (2002).
J. Foulds and R. Viswanathan: Determination of the toughness of in-service steam turbine disks using small punch testing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 10 (5), 614 (2001).
Y.J. Chao, J.D. Ward, Jr., and R.G. Sands: Charpy impact energy, fracture toughness and ductile–brittle transition temperature of dual-phase 590 Steel. Mater. Des. 28 (2), 551 (2007).
J.W. Kim, K. Lee, J.S. Kim, and T.S. Byun: Local mechanical properties of alloy 82/182 dissimilar weld joint between SA508 Gr.1a and F316 SS at RT and 320 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 384 (3), 212 (2009).
A. Eghlimi, M. Shamanian, M. Eskandarian, A. Zabolian, and J.A. Szpunar: Characterization of microstructure and texture across dissimilar super duplex/austenitic stainless steel weldment joint by austenitic filler metal. Mater. Charact. 106, 208 (2015).
C. Lundin, K. Khan, and D. Yang: Report No. 1: Effect of carbon migration in Cr-Mo weldments on metallurgical structure and mechanical properties (Bulletin-Welding Research Council, 1995).
A. Celik and A. Alsaran: Mechanical and structural properties of similar and dissimilar steel joints. Mater. Charact. 43 (5), 311 (1999).
A. Salemi and A. Abdollah-Zadeh: The effect of tempering temperature on the mechanical properties and fracture morphology of a NiCrMoV steel. Mater. Charact. 59 (4), 484 (2008).
M.L. Zhu, D.Q. Wang, and F.Z. Xuan: Effect of long-term aging on microstructure and local behavior in the heat-affected zone of a Ni–Cr–Mo–V steel welded joint. Mater. Charact. 87, 45 (2014).
A. Eghlimi, M. Shamanian, M. Eskandarian, A. Zabolian, and J.A. Szpunar: Characterization of microstructure and texture across dissimilar super duplex/austenitic stainless steel weldment joint by super duplex filler metal. Mater. Charact. 106, 207 (2015).
I. Sattari-Far and M.R. Farahani: Effect of the weld groove shape and pass number on residual stresses in butt-welded pipes. Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping 86, 723 (2009).
L. Lan, C. Qiu, D. Zhao, X. Gao, and L. Du: Microstructural characteristics and toughness of the simulated coarse grained heat affected zone of high strength low carbon bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 529, 192 (2011).
T.H. Chen and J.R. Yang: Microstructural characterization of simulated heat affected zone in a nitrogen-containing 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 338, 166 (2002).
A. Lambert-Perlade, A.F. Gourgues, and A. Pineau: Austenite to bainite phase transformation in the heat-affected zone of a high strength low alloy steel. Acta Metall. 52, 2337 (2004).
J.A. Francis, W. Mazur, and H. Bhadeshia: Review type IV cracking in ferritic power plant steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 22 (12), 1387 (2006).
W. Liu, X. Liu, and F. Lu: Creep behavior and microstructure evaluation of welded joint in dissimilar modified 9Cr–1Mo steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 644, 337 (2015).
M. Huang and D.L. Wang: Carbon migration in 5Cr–0.5Mo/21Cr–12Ni dissimilar metal welds. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 29 (12), 3037 (1998).
Y.Y. You, R.K. Shiue, R.H. Shiue, and C. Chen: The study of carbon migration in dissimilar welding of the modified 9Cr–1Mo steel. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 20 (15), 1429 (2001).
R. Cao, W. Feng, Y. Peng, W.S. Du, Z.L. Tian, and J.H. Chen: Investigation of abnormal high impact toughness in simulated welding CGHAZ of a 8% Ni 980 MPa high strength steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528 (2), 631 (2010).
K. Arioka, T. Yamada, T. Terachi, and G. Chiba: Influence of carbide precipitation and rolling direction on intergranular stress corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steels in hydrogenated high-temperature water. Corrosion 62 (7), 568 (2006).
N.J. Petch: The influence of grain boundary carbide and grain size on the cleavage strength and impact transition temperature of steel. Acta Metall. 34 (7), 1387 (1986).
M.A. Islam: Grain boundary segregation behavior in 2.25Cr–1Mo steel during reversible temper embrittlement. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 16 (1), 73 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, R., Cui, H., Lu, F. et al. Study on the microstructure and toughness of dissimilarly welded joints of advanced 9Cr/CrMoV. Journal of Materials Research 31, 3597–3609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.381
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.381