Abstract
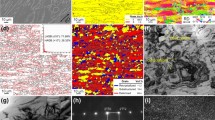
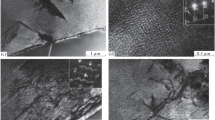
In the present work, the effect of cooling rate on the evolution of the microstructure and mechanical properties of an α + β titanium alloy has been systematically investigated. Titanium alloy samples were heated to 1066 °C (above the β transus), 930 °C (just below the β transus), and 850 °C (well below the β transus) followed by oil quenching, air cooling, and furnace cooling, respectively. Primary alpha (αp), lamellar alpha (αL), and martensite (α′) were the dominant features of the microstructures for all the samples heated below the β transus. Furnace-cooled samples showed variation in the size and shape of the αp and fraction of αL according to the heating temperature. At slower cooling rates, the thickness of the αL increased with the increase in temperature. Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction confirmed the presence of α′ in all the quenched samples. The volume fraction and size of the αp decreased with the increase in temperature but was independent of the cooling rate. The microhardness was relatively unaffected by the cooling rate for heating just below the β transus, i.e., 930 °C. The modulus of elasticity was found to be extremely sensitive to the microstructure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Contieri, M. Zanotello, and R. Caram: Recrystallization and grain growth in highly cold worked CP-titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 3994 (2010).
I. Weiss and S.L. Semiatin: Thermomechanical processing of beta titanium alloys—An overview. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 243, 46 (1998).
G. Lutjering and J.C. Williams: Titanium (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2007).
I. Weiss and S.L. Semiatin: Thermomechanical processing of alpha titanium alloys—An overview. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 263, 243 (1999).
A. Ghaderi, P.D. Hodgson, and M.R. Barnett: Microstructure and texture development in Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr alloy during cold rolling and annealing. Key Eng. Mater. 551, 210 (2013).
D.F. Williams, D.M. Brunette, P. Tengvall, M. Textor, and P. Thomsen: Titanium in Medicine, Vol. 13 (Spinger-Verlag, Berlin, 2001).
C. Layens and M. Peters: Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications (Wiley-VCH, 2003), Weinheim.
T. Ahmed and H. Rack: Phase transformations during cooling in α + β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 243, 206 (1998).
H.H. Weigand: Umwandlung von (α + β) — titan legierungen mit aluminium. Metallkunde 54, 43 (1963).
I. Weiss, F.H. Froes, D. Eylon, and G.E. Welsch: Modification of alpha morphology in Ti–6Al–4V by thermomechanical processing. Metall. Trans. A 17, 1935 (1986).
F.H. Froes and W.T. Highberger: Synthesis of CORONA 5 (Ti–4.5 Al–5Mo–1.5 Cr). J. Met. 32, 57 (1980).
M. Peters, A. Gysier, and G. Lütjering: Titanium’ 80, 4th International Conference on Titanium, 1777 (Kyoto, Japan, 1980), Metallurgical Society of AIME.
M. Peters and G. Lütjering: Titanium’ 80, 4th International Conference on Titanium, 925 (Kyoto, Japan, 1980).
R. Dabrowski: The kinetics of phase transformations during continuous cooling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy from the diphase α + β range. Arch. Metall. Mater. 56, 217 (2011).
S.L. Semiatin, V. Seetharaman, and I. Weiss: The thermomechanical processing of alpha/beta titanium alloys. JOM 49, 33 (1997).
P. Pinke, L. Aplovi, and T. Kovacs: The influence of heat treatment on the microstructure of the casted Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. J. Metall. Eng. 1 (2012).
J. Xu, W. Zeng, Y. Zhao, X. Sun, and Z. Du: Influence of cooling rate following heat treatment on microstructure and phase transformation for a two-phase alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 301 (2016).
J. Zhang, C.C. Tasan, M.J. Lai, A-C. Dippel, and D. Raabe: Complexion-mediated martensitic phase transformation in titanium. Nat. Commun. 8, 14210 (2017).
T.W. Duerig, G.T. Terlinde, and J.C. Williams: Phase transformations and tensile properties of Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al. Metall. Trans. A 11, 1987 (1980).
E.S.K. Menon, J.K. Chakravartty, S.L. Wadekar, and S. Banerjee: Stress induced martensitic transformation in Ti–20V. J. Phys. C4–43, 321 (1982).
H.M. Flower: Fifth International Conference on Titanium Science and Technology, 1651, G. Lutjering, U. Zwicker, and W. Blunk, eds. (Deutche Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde, Munich, Germany, 1985).
M. Ninomi, T. Kobayashi, I. Inagaki, and A.W. Thompson: The effect of deformation-induced transformation on the fracture toughness of commercial titanium alloys. Metall. Trans. A 21, 1733 (1990).
S. Ishiyama, S. Hanada, and O. Izumi: Effect of Zr, Sn and Al additions on deformation mode and beta phase stability of metastable beta Ti alloys. ISIJ Int. 31, 807 (1991).
S. Ishiyama and S. Hanada: Effect of zirconium, tin and aluminium addition on the mechanical properties of metastable beta-titanium alloys. Sumimoto Search 54, 41 (1993).
A.I.P. Nwobu, H.M. Flower, and D.R.F. West: Seventh International Conference on Titanium, 531, F.H. Froes and I.L. Caplan, eds. (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Warrendale, PA, 1993).
O.M. Ivasishin, P.E. Markovsky, Y.V. Matviychuk, and S.L. Semiatin: Precipitation and recrystallization behaviour of beta titanium alloys during continuous heat treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 147 (2003).
H. Shao, Y.Q. Zhao, P. Ge, and W.D. Zeng: Influence of cooling rate and aging on the lamellar microstructure and fractography of TC21 titanium alloy. Metallogr., Microstruct., Anal. 2, 35 (2013).
S.L. Semiatin, S.L. Knisley, P.N. Fagin, F. Zhang, and D.R. Barker: Microstructure evolution during alpha-beta heat treatment of Ti–6Al–4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 2377 (2003).
F.J. Gil, M.P. Ginebra, J.M. Manero, and J.A. Planell: Formation of α-Widmanstätten structure: Effects of grain size and cooling rate on the Widmanstätten morphologies and on the mechanical properties in Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 329, 142 (2001).
C.L. Li, X.J. Mi, W.J. Ye, S.X. Hui, Y. Yu, and W.Q. Wang: A study on the microstructures and tensile properties of new beta high strength titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 550, 23 (2013).
T. Grosdidier and M.J. Philippe: Deformation induced martensite and superelasticity in a β-metastable titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 291, 218 (2000).
S. Ankem and C.A. Greene: Recent development in microstructure/property relationships of the beta titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 263, 127 (1999).
S. Malinov, W. Sha, Z. Guo, C.C. Tang, and A.E. Long: Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of the phase transformations in titanium alloys. Mater. Charact. 48, 279 (2002).
B.D. Cullity: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Philippines, 1956).
A.S.M. Handbook: Metallography and Microstructures (ASM International, Materials Park, 2004).
OIM: Analysis Version 7.2. User Manual (TexSEM Laboratories Inc., Draper, 2013).
PDF-2, Powder diffraction Pattern Database, ICCD, Record number 044–1294.
O.P. Karasevskaaya, O.M. Ivasishin, S.L. Semiatin, and Y.V. Matviychuk: Deformation behavior of beta-titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 354, 121 (2003).
B. Guelorget, M. Francois, and J. Lu: Micro-indentation as a local damage measurement technique. Mater. Lett. 61, 34 (2007).
L.W. Meyer, L. Kruger, K. Sommer, T. Halle, and M. Hockauf: Dynamic strength and failure behavior of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V for a variation of heat treatments. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 12, 237 (2008).
S.S. da Rocha, G.L. Adabo, L.G. Vaz, and G.E.P. Henriques: Effect of thermal treatments on tensile strength of commercially cast pure titanium and Ti–6Al–4V alloys. J. Mater. Med. 16, 759 (2005).
W. Burgers: On the process of transition of the cubic-body-centered modification into the hexagonal-close-packed modification of zirconium. Physica 1, 561 (1934).
N. Gey and M. Humbert: Characterization of the variant selection occurring during the α → β → α phase transformation of a cold rolled titanium sheet. Acta Mater. 50, 277 (2002).
D. Banerjee and J.C. Williams: Prospectives on titanium science and technology. Acta Mater. 61, 844 (2013).
X. Ma, F. Li, J. Li, J. Cao, P. Li, and J. Dong: Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and micro-mechanical behaviour of quenched Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 3761 (2015).
G. Lutjering: Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α + β) titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 243, 32 (1998).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are thankful to the Director of VNIT Nagpur for providing the necessary facilities and constant encouragement to publish this paper. The authors would like to acknowledge the use of National Facility for Texture and OIM (A DST-IRPHA project), IIT Bombay for EBSD measurements. One of the authors RKK wishes to acknowledge Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) for financial assistance (grant no. EEQ/2016/000408 dated 08/02/2017) to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Khatirkar, R.K., Kumar, A. et al. Investigations on the effect of heating temperature and cooling rate on evolution of microstructure in an α + β titanium alloy. Journal of Materials Research 33, 946–957 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.54
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.54