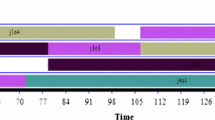
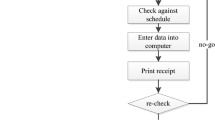
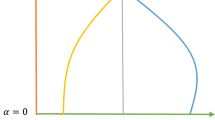
Abstract
In the environment of customization, disturbances such as rush orders and material shortages often occur in the manufacturing system, so rescheduling is necessary for the manufacturing system. The rescheduling methodology should be able to dispose of the disturbance efficiently so as to keep production going smoothly. This aims researching flow shop rescheduling problem (FSRP) necessitated by rush orders. Disjunctive graph is employed to demonstrate the FSRP. For a flow shop processingn jobs, after the original schedule has been made, andz out ofn jobs have been processed in the flow shop,x rush orders come, so the originaln jobs together withx rush orders should be rescheduled immediately so that the rush orders would be processed in the shortest time and the original jobs could be processed subject to some optimized criteria. The weighted mean flow time of both original jobs and rush orders is used as objective function. The weight for rush orders is much bigger than that of the original jobs, so the rush orders should be processed early in the new schedule. The ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm used to solve the rescheduling problem has a weakness in that the search may fall into a local optimum. Mutation operation is employed to enhance the ACO performance. Numerical experiments demonstrated that the proposed algorithm has high computation repeatability and efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin, M.E., Öztemel, E., 2000. Dynamic job-shop scheduling using reinforcement learning agents.Robotics and Autonomous Systems,33:169–178.
Beasley, J.E., 1990. OR-Library: Distributing test problems by electronic mail.Journal of the Operational Research Society,41(11):1069–1072.
Colorni, A., Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., 1991. Distributed Optimization by Ant Colonies. Proceedings of First European Conference on Artificial Life, Elsevier Publishing, Amsterdam, p. 134–142.
Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., Colorni, A., 1996. Ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents.IEEE Trans on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics,26(1):24–29.
Gagne, C., Price, W.L., Gravel, M., 2002. Comparing an ACO algorithm with other heuristics for the single machine scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times.Journal of the Operational Research Society,53:895–906.
Gourgand, M., Grangeon, N., Norre, S., 2003. Markovian analysis for performance evaluation and scheduling inm machine stochastic flow-shop with buffers of any capacity.European Journal of Operational Research,12:1–22.
Kumar, K., Tiwari, M.K., Shankar, R., 2003. Scheduling of flexible manufacturing systems: an ant colony optimization approach.Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B-Journal of Engineering Manufacture,217:1443–1453.
Li, H., Li, Z.C., Li, L.X., Hu, B., 2000. A production rescheduling expert simulation system.European Journal of Operational Research,124:283–293.
Rangsaritratsamee, R., Ferrell, W.G.J., Kurz, M.B., 2004. Dynamic rescheduling that simultaneously considers efficiency and stability.Computers and Industrial Engineering,46:1–15.
Sousa, P., Ramos, C., 1999. Distributed Task Scheduling. Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Symposium on Assembly and Task Planning, p.436–441.
T’kindt, V., Monmarché, N., Tercinet, F., Laügt, D., 2002. An Ant Colony Optimization algorithm to solve a 2-machine bicriteria flowshop scheduling problem.European Journal of Operational Research,142:250–257.
Wang, X.R., Wu, T.J., 2003. An Ant Colony Optimization Approach for No-wait Flow-line Batch Scheduling with Limited Batch Sizes. Proceedings of 42nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, Hawaii, USA, p.2959–2964.
Ying, K.C., Liao, C.J., 2004. An ant colony system for permutation flow-shop sequencing.Computers and Operations Research,31:791–801.
Zhang, Q., Rao, Y.Q., 2003. Study on dynamic scheduling method for job shop.Mechanical Manufacturing,41(461):39–41 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 70171042) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation. China (Nos. Z604342 and M703100), and Ningbo Municipal Youth Foundation, China (No. 2005A620004)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan-hai, H., Jun-qi, Y., Fei-fan, Y. et al. Flow shop rescheduling problem under rush orders. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. A 6, 1040–1046 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.A1040
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.A1040