Abstract
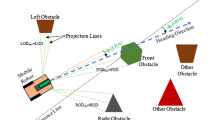
A novel robot navigation algorithm with global path generation capability is presented. Local minimum is a most intractable but is an encountered frequently problem in potential field based robot navigation. Through appointing appropriately some virtual local targets on the journey, it can be solved effectively. The key concept employed in this algorithm are the rules that govern when and how to appoint these virtual local targets. When the robot finds itself in danger of local minimum, a virtual local target is appointed to replace the global goal temporarily according to the rules. After the virtual target is reached, the robot continues on its journey by heading towards the global goal. The algorithm prevents the robot from running into local minima anymore. Simulation results showed that it is very effective in complex obstacle environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borenstein, J. and Koren, Y., 1989. Real-time obstacle avoidance for fast mobile robots.IEEE Trans. On Systems, Man and Cybernetics,19(5): 1179–1187.
Chang, H., 1996. A new technique to handle local minimum for imperfect potential field based motion planning.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, USA,1: 108–112.
Connolly, C. I., 1992. Applications of harmonic functions to robotics.In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, p. 498–502.
Ge, S. S. and Cui, Y. J., 2000. New potential functions for mobile robot path planning.IEEE Trans. on Robotics And Automation,16(5): 615–620.
Haddad, H., Khatib, M., Lacroix S. and Chatla, R., 1998. Reactive navigation in outdoor environments using potential fields.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Lewen, Belgium,2:1232–1237.
Janabi-Sharifi, F. and Vinke, D., 1993. Integration of the artificial potential field approach with simulated annealing for robot path planning,In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, Chicago, USA, p.536–541.
Liu, C. Q., Marcelo, H. Ang. Jr, Hariharan, K. and Lim, S. Y., 2000. Virtual obstacle concept for localminimum-recovery in potential-field based navigation.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, USA,2:983–988.
Podsedkowski, L., Nowakowski, J. and Idzikowski, M., 1999. Modified A* algorithm suitable for online carlike mobile robot control.In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Robot Motion and Control, Kiekrz, Poland, p. 235–240.
Rimon, E. and Koditschek, D. E., 1992. Exact robot navigation using artificial potential functions.IEEE Trans. on Robotics And Automation,8(5): 501–518.
Singh, L., Stephanou, H. and Wen, J., 1996. Real-time robot motion control with circulatory fields.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Minneapolis, USA,3: 2737–2742.
Volpe, R. and Khosla, P., 1990. Manipulator control with superquadric artificial potential functions: theory and experiments.IEEE Trans. On Systems, Man and Cybernetics,20(6): 1423–1436.
Wang, Y. F. and Chirikjian, G. S., 2000. A new potential field method for robot path planning.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, USA,2:977–982.
Wu, K. H., Chen, C. H. and Lee, J. D., 1995. A fuzzy potential approach with the cache genetic learning algorithm for robot path planning.In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vancouver, CA,1:478–482.
Yun, X. P. and Tan, K. C., 1997. A wall-following method for escaping local minima in potential field based motion planning.In: Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Monterey, USA, p.421–426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 69904009) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Xy., Zhu, J. Virtual local target method for avoiding local minimum in potential field based robot navigation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 4, 264–269 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0264
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0264