Abstract
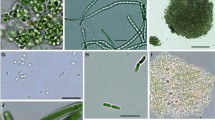
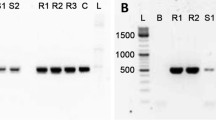
Some species of cyanobacteria synthesize toxins whose concentration during water bloom can reach values dangerous for human and animal health. Planktonic cyanobacteria are the most common and well-studied microcystins producers, hepatotoxic cyclic heptapeptides, whereas microcystin-producing benthic cyanobacteria are less known. In recent years, the mass development of benthic cyanobacteria forming extensive fouling on different substrates has been detected in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal. We found microcystins produced by benthic cyanobacteria in the biofouling on different natural and artificial substrates, including diseased and dead endemic sponges Lubomirskia baicalensis and Baikalospongia spp. collected from the littoral area of Lake Baikal. Microscopic analysis of the biofouling revealed prevalence of representatives of Nostocales and Oscillatoriales with predominance of Tolypothrix distorta that is likely the main microcystin producer in Lake Baikal. According to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), microcystin concentrations in biofouling were 29.8–3050 μg/kg dry weight. We identified eight microcystin variants using MALDI-TOF/TOF; [Dha7]MC-YR was detected in most samples. The presence of microcystins in biofilms formed on the surface of the artificial substrate by Phormidium autumnale was also recorded. The data obtained demonstrated the necessity to monitor potentially toxic species and concentrations of cyanotoxins in plankton and benthos in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal, especially in the regions with intense tourist and recreational activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Public Health Significance, Monitoring and Management, Chorus, I. and Bartram, J., Eds., London: Chapman & Hall, 1999.
Chorus, I., Cyanotoxins—Occurrence, Causes, Consequences, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2001.
Quiblier, C., Wood, S., Echenique-Subiabre, I., Heath, M., Villeneuve, A., and Humbert, J.-F., A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria—ecology, toxin production and risk management, Water Res., 2013, vol. 47, no. 15, pp. 5464–5479.
Paerl, H.W. and Otten, T.G., Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls, Microb. Ecol., 2013, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 995–1010.
Mez, K., Beattie, K.A., Codd, G.A., Hanselmann, K., Hauser, B., Naegeli, H., and Preisig, H.R., Identification of a microcystin in benthic cyanobacteria linked to cattle deaths on alpine pastures in Switzerland, Eur. J. Phycol., 1997, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 111–117.
Richardson, L.L., Miller, A.W., Broderick, E., Kaczmarsky, L., Gantar, M., Stanic, D., and Sekar, R., Sulfide, microcystin, and the etiology of black band disease, Dis. Aquat. Org., 2009, vol. 87, nos. 1–2, pp. 79–90.
Webster, N.S. and Thomas, T., The sponge hologenome, MBio, 2016, vol. 7, no. 2.
Timoshkin, O.A., Samsonov, D.P., Yamamuro, M., et al., Rapid ecological change in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Is the site of the world’s greatest freshwater biodiversity in danger?, J. Great Lakes Res., 2016, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 487–497.
Belykh, O.I., Tikhonova, I.V., Kuzmin, A.V., Sorokovikova, E.G., Fedorova, G.A., Khanaev, I.V., Sherbakova, T.A., and Timoshkin, O.A., First detection of benthic cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal producing paralytic shellfish toxins, Toxicon, 2016, vol. 121, pp. 36–40.
Komárek, J. and Anagnostidis, K., Cyanoprokaryota—1. Teil: Chroococcales, vol. 19/1 of Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., and Mollenhauer, D., Eds., Gustav Fischer Verlag, 1999.
Komárek, J. and Anagnostidis, K., Cyanoprokaryota—2. Teil: Oscillatoriales, vol. 19/2 of Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Büdel, B., Krienitz, L., Gärtner, G., and Schagerl, M., Eds., Heidelberg: Elsevier/Spektrum, 2005.
Komárek, J., Cyanoprokaryota—3. Teil: Heterocytous Genera, vol. 19/3 of Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., and Krienitz, L., Eds., Springer Spektrum, 2013.
Belykh, O.I., Gladkikh, A.S., Sorokovikova, E.G., Tikhonova, I.V., Potapov, S.A., and Fedorova, G.A., Microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in water reservoirs of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine, Chem. Sustain. Dev., 2013, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 347–361.
Gladkikh, A.S., Kalyuzhnaya, O.V., Belykh, O.I., Ahn, T.S., and Parfenova, V.V., Analysis of bacterial communities of two Lake Baikal endemic sponge species, Microbiology, 2014, vol. 83, no. 6, pp. 787–797.
Izhboldina, L.A., Atlas i opredelitel’ vodoroslei bentosa i perifitona ozera Baikal (meio-i makrofity) s kratkimi ocherkami po ikh ekologii (Atlas and Key of Algae of Benthos and Periphyton of Lake Baikal (Meio-and Macrophytes) with Short Essays on Their Ecology), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 2007.
Pineda-Mendoza, R.M., Olvera-Ramírez, R., and Martinez-Jerónimo, F., Microcystins produced by filamentous cyanobacteria in urban lakes. A case study in Mexico City, Hidrobiologica, 2012, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 290–298.
Teneva, I., Mladenov, R., and Dzhambazov, B., Toxic effects of extracts from Pseudanabaena galeata (Cyanoprokaryota) in mice and cell cultures in vitro, Nat. Sci. Hum., 2009, vol. 12, pp. 237–243.
Aboal, M., Puig, M.Á., and Asencio, A.D., Production of microcystins in calcareous Mediterranean streams: The Alharabe River, Segura River basin in south-east Spain, J. Appl. Phycol., 2005, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 231–243.
Shams, S., Capelli, C., Cerasino, L., Ballot, A., Dietrich, D.R., Sivonen, K., and Salmaso, N., Anatoxin-a producing Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) in European waterbodies, Water Res., 2015, vol. 69, pp. 68–79.
McAllister, T.G., Wood, S.A., and Hawes, I., The rise of toxic benthic Phormidium proliferations: A review of their taxonomy, distribution, toxin content and factors regulating prevalence and increased severity, Harmful Algae, 2016, vol. 55, pp. 282–294.
Wood, S.A., Mountfort, D., Selwood, A.I., Holland, P.T., Puddick, J., and Cary, S.C., Widespread distribution and identification of eight novel microcystins in antarctic cyanobacterial mats, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 74, no. 23, pp. 7243–7251.
Kleinteich, J., Wood, S.A., Puddick, J., Schleheck, D., Kupper, F.C., and Dietrich, D., Potent toxins in Arctic environments—presence of saxitoxins and an unusual microcystin variant in Arctic freshwater ecosystems, Chem. Biol. Interact., 2013, vol. 206, no. 2, pp. 423–431.
Kleinteich, J., Wood, S.A., Kupper, F.C., Camacho, A., Quesada, A., Frickey, T., and Dietrich, D.R., Temperature- related changes in polar cyanobacterial mat diversity and toxin production, Nat. Clim. Change, 2012, vol. 2, pp. 356–360.
Shimaraev, M.N. and Domysheva, V.M., Trends in hydrological and hydrochemical processes in Lake Baikal under conditions of modern climate change, in Climatic Change and Global Warming of Inland Waters, Goldman, C., Kumagai, M., and Robarts, R., Eds., New York: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013, pp. 43–66.
Popovskaya, G.I., Ecological monitoring of phytoplankton in Lake Baikal, Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manage., 2000, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 215–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.I. Belykh, G.A. Fedorova, A.V. Kuzmin, I.V. Tikhonova, O.A. Timoshkin, E.G. Sorokovikova, 2017, published in Vestnik Moskovskogo Universiteta, Seriya 16: Biologiya, 2017, Vol. 72, No. 4, pp. 262–269.
About this article
Cite this article
Belykh, O.I., Fedorova, G.A., Kuzmin, A.V. et al. Microcystins in Cyanobacterial Biofilms from the Littoral Zone of Lake Baikal. Moscow Univ. Biol.Sci. Bull. 72, 225–231 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392517040022
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392517040022