Abstract
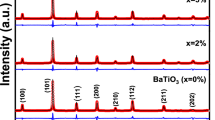
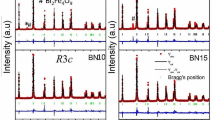
Bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric (BLSF)-type Bi4Ti3O12 (BiT), Bi3.25La0.75Ti3O12 (BLaT), and Bi3.1Nd0.9Ti3O12 (BNdT) ceramics and intergrowth BLSF-type BiT-CaBi4Ti4O15 (CBTO), BLaT-CBTO, and BNdT-CBTO ceramics were prepared using the solid-state reaction method. The electrical and the high-temperature properties of the intergrowth BLSF ceramics were compared with those of BLSF ceramics to investigate the possibility of using the former for high-temperature applications. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed well-formed stable structures in all BLSF and intergrowth BLSF ceramics without any second-phase formation. When their electrical properties were examined, the intergrowth BLSF ceramics BiT-CBTO, BLaT-CBTO, and BNdT-CBTO were found to outperform the BLSF ceramics BiT, BLaT, and BNdT, respectively, in terms of the remanent polarization and piezoelectric coefficient values. Among the intergrowth BLSF ceramics, those doped with rare-earth ions La and Nd, i.e., BLaT-CBTO and BNdT-CBTO ceramics, were found to have improved electrical properties compared to the BiT-CBTO ceramics. In particular, the dielectric constants and the piezoelectric coefficients of the BNdT-CBTO ceramics were observed to be as high as 146 and 15.4 pC/N, respectively, which were 28% and 10% higher than those of BNdT ceramics. In the thermal depoling behavior measured to examine high-temperature stability, the intergrowth BLSF ceramics, compared to the BLSF ceramics, demonstrated improvements in the thermal depoling temperature ranging from 100 to 300 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Gao, Z. Zhou and J. Xue, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 1037 (2005).
Z. Shen, H. Sun, Y. Tang, Y. Li and S. Zhang, Mater. Res. Bull. 63, 129 (2015).
S. Y. Cho, G. P. Choi, D. H. Jeon, T. A. Johnson, M. K. Lee, G. J. Lee and S. D. Bu, Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, 1332 (2015).
T. Shigyo, H. Kiyono, J. Nakano, H. Itoh and J. Takahashi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 7617 (2008).
B. H. Park, B. S. Kang, S. D. Bu, T. W. Noh, J. Lee and W. Jo, Nature 401, 682 (1999).
G. P. Choi, S. Y. Cho, D. H. Jeon, S. D. Bu, G. J. Lee and M. K. Lee, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 65, 657 (2015).
L. Fei, Z. Zhou, S. Hui and X. Dong, Ceram. Int. 41, 9729 (2015).
W. Wang, D. Shan, J. Sun, X. Mao and X. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 044102 (2008).
T. Jardiel, A. C. Caballero and M. Villegas, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 116, 511 (2008).
G. P. Choi, S. Y. Cho and S. D. Bu, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 69, 816 (2016).
C. Wang, J. Wang and Z. Gai, Scr. Mater. 57, 789 (2007).
Y. Yoneda, J. Mizuki, R. Katayama, K. Yagi, H. Terauchi, S. Hamazaki and M. Takashige, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 275 (2003).
L. Nibou, A. Aftati, M. E. Farissi and J. P. Mercurio, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1383 (1999).
J. S. Kim and I. W. Kim, J. Electroceram. 16, 373 (2006).
J. Zeng, Y. Wang, Y. Li, Q. Yang and Q. Yin, J. Electroceram. 21, 305 (2008).
H. Yan, H. Zhang, M. J. Reece and X. Dong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 082911 (2005).
S. Hong, S. Trolier-Mckinstry and G. L. Messing, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 113 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, S.Y., Choi, G.P. & Bu, S.D. Comparison between the electrical properties of bismuth layer-structured and intergrowth bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric ceramics. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 70, 934–938 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.934
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.934