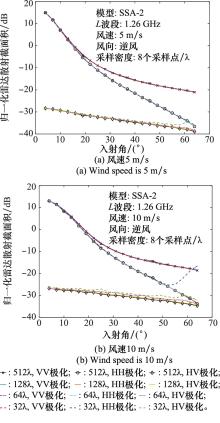
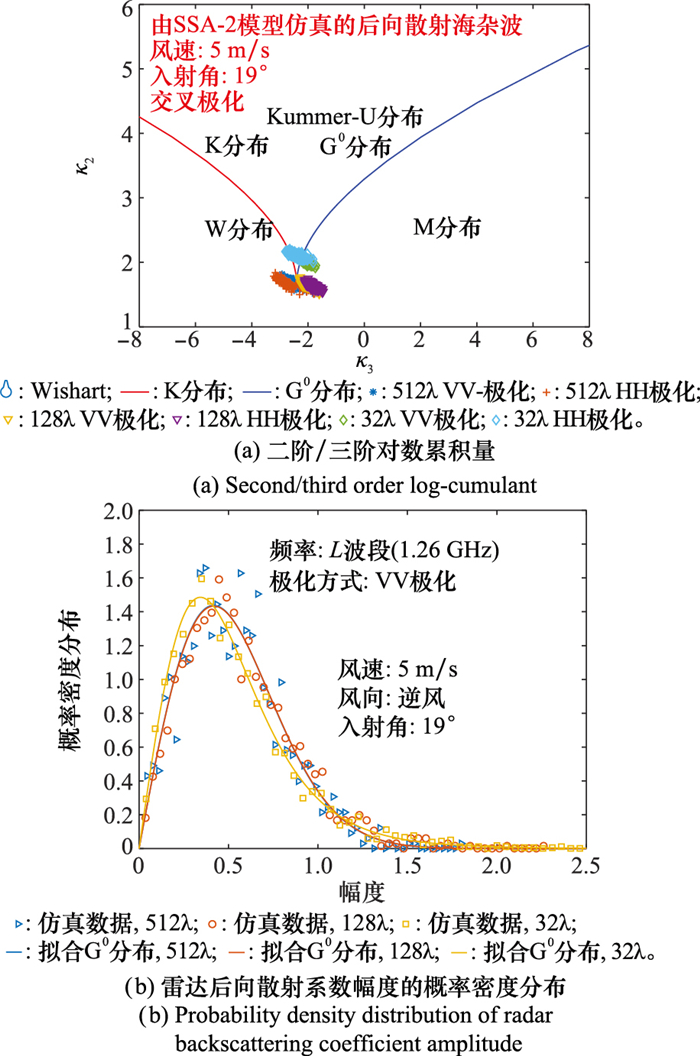
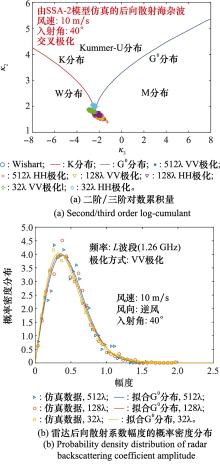
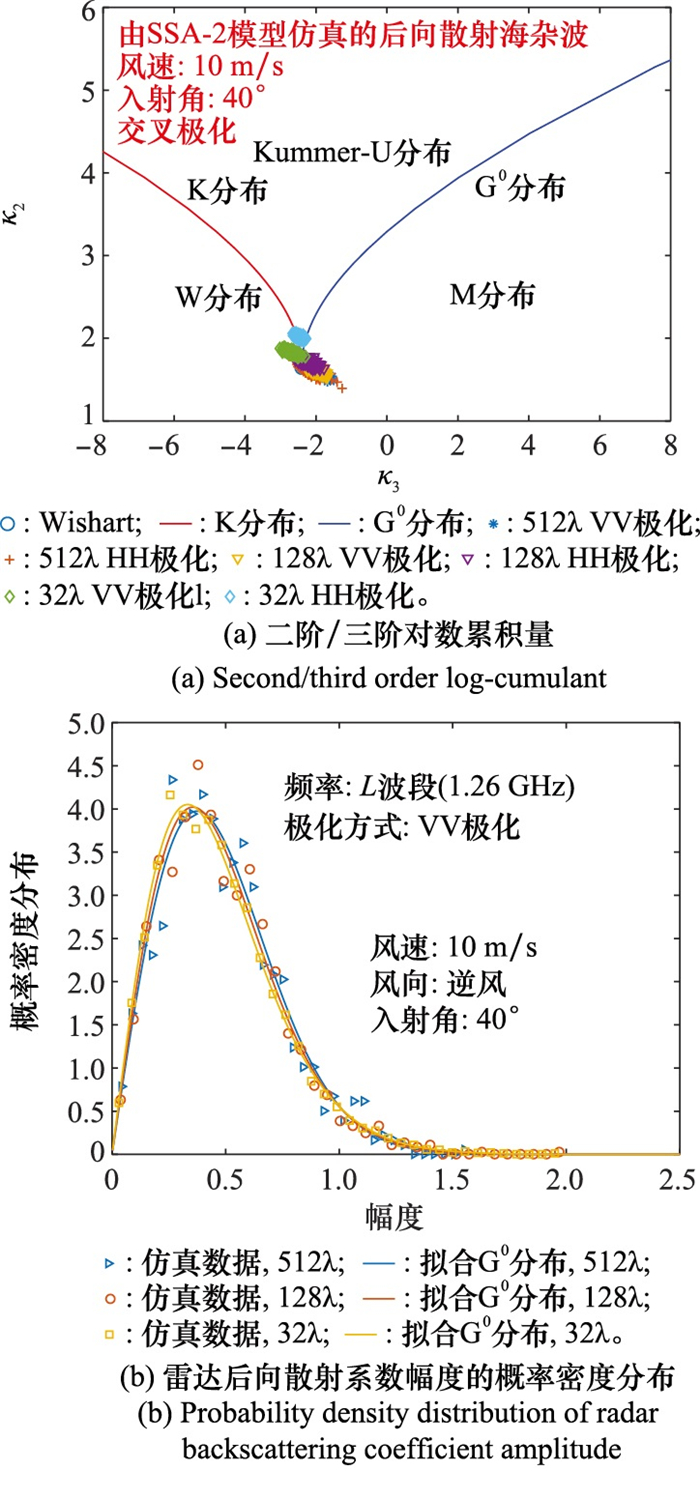
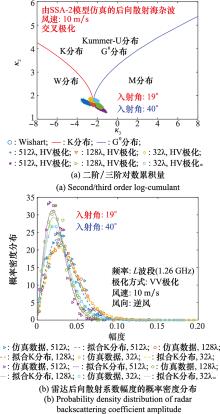
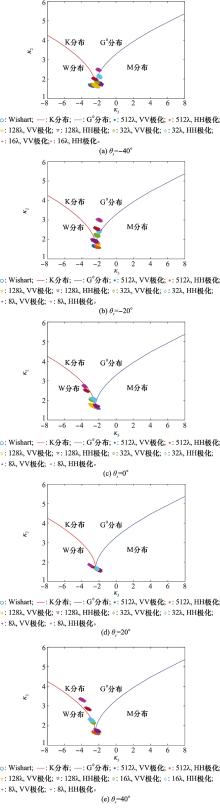
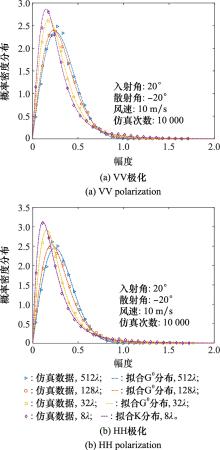
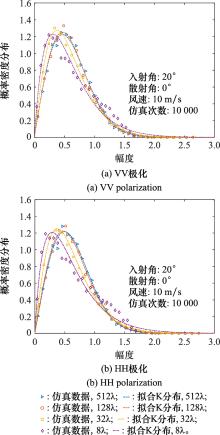
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 3806-3818.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.12.10
• Sensors and Signal Processing • Previous Articles
Numerical investigation on the spatial ergodicity of ocean radar scattering and sea clutter amplitude statistical characteristics
Yanlei DU1, Xiaofeng YANG1,*, Sheng WANG1, Junjun YIN2, Huizhang YANG3, Jian YANG3
- 1. Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
2. School of Computer and Communication Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
3. Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2022-04-09Online:2023-11-25Published:2023-12-05 -
Contact:Xiaofeng YANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yanlei DU, Xiaofeng YANG, Sheng WANG, Junjun YIN, Huizhang YANG, Jian YANG. Numerical investigation on the spatial ergodicity of ocean radar scattering and sea clutter amplitude statistical characteristics[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(12): 3806-3818.
share this article
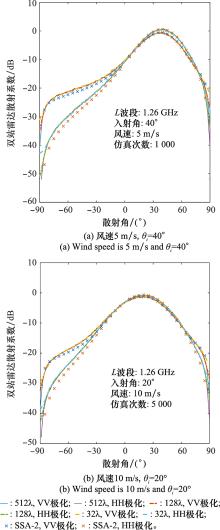
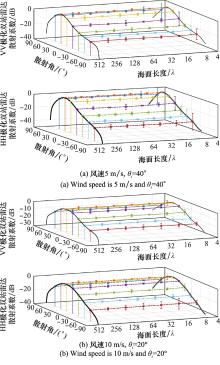
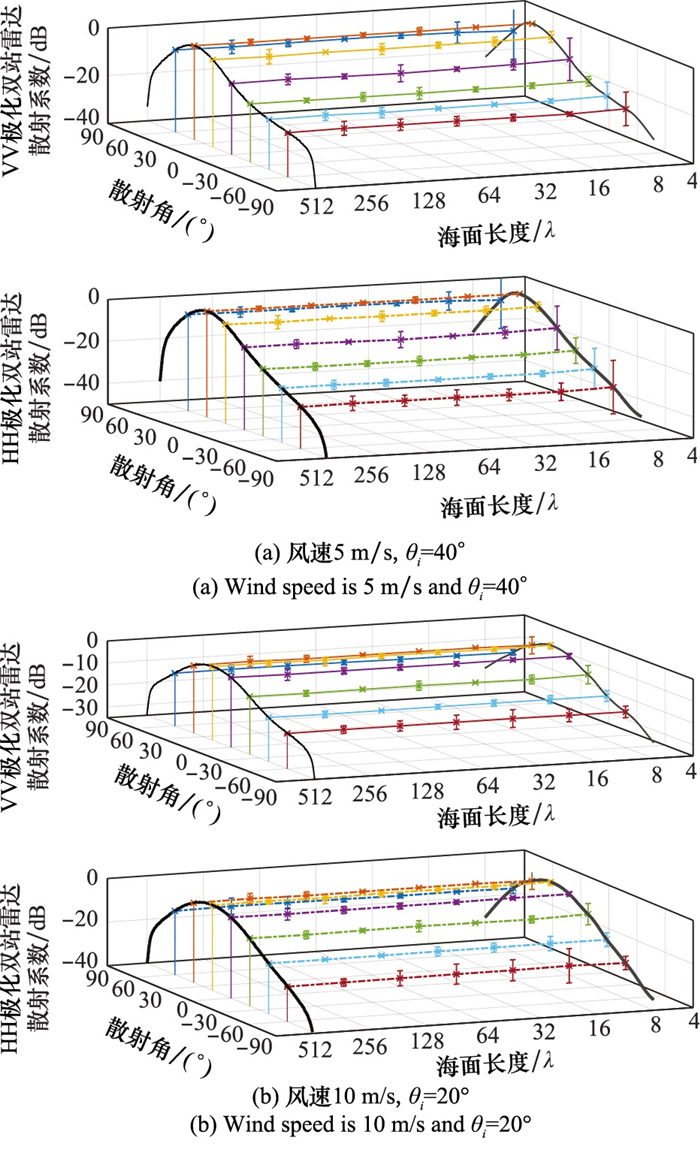
Table 1
Deviations of ocean radar scattering simulations induced by using smaller ocean surfaces"
| 海面尺寸/λ | 风速5 m/s, θi=40°/dB | 风速10 m/s, θi=20°/dB | |||||||||
| θs∈[-60°, 60°] | θs∈[-90°, 90°] | θs∈[-60°, 60°] | θs∈[-90°, 90°] | ||||||||
| VV极化 | HH极化 | VV极化 | HH极化 | VV极化 | HH极化 | VV极化 | HH极化 | ||||
| 512 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| 256 | 0.141 | 0.144 | 0.185 | 0.214 | 0.150 | 0.154 | 0.207 | 0.265 | |||
| 128 | 0.146 | 0.150 | 0.241 | 0.299 | 0.168 | 0.180 | 0.254 | 0.357 | |||
| 64 | 0.156 | 0.160 | 0.326 | 0.397 | 0.178 | 0.195 | 0.352 | 0.474 | |||
| 32 | 0.171 | 0.193 | 0.430 | 0.589 | 0.186 | 0.205 | 0.400 | 0.474 | |||
| 16 | 0.183 | 0.217 | 0.462 | 0.776 | 0.185 | 0.207 | 0.450 | 0.617 | |||
| 8 | 0.462 | 0.664 | 0.803 | 1.448 | 0.293 | 0.325 | 0.548 | 0.767 | |||
Table 2
Deviations of normalized radar backscatter coefficients given by SSA-2 model relative to those from ocean surface with size of 512λ×512λ dB"
| 风速/(m/s) | 极化方式 | 海面尺寸/λ | ||
| 128 | 64 | 32 | ||
| 5 | VV极化 | 0.143 | 0.123 | 0.119 |
| HH极化 | 0.140 | 0.135 | 0.132 | |
| HV极化 | 0.161 | 0.262 | 0.862 | |
| 10 | VV极化 | 0.153 | 0.151 | 0.217 |
| HH极化 | 0.165 | 0.253 | 0.345* | |
| HV极化 | 0.312 | 0.852 | 1.673 | |
| 1 | ULABY F T , LONG D G . Microwave radar and radiometric remote sensing[M]. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2015. |
| 2 | TSANG L , KONG J , SHIN R T . Theory of microwave remote Sening[M]. New York: Wiley, 1985. |
| 3 | 杨健, 殷君君. 极化雷达理论与遥感应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. |
| YANG J , YIN J J . Polarimetric radar theory and remote sensing application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. | |
| 4 | 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9 (4): 684- 714. |
| XU S W , BAI X H , GUO Z X , et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9 (4): 684- 714. | |
| 5 |
DE OLIVEIRA R , DUSSEAUX R , AFIFI S . Analytical derivation of the stationarity and the ergodicity of a field scattered by a slightly rough random surface[J]. Wave Random Complex, 2010, 20 (3): 396- 418.
doi: 10.1080/17455031003628392 |
| 6 | TSANG L , KONG J A , SHIN R T . Scattering of electroma-gnetic waves: numerical simulations[M]. New York: Wiley, 2000. |
| 7 | 丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8 (3): 281- 302. |
| DING H , LIU N B , DONG Y L , et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8 (3): 281- 302. | |
| 8 |
OZGUN O , KUZUOGLU M . Physics-based modeling of sea clutter phenomenon by a full-wave numerical solver[J]. Wave Motion, 2022, 109, 102872.
doi: 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2021.102872 |
| 9 | BERRY M V . The statistical properties of echoes diffracted from rough surfaces[J]. Philosophical Transactions on Royal Society A, 1973, 273 (1237): 611- 654. |
| 10 |
DUSSEAUX R , DE OLIVEIRA R . Effect of the illumination length on the statistical distribution of the field scattered from one-dimensional random rough surfaces: analytical formulae derived from the small perturbation method[J]. Wave Random Complex, 2007, 17 (3): 305- 320.
doi: 10.1080/17455030701197056 |
| 11 |
LAM K W , LI Q , TSANG L , et al. On the analysis of statistical distributions of UWB signal scattering by random rough surfaces based on Monte Carlo simulations of Maxwell equations[J]. IEEE Trans.on Antennas and Propagation, 2004, 52 (12): 3200- 3206.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2004.836414 |
| 12 |
AFIFI S , DUSSEAUX R , DE OLIVEIRA R . Statistical distribution of the field scattered by rough layered interfaces: formula derived from the small perturbation method[J]. Wave Random Complex, 2010, 20 (1): 1- 22.
doi: 10.1080/17455030903329374 |
| 13 |
FRANCESCHETTI G , MIGLIACCIO M , RICCIO D . An electromagnetic fractal-based model for the study of fading[J]. Radio Science, 1996, 31 (6): 1749- 1759.
doi: 10.1029/96RS02811 |
| 14 |
EL-BAH S , DUSSÉAUX R , AFIFI S . Some statistical and spatial properties of signal scattering by 2D slightly rough random surfaces[J]. IEEE Trans on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64 (2): 721- 729.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2511803 |
| 15 |
YANG X F , LI X F , PICHEL W G , et al. Comparison of ocean surface winds from ENVISAT ASAR, MetOp ASCAT scatterometer, buoy measurements, and NOGAPS model[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49 (12): 4743- 4750.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2159802 |
| 16 |
DU Y L , YIN J J , TAN S R , et al. A numerical study of roughness scale effects on ocean radar scattering using the second-order SSA and the moment method[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58 (10): 6874- 6887.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977368 |
| 17 | 杜延磊. 随机粗糙海面微波散射/辐射的仿真与分析: 解析近似模型和数值方法[D]. 北京: 中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所, 2019. |
| DU Y L. Simulations and analysis of microwave scattering and emission from randomly rough ocean surfaces: analytic approximate models and numerical methods[D]. Beijing: Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. | |
| 18 | 杜延磊, 高帆, 刘涛, 等. 基于数值仿真的X波段极化SAR海杂波统计建模与特性分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43 (10): 2742- 2755. |
| DU Y L , GAO F , LIU T , et al. Statistical modeling and cha-racteristic analysis of polarimetric SAR sea clutter at X-band based on numerical simulations[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43 (10): 2742- 2755. | |
| 19 | KUDRYAVTSEV V , HAUSER D , CAUDAL G , et al. A semi-empirical model of the normalized radar cross-section of the sea surface-1. Background model[J]. Journal of Geophys Res-Oceans, 2003, (3): 1- 24. |
| 20 |
DU Y L , YANG J , YANG X F , et al. Electromagnetic scattering and emission from large rough surfaces with multiple elevations using the MLSD-SMCG method[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59 (7): 5393- 5406.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3016997 |
| 21 |
DU Y L , TSANG L . Accurate calculations of emissivities of polar ocean surfaces between 0.5 and 2 GHz using an NIBC/Nystrom/SMCG method[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58 (4): 2732- 2744.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2954886 |
| 22 |
VORONOVICH A G , ZAVOROTNY V U . Full-polarization modeling of monostatic and bistatic radar scattering from a rough sea surface[J]. IEEE Trans.on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62 (3): 1362- 1371.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2295235 |
| 23 | LI J X , ZHANG M , ZHAO Y , et al. Efficient numerical full-polarized facet-based model for EM scattering from rough sea surface within a wide frequency range[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11 (1): 1- 18. |
| 24 |
JOHNSON J T . A study of ocean-like surface thermal emission and reflection using Voronovich's small slope approximation[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43 (2): 306- 314.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.841480 |
| 25 |
VORONOVICH A . Small-slope approximation for electromagnetic-wave scattering at a rough interface of dielectric half-spaces[J]. Wave Random Media, 1994, 4 (3): 337- 367.
doi: 10.1088/0959-7174/4/3/008 |
| 26 |
LIU T , YANG Z Y , MARINO A , et al. Robust CFAR detector based on truncated statistics for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58 (9): 6731- 6747.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2979252 |
| 27 | 郭立新, 王蕊, 吴振森. 随机粗糙面散射的基本理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| GUO L X , WANG R , WU Z S . Basic theory and method of random rough surface scattering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. | |
| 28 | 丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5 (5): 499- 516. |
| DING H , DONG Y L , LIU N B , et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5 (5): 499- 516. | |
| 29 |
LIU T , HUANG G M , WANG X S , et al. Statistics of the polarimetric Weibull-distributed electromagnetic wave[J]. IEEE Trans.on Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 57 (10): 3232- 3248.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2028597 |
| 30 | 刘涛, 黄高明, 王雪松, 等. Weibull分布随机波的瞬态极化统计分析——相同形状参数情形[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58 (5): 3140- 3153. |
| LIU T , HUANG G M , WANG X S , et al. Statistics of the instantaneous polarization in Weibull-distributed fields-the same shape parameter case[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58 (5): 3140- 3153. | |
| 31 |
DENG X P , LOPEZ-MARTINEZ C , CHEN J S , et al. Statistical modeling of polarimetric SAR data: a survey and challenges[J]. Remote Sens-Basel, 2017, 9 (4): 348.
doi: 10.3390/rs9040348 |
| 32 |
DENG X P , LOPEZ-MARTINEZ C , VARONA E M . A Physical analysis of polarimetric SAR data statistical models[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54 (5): 3035- 3048.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2510399 |
| 33 |
ANFINSEN S N , ELTOFT T . Application of the matrix-variate Mellin transform to analysis of polarimetric radar images[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49 (6): 2281- 2295.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2103945 |
| 34 | NICOLAS J M . Introduction to second kind statistics: application of log-moments and Log-cumulants to SAR image law analysis[J]. Traitement du Signal, 2002, 3 (3): 139- 167. |
| 35 | BOMBRUN L, ANFINSEN S N, HARANT O. A complete coverage of log-cumulant space in terms of distributions for polarimetric SAR data[C]//Proc. of the International Workshop on Science & Applications of SAR Polarimetry & Polarimetric Interferometry, 2011: 1-8. |
| 36 | LIU T , CUI H G , MAO T , et al. Modeling multilook polarimetric SAR images with heavy-tailed Rayleigh distribution and novel estimation based on matrix log-cumulants[J]. Science China-information Sciences, 2013, 56 (6): 1- 14. |
| 37 |
LIU T , ZHANG J F , GAO G , et al. CFAR ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on whitening filter[J]. IEEE Trans.on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58 (1): 58- 81.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931353 |
| 38 | 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8 (5): 656- 667. |
| LIU N B , DONG Y L , WANG G Q , et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8 (5): 656- 667. | |
| 39 | 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10 (1): 173- 182. |
| LIU N B , DING H , HUANG Y , et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10 (1): 173- 182. |
| [1] | Hanyi HUANG, Shiyou HU, Shenglong GUO, Shanjun LI, Qin SHU. Sea surface micro-moving target recognition based on sparse decomposition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 1016-1023. |
| [2] | Junling ZHANG, Mei DONG, Baixiao CHEN. Sea clutter suppression algorithm based on tunable Q-factor wavelet transform [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 343-351. |
| [3] | Yanling SHI, Lei WANG, Junhao LI. CFAR detection for small targets on sea surface based on singular value decomposition in projection space [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 512-519. |
| [4] | Chunling XUE, Fei CAO, Qing SUN, Jianqiang QIN, Xiaowei FENG. Sea-surface weak target detection based on multi-feature information fusion [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3338-3345. |
| [5] | Weiqiang YU, Fei WANG, Ping SUN, Jianjiang ZHOU, Jun CHEN. RF stealth optimization of airborne radar signal parametersunder clutter background [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3194-3201. |
| [6] | Yanlei DU, Fan GAO, Tao LIU, Jian YANG. Statistical modeling and characteristic analysis of polarimetric SAR sea clutter at X-band based on numerical simulations [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(10): 2742-2755. |
| [7] | Sainan SHI, Zeyuan DONG, Jing YANG, Chunjiao YANG. Sea-surface small target detection based on autonomic learning of time-frequency graph [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(1): 33-41. |
| [8] | Xin LI, Xiaoyun XIA, Yushi ZHANG, Penglang SHUI, Jinpeng ZHANG. Modified reflectivity model of UHF-band sea clutter at low grazing angle [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(5): 1035-1040. |
| [9] | Hai LI, Zhixin LIU, Weijie CHENG, Zibo ZHUANG, Yi FAN. Low-altitude wind shear wind speed estimation method based on MBMC under sea clutter [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(11): 2481-2487. |
| [10] | Ziwei DONG, Jun SUN, Jingming SUN, Meiyan PAN. Marine weak moving target detection based on sparse dictionary learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(1): 30-36. |
| [11] | SHI Yanling, LIN Yufeng, LIANG Dandan. Subband segmented ANMF detector in non-stationary sea clutter [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 782-789. |
| [12] | ZHAO Wenjing, JIN Minglu, LIU Wenlong. Modified median matrix detection method for sea clutter environment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2173-2179. |
| [13] | XU Xinyu, ZHANG Yushi, LI Xin, LI Shanbin, LI Huiming. Influence of sea condition on the temporal correlation properties of UHF band sea clutter [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(6): 1203-1207. |
| [14] | SHI Sainan, SHUI Penglang, YANG Chunjiao, XU Shuwen. Radar target detection based on spatial correlation of inverse-Gaussian texture [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(10): 2215-2220. |
| [15] | GUO Yue-yu, WEI Yin-sheng, XU Rong-qing, LU Yao-bing. Geometry design of two-dimensional non-filled array for multimode separation in skywave radar [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(9): 2033-2039. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||