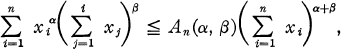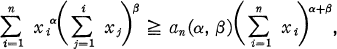Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Mitrinović, Dragoslav S.
1970.
Analytic Inequalities.
p.
186.
Beesack, P. R.
1971.
Integral Inequalities Involving a Function and its Derivative.
The American Mathematical Monthly,
Vol. 78,
Issue. 7,
p.
705.
Fink, A. M.
1974.
Discrete Inequalities of Generalized Wirtinger Type.
Aequationes Mathematicae,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 1,
p.
31.
Shum, Daniel T.
1975.
On a class of new inequalities.
Transactions of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 204,
Issue. 0,
p.
299.
Mitrinović, D. S.
Pečarić, J. E.
and
Fink, A. M.
1991.
Inequalities Involving Functions and Their Integrals and Derivatives.
p.
114.
Agarwal, Ravi P.
1992.
Opial's and wirtinger's type discrete inequalities in two independent variables.
Applicable Analysis,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
47.
Agarwal, Ravi P.
and
Pang, Peter Y. H.
1995.
Opial Inequalities with Applications in Differential and Difference Equations.
p.
283.
Agarwal, R.P.
and
Pang, P.Y.H.
1995.
Opial-type inequalities involving higher order differences.
Mathematical and Computer Modelling,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 5,
p.
49.
Agarwal, Ravi P.
and
Pang, Peter Y.H.
1996.
Discrete opial-type inequalities involving higher order partial differences.
Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 4,
p.
429.
Gerhold, Stefan
and
Kauers, Manuel
2005.
A procedure for proving special function inequalities involving a discrete parameter.
p.
156.
Vi Nhan, Nguyen Du
Duc, Dinh Thanh
Tuan, Vu Kim
and
Huy Vu, Nguyen Du
2014.
Inequalities for differences and their applications.
Journal of Difference Equations and Applications,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 9,
p.
1319.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
1.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
423.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
535.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
233.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
765.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
885.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
261.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
989.
Qin, Yuming
2016.
Integral and Discrete Inequalities and Their Applications.
p.
345.